Abstract
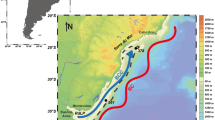
Seasonal and spatial variations of particulate organic carbon (POC) flux were observed with sediment traps at three sites in the Japan Sea (western and eastern Japan Basin and Yamato Basin). In order to investigate the transport processes of POC, radiocarbon (14C) measurements were also carried out. Annual mean POC flux at 1 km depth was 30.7 mg m−2day−1 in the western Japan Basin, 12.0 mg m−2day−1 in the eastern Japan Basin and 23.8 mg m−2day−1 in the Yamato Basin. At all stations, notably higher POC flux was observed in spring (March–May), indicating biological production and rapid sinking of POC in this season. Sinking POC in the high flux season showed modern Δ14C values (>0‰) and aged POC (Δ14C < −40‰) was observed in winter (December–January). The Δ14C values in sinking POC were negatively correlated with aluminum concentration, indicating that Δ14C is strongly related to the lateral supply of lithogenic materials. The Δ14C values also showed correlations with excess manganese (Mnxs) concentrations in sinking particles. The Δ14C-Mnxs relationship suggested that (1) the majority of the aged POC was advected by bottom currents and incorporated into sinking particles, and (2) some of the aged POC might be supplied from the sea surface at the trap site as part of terrestrial POC. From the difference in the Δ14C-Mnxs relationships between the Japan Basin and the Yamato Basin, we consider that basin-scale transport processes of POC occur in the Japan Sea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aramaki, T., T. Senjyu, O. Togawa, S. Otosaka, T. Suzuki, T. Kitamura, H. Amano and Y. N. Volkov (2007): Circulation in the northern Japan Sea studied chiefly with radiocarbon. Radiocarbon, 49, 915–924.
Bauer, J. E. and E. R. M. Druffel (1998): Ocean margins as a significant source of organic matter to the deep open ocean. Nature, 392, 482–485.
Biscaye, P. E. and R. F. Anderson (1994): Fluxes of particulate matter on the slope of the southern Middle Atlantic Bight: SEEP-II. Deep-Sea Res. II, 41, 459–509.
Butman, D., P. Raymond, N.-H. Oh and K. Mull (2007): Quantity, 14C age and lability of desorbed soil organic carbon in fresh water and seawater. Organic Geochem., 38, 1547–1557.
Chen, C. T. A., A. S. Bychkov, S. L. Wang and G. Y. Pavlova (1999): An anoxic Sea of Japan by the year 2200? Mar. Chem., 67, 249–265.
Drenzek, N. J., D. B. Montluçon, M. B. Yunker, R. W. Macdonald and T. I. Eglinton (2007): Constraints on the origin of sedimentary organic carbon in the Beaufort Sea from coupled molecular 13C and 14C measurements. Mar. Chem., 103, 146–162.
Druffel, E. R. M. and P. M. Williams (1990): Identification of a deep marine source of particulate organic carbon using bomb 14C. Nature, 347, 172–174.
Druffel, E. R. M., J. E. Bauer, S. Griffin and J. Hwang (2003): Penetration of anthropogenic carbon into organic particles of the deep ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, doi:10.1029/2003GL017423.
Fukue, M., C. N. Mulligan, Y. Sato and T. Fujikawa (2007): Effect of organic suspended solids and their sedimentation on the surrounding sea area. Environ. Pollut., 149, 70–78.
Gamo, T. (1999): Global warming may have slowed down the deep conveyor belt of a marginal sea of the northwestern Pacific: Japan Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett., 26, 3137–3140.
Gustavson, K. H. (1947): Note on the reaction of formaldehyde with collagen. J. Biol. Chem., 169, 531–537.
Honda, M. C. (1996): Inorganic radiocarbon in time-series sediment trap samples: implication of seasonal variation of 14C in the upper ocean. Radiocarbon, 38, 583–595.
Honda, M. C., M. Kusakabe, S. Nakabayashi and M. Katagiri (2000): Radiocarbon of sediment trap samples from the Okinawa trough: lateral transport of 14C-poor sediment from the continental slope. Mar. Chem., 68, 231–247.
Honda, M. C., K. Imai, Y. Nojiri, F. Hoshi, T. Sugawara and M. Kusakabe (2002): The biological pump in the northwestern North Pacific based on fluxes and major components of particulate matter obtained by sediment-trap experiments (1997–2000). Deep-Sea Res. II, 49, 5595–5625.
Hong, G.-H., S. H. Kim, C. S. Chung, D.-J. Kang, D.-H. Shin, H. J. Lee and S.-J. Han (1997): 210Pb-derived sediment accumulation rates in the southwestern East Sea (Sea of Japan). Geo-Mar. Lett., 17, 126–132.
Hong, G.-H., M. Baskaran, H.-K. Lee and S.-H. Kim (2008): Sinking fluxes of particulate U-Th radionuclides in the East Sea (Sea of Japan). J. Oceanogr., 64, 267–276.
Honjo, S. (1982): Seasonality and interaction of biogenic and lithogenic particulate flux at the Panama Basin. Science, 218, 883–884.
Hwang, J. and E. R. M. Druffel (2003): Lipid-like material as the source of the uncharacterized organic carbon in the ocean? Science, 299, 881–884.
Hwang, J., E. R. M. Druffel and J. E. Bauer (2006): Incorporation of aged dissolved organic carbon (DOC) by oceanic particulate organic carbon (POC): An experimental approach using natural carbon isotopes. Mar. Chem., 98, 315–322.
Ingalls, A. E., L. Cindy, S. G. Wakeham and J. I. Hedges (2003): The role of biominerals in the sinking flux and preservation of amino acids in the Southern Ocean along 170°W. Deep-Sea Res. II, 50, 713–738.
Iseki, K., K. Okamura and Y. Kiyomoto (2003): Seasonality and composition of downward particulate fluxes at the continental shelf and Okinawa Trough in the East China Sea. Deep-Sea Res. II, 50, 457–473.
Jenkins, W. J. (2008): The biogeochemical consequences of changing ventilation in the Japan/East Sea. Mar. Chem., 108, 137–147.
Kang, D.-J., J.-Y. Kim, T. Lee and K.-R. Kim (2004): Will East/Japan Sea become an anoxic sea in the next century? Mar. Chem., 91, 77–84.
Keil, R. G. and J. I. Hedges (1993): Sorption of organic matter to mineral surfaces and the preservation of organic matter in coastal marine sediments. Chem. Geol., 107, 385–388.
Kumamoto, Y., M. Yoneda, Y. Shibata, H. Kume, A. Tanaka, T. Uehiro, M. Morita and K. Shitashima (1998): Direct observation of the rapid turnover of the Japan Sea bottom water by means of AMS radiocarbon measurement. Geophys. Res. Lett., 25, 651–654.
Masuzawa, T., S. Noriki, T. Kurosaki, S. Tsunogai and M. Koyama (1989): Compositional change of settling particles with water depth in the Japan Sea. Mar. Chem., 27, 61–78.
McLennan S. M. (2001): Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst., 2, doi:10.1029/2000GC00109.
Menon, S., J. Hansen, L. Nazarenko and Y. Luo (2002): Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science, 297, 2250–2253.
Minakawa, M., S. Noriki and S. Tsunogai (1996): Manganese in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. Geochem. J., 30, 41–55.
Monaco, A., P. Biscaye, J. Soyer, R. Pocklington and S. Heussner (1990): Particulate fluxes and ecosystem response on a continental margin: the 1985–1988 Mediterranean ECOMARGE experiment. Cont. Shelf Res., 10, 809–839.
Nagao, S., T. Usui, M. Yamamoto, M. Minagawa, T. Iwatsuki and A. Noda (2005): Combined use of Δ14C and δ 13C values to trace transportation and deposition processes of terrestrial particulate organic matter in coastal marine environments. Chem. Geol., 218, 63–72.
Nakanishi, T. and M. Minagawa (2003): Stable carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions of sinking particles in the northeast Japan Sea. Geochem. J., 37, 261–275.
Nakatsuka, T., N. Handa, N. Harada, T. Sugimoto and S. Imaizumi (1997): Origin and decomposition of sinking particulate organic matter in the deep water column inferred from the vertical distributions of its δ 15N, δ 13C and Δ14C. Deep-Sea Res. I, 44, 1957–1979.
Nakatsuka, T., A. Hosokawa, N. Handa, E. Matsumoto and T. Masuzawa (2000): 14C budget of sinking particulate organic matter in the Japan Trench: A new approach to estimate the contribution from resuspended particles in deep water column. p. 169–186. In Dynamics and Characterization of Marine Organic Matter, ed. by N. Handa and T. Hama, Terra Scientific Publ. Co., Tokyo.
Nakayama, N., H. Obata and T. Gamo (2007): Consumption of dissolved oxygen in the deep Japan Sea, giving a precise isotopic fractionation factor. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, doi:10.1029/2007GL029917.
Noriki, S. and S. Tsunogai (1986): Particulate fluxes and major components of settling particles from sediment trap experiments in the Pacific Ocean. Deep-Sea Res., 33, 903–912.
Nozaki, Y., H.-S. Yang and M. Yamada (1987): Scavenging of thorium in the ocean. J. Geophys. Res., 92, 772–778.
Obata, H., D. S. Alibo and Y. Nozaki (2007): Dissolved aluminum, indium, and cerium in the Sea of Japan and the Sea of Okhotsk: Composition to the marginal seas of the western North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res., 112, doi:10.1029/2006JC003944.
Onitsuka, G., T. Yanagi and J.-H. Yoon (2007): A numerical study on nutrient sources in the surface layer of the Japan Sea using a coupled physical-ecosystem model. J. Geophys. Res., 112, C05042, doi: 10.1029/2006JC003981.
Otosaka, S. and S. Noriki (2000): REEs and Mn/Al ratio of settling particles: horizontal transport of particulate material in the northern Japan Trench. Mar. Chem., 72, 329–342.
Otosaka, S. and S. Noriki (2005): Relationship between composition of settling particles and organic carbon flux in the western North Pacific and the Japan Sea. J. Oceanogr., 61, 25–40.
Otosaka, S., O. Togawa, M. Baba, E. Karasev, Y. N. Volkov, N. Omata and S. Noriki (2004): Lithogenic flux in the Japan Sea measured with sediment traps. Mar. Chem., 91, 143–163.
Otosaka, S., H. Amano, T. Ito, H. Kawamura, T. Kobayashi, T. Suzuki, O. Togawa, E. L. Chaykovskaya, T. S. Lishavskaya, V. P. Novichkov, E. V. Karasev, A. V. Tkalin and Y. N. Volkov (2006): Anthropogenic radionuclides in sediment in the Japan Sea: Distribution and transport processes of particulate radionuclides. J. Environ. Radioactivity, 91, 128–145.
Raymond, P. A. and J. E. Bauer (2001): Riverine export of aged terrestrial organic matter to the North Atlantic Ocean. Nature, 409, 497–500.
Senjyu, T., T. Aramaki, S. Otosaka, O. Togawa, M. Danchenkov, E. Karasev and Y. Volkov (2002): Renewal of the bottom water after the winter 2000–2001 may spin-up the thermohaline circulation in the Japan Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett., 29, doi:10.1029/2001GL14093.
Sherrell, R. M., M. P. Field and Y. Gao (1998): Temporal variability of suspended mass and composition in the Northeast Pacific water column: relationships to sinking flux and lateral advection. Deep-Sea Res. II, 45, 733–761.
Stuiver, M. and H. A. Polach (1977): Reporting of 14C data. Radiocarbon, 19, 355–363.
Takata, H., K. Kuma, Y. Isoda, S. Otosaka, T. Senjyu and M. Minagawa (2008): Iron in the Japan Sea and its implications for the physical processes in deep water. Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, doi: 10.1029/2007GL031794.
Turner, J. T. (2002): Zooplankton fecal pellets, marine snow and sinking phytoplankton blooms. Aquat. Microb. Ecol., 27, 57–102.
Uda, M. (1934): The results of simultaneous oceanographical investigations in the Japan Sea and its adjacent waters in May and June, 1932. J. Imperial Fishery Experimental Sta., 5, 57–190 (in Japanese).
Watanabe, Y. W., M. Wakita, N. Maeda, T. Ono and T. Gamo (2003): Synchronous bidecadal periodic changes of oxygen, phosphate and temperature between the Japan Sea deep water and the North Pacific intermediate water. Geophys. Res. Lett., 30, doi:10.1029/2003GL018338.
Yeats, P. J., B. Sunday and J. M. Bewers (1979): Manganese recycling in coastal waters. Mar. Chem., 8, 43–55.
Yoo, S. and H.-C. Kim (2004): Suppression and enhancement of the spring bloom in the southwestern East Sea/Japan Sea. Deep-Sea Res. II, 51, 1093–1111.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otosaka, S., Tanaka, T., Togawa, O. et al. Deep sea circulation of particulate organic carbon in the Japan Sea. J Oceanogr 64, 911–923 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-008-0075-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-008-0075-4