Abstract
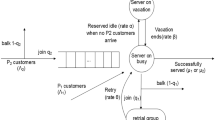
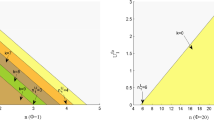
In this paper, equilibrium strategies and optimal balking strategies of customers in a constant retrial queue with multiple vacations and the N-policy under two information levels, respectively, are investigated. We assume that there is no waiting area in front of the server and an arriving customer is served immediately if the server is idle; otherwise (the server is either busy or on a vacation) it has to leave the system to join a virtual retrial orbit waiting for retrials according to the FCFS rules. After a service completion, if the system is not empty, the server becomes idle, available for serving the next customer, either a new arrival or a retried customer from the virtual retrial orbit; otherwise (if the system is empty), the server starts a vacation. Upon the completion of a vacation, the server is reactivated only if it finds at least N customers in the virtual orbit; otherwise, the server continues another vacation. We study this model at two levels of information, respectively. For each level of information, we obtain both equilibrium and optimal balking strategies of customers, and make corresponding numerical comparisons. Through Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm, we explore the impact of parameters on the equilibrium and social optimal thresholds, and obtain the trend in changes, as a function of system parameters, for the optimal social welfare, which provides guiding significance for social planners. Finally, by comparing the social welfare under two information levels, we find that whether the system information should be disclosed to customers depends on how to maintain the growth of social welfare.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Balachandran K (1973) Control policies for a single server system. Manag Sci 19(9):1013–1018
Burnetas A, Economou A (2007) Equilibrium customer strategies in a single server Markovian queue with setup times. Queueing Syst 56(3–4):213–228
Chen H, Frank MZ (2001) State dependent pricing with a queue. IIE Trans 33(10):847–860
Doshi B (1986) Queueing systems with vacations—a survey. Queueing Syst 1(1):29–66
Eberhart R, Kennedy J (1995) A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. In: Proceedings of the sixth international symposium on micro machine and human science MHS’95, pp 39–43
Economou A, Kanta S (2008) Equilibrium balking strategies in the observable single-server queue with breakdowns and repairs. Oper Res Lett 36(6):696–699
Economou A, Kanta S (2011) Equilibrium customer strategies and social-profit maximization in the single-server constant retrial queue. Nav Res Logist 58(2):107–122
Edelson NM, Hilderbrand DK (1975) Congestion tolls for Poisson queuing processes. Econometrica 43(1):81–92
Guo P, Hassin R (2011) Strategic behavior and social optimization in Markovian vacation queues. Oper Res 59(4):986–997
Guo P, Hassin R (2012) Strategic behavior and social optimization in Markovian vacation queues: the case of heterogeneous customers. Eur J Oper Res 222(2):278–286
Guo P, Li Q (2013) Strategic behavior and social optimization in partially-observable Markovian vacation queues. Oper Res Lett 41(3):277–284
Hassin R, Haviv M (2003) To queue or not to queue: equilibrium behavior in queueing systems. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Johansen SG, Stidham S (1980) Control of arrivals to a stochastic input–output system. Adv Appl Probab 12(4):972–999
Kulkarni VG (1983) A game theoretic model for two types of customers competing for service. Oper Res Lett 2(3):119–122
Kumar BK, Vijayalakshmi G, Krishnamoorthy A, Basha SS (2010) A single server feedback retrial queue with collisions. Comput Oper Res 37(7):1247–1255
Liu W, Ma Y, Li J (2012) Equilibrium threshold strategies in observable queueing systems under single vacation policy. Appl Math Model 36(12):6186–6202
Ma Y, Liu W, Li J (2013) Equilibrium balking behavior in the Geo/Geo/1 queueing system with multiple vacations. Appl Math Model 37(6):3861–3878
Naor P (1969) The regulation of queue size by levying tolls. Econometrica 37(1):15–24
Neuts MF (1981) Matrix-geometric solutions in stochastic models. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Shanthikumar J (1981) Optimal control of an M/G/1 priority queue via N-control. Am J Math Manag Sci 1(3):191–212
Stidham S (1985) Optimal control of admission to a queueing system. IEEE Trans Autom Control 30(8):705–713
Sun W, Li S, Cheng-Guo E (2016) Equilibrium and optimal balking strategies of customers in Markovian queues with multiple vacations and N-policy. Appl Math Model 40(1):284–301
Sun W, Li S, Tian N (2017) Equilibrium and optimal balking strategies of customers in unobservable queues with double adaptive working vacations. Qual Technol Quant Manag 14(1):94–113
Wang J, Zhang F (2013) Strategic joining in M/M/1 retrial queues. Eur J Oper Res 230(1):76–87
Wang J, Zhang X, Huang P (2017) Strategic behavior and social optimization in a constant retrial queue with the N-policy. Eur J Oper Res 256(3):841–849
Yadin M, Naor P (1963) Queueing systems with a removable service station. J Oper Res Soc 14(4):393–405
Zhang F, Wang J, Liu B (2012) On the optimal and equilibrium retrial rates in an unreliable retrial queue with vacations. J Ind Manag Optim 8(4):861–875
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the anonymous reviewers and editors for their constructive comments and feedback that help us to improve the presentation and quality of this manuscript. This work was supported in part by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61773014), the Research Fund for the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. KYCX20_0240), and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (No. 315660).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any competing interests in the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Liu, L. & Zhao, Y.Q. Equilibrium customer and socially optimal balking strategies in a constant retrial queue with multiple vacations and N-policy. J Comb Optim 43, 870–908 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-021-00814-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-021-00814-1
Keywords
- Multiple vacations
- Equilibrium strategies
- Balking strategies
- Particle swarm optimization algorithm
- Information accuracy