Abstract
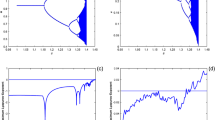
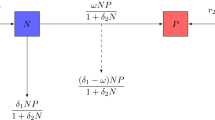
We consider a generalised Gause predator–prey system with a generalised Holling response function of type III: \(p(x) = \frac{mx^2}{ax^2+bx+1}\). We study the cases where b is positive or negative. We make a complete study of the bifurcation of the singular points including: the Hopf bifurcation of codimensions 1 and 2, the Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation of codimensions 2 and 3. Numerical simulations are given to calculate the homoclinic orbit of the system. Based on the results obtained, a bifurcation diagram is conjectured and a biological interpretation is given.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews J.F. (1968). A mathematical model for the continuous culture of microorganisms utilizing inhibitory substrates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 10: 707–723
Bogdanov R.I. (1981). Versal deformation of singularity of a vector field on the plane in the case of zero eigenvalues. Selecta Math. Soviet. 1(4): 389–421
Bonin G. and Legault J. (1988). Comparaison de la méthode des constantes de Lyapunov et de la bifurcation de Hopf. Canad. Math. Bull. 31(2): 200–209
Broer H.W., Naudot V., Roussarie R. and Saleh K. (2006). A predator–prey model with non-monotonic response function. Regul. Chaotic Dyn. 11: 155–165
Broer H.W., Naudot V., Roussarie R. and Saleh K. (2007). Dynamics of a predator–prey model with non- monotonic response function. Disc. Cont. Dyn. Sys. 18: 221–251
Caubergh M. and Dumortier F. (2004). Hopf–Takens bifurcations and centres. J. Differ. Equ. 202: 1–31
Chicone C. (1999). Ordinary differential equations with applications. Springer-Verlag, New York
Chow S.-N., Li C. and Wang D. (1994). Normal Forms and Bifurcation of Planar Vector Fields. Cambridge University Press, New York
Coutu, C.: Étude du diagramme de bifurcation d’un système prédateur-proie. Mémoire de maî trise, Université de Montréal (2003)
Doedel E.J., Keller H.B. and Kernevez J.-P. (1991). Numerical analysis and control of bifurcation problems (II): bifurcation in infinite dimensions. Int. J. Bifurcations Chaos 1: 745–772
Dumortier F., Roussarie R. and Sotomayor J. (1987). Generic 3-parameter families of vector fields on the plane, unfolding a singularity with nilpotent linear part. The cusp case of codimention 3. Ergodic Theor. Dyn. Syst. 7(3): 375–413
Freedman H.I. (1979). Stability analysis of a predator–prey system with mutual interference and density-dependent death rates. Bull. Math. Biol. 41: 67–78
Freedman H.I. (1980). Deterministic Mathematical Models in Population Ecology. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
Freedman H.I. and Wolkowicz G.S.K. (1986). Predator–prey systems with group defence: the paradox of enrichment revisited. Bull. Math. Biol. 485(5/6): 493–508
Gause G.F. (1969). The Struggle for Existence. Hafner Publishing Company, New York
Göbber F. and Willamowski K.-D. (1979). Ljapunov approach of multiple Hopf bifurcation. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 71: 333–350
Guckenheimer J. and Holmes P. (1983). Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems and Bifurcations of Vector Fields. Springer-Verlag, New York
Holling C.S. (1965). The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 45: 3–60
Jost J.L., Drake J.F., Fredrickson A.G. and Tsuchiya H.M. (1973). Interactions of Tetrahymena pyrisformis, Escherichia coli, Azotobacter vinelandii, and glucose in a minimal medium. J. Bacteriol. 113: 834–840
Jost J.L., Drake J.F., Tsuchiya H.M. and Fredrickson A.G. (1973). Microbial food chains and food webs. J. Theor. Biol. 41: 461–484
Lamontagne, Y.: Étude d’un système prédateur-proie avec fonction de réponse Holling de type III généralisée. Mémoire de maîtrise, Université de Montréal (2006)
Ruan S. and Xiao D. (2001). Global analysis in a predator–prey system with nonmonotonic functional response. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 61(4): 1445–1472
Wolkowicz G.S.K. (1988). Bifurcation analysis of a predator–prey system involving group defence. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 48(3): 592–606
Zhu H., Campbell S.A. and Wolkowicz G.S.K. (2002). Bifurcation analysis of a predator–prey system with nonmonotonic functional response. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 63(2): 636–682
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamontagne, Y., Coutu, C. & Rousseau, C. Bifurcation Analysis of a Predator–Prey System with Generalised Holling Type III Functional Response. J Dyn Diff Equat 20, 535–571 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10884-008-9102-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10884-008-9102-9
Keywords
- Predator–prey system
- Response function
- Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation
- Hopf bifurcation
- Limit cycles
- Homoclinic orbit
- Homoclinic bifurcation
- Generalised Holling response function of type III