Abstract
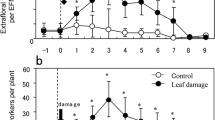
In response to herbivory by spider mites (Tetranychus urticae), lima bean plants produced significantly greater quantities of extrafloral nectar (EFN) than intact conspecific plants. Moreover, EFN amounts of infested plants depended on exposure to odor of infested neighbor plants. Two d after spider mite infestation, a test plant produced more EFN when exposed prior to infestation to volatiles from infested neighbor plants than when exposed to volatiles from uninfested conspecific plants. However, this effect was only detectable 2 d after spider mite infestation and vanished 4 d after infestation. These results suggest that EFN production is enhanced during the earlier stages of damage by T. urticae in response to previous exposure to volatiles from infested neighbor plants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimura, G., Ozawa, R., Shimoda, T., Nishioka, T., Boland, W., and Takabayashi, J. 2000. Herbivory-induced volatiles elicit defence genes in lima bean leaves. Nature 406:512–515.
Bruin, J. and Sabelis, M. W. 2001. Meta-analysis of laboratory experiments on plant–plant information transfer. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 29:1089–1102.
Choh, Y., Shimoda, T., Ozawa, R., Dicke, M., and Takabayashi, J. 2004. Exposure of lima bean leaves to volatiles from herbivore-induced conspecific plants results in emission of carnivore attractants: Active or passive process? J. Chem. Ecol. 30:1305–1317.
Choh, Y., Kugimiya, S., and Takabayashi, J. 2006. Induced production of extrafloral nectar in intact lima bean plants in response to volatiles from spider mite-infested conspecific plants as a possible indirect defense against spider mites. Oecologia 147:455–460.
Conrath, U., Pieterse, C. M. J., and Mauch-Mani, B. 2002. Priming in plant–pathogen interactions. Trends Plant Sci. 7:210–216.
Dicke, M. and Vet, L. E. M. 1999. Plant–carnivore interactions: evolutionary and ecological consequences for plant, herbivore and carnivore, pp. 483–520, in H. Olff, V. K. Brown, and R. H. Drent (eds.). Herbivores: Between Plants and Predators. Blackwell Science, Oxford.
Dicke, M., Sabelis, M. W., Takabayashi, J., Bruin, J., and Posthumus, M. A. 1990. Plant strategies of manipulating predator-prey interactions through allelochemicals: prospects for application in pest control. J. Chem. Ecol. 16:3091–3118.
Heil, M. 2004. Induction of two indirect defences benefits lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus, Fabaceae) in nature. J. Ecol. 92:527–536.
Kost, C. and Heil, M. 2005. Increased availability of extrafloral nectar reduces herbivory in Lima bean plants (Phaseolus lunatus, Fabaceae). Basic Appl. Ecol. 6:237–248.
Kost, C. and Heil, M. 2006. Herbivore-induced plant volatiles induce an indirect defence in neighbouring plants. J. Ecol. 94:619–628.
Raine, N. E., Willmer, P., and Stone, G. N. 2002. Spatial structuring and floral avoidance behavior prevent ant-pollinator conflict in Mexican ant–acacia. Ecology 83:3086–3096.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by CREST of Japan Science and Technology (JST) Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choh, Y., Takabayashi, J. Herbivore-Induced Extrafloral Nectar Production in Lima Bean Plants Enhanced by Previous Exposure to Volatiles from Infested Conspecifics. J Chem Ecol 32, 2073–2077 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9130-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-006-9130-z