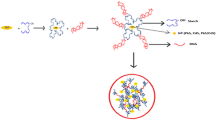
Abstract
In the present research, water soluble thioglycolic acid-capped CdS quantum dots (QDs) were synthesized by chemical precipitation method. The characteristics of prepared quantum dots were determined using X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). The obtained results revealed that CdS QDs have 5.60 nm crystallite size, hexagonal wurtzite structure and spherical morphology with less than 10 nm diameter. The photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy was performed in order to study the effect of the presence of starch solutions. Blue emission peaks were positioned at 488 nm and its intensity quenched by increasing the concentration of starch solutions. The result of PL quenches in range of studied concentrations (0–100 ppm) was best described by Michaelis-Menten model. The amount of Michaelis constant (Km) for immobilized α-amylase in this system was about 68.08 ppm which showed a great tendency of enzyme to hydrolyze the starch as substrate. Finally, the limit of detection (LOD) was found to be about 2.24 ppm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang J, Zhang F, Luo Y, Yang H (2006) A preliminary study on cactus as coagulant in water treatment. Process Biochem. 41:730–733
Chen YC, Xiao J (1999) Researches and applications of natural macromolecular flocculants. Evolve Environ Sci 7:83–88
Ye A, Hemar Y, Singh H (2004) Flocculation and coalescence of droplets in oil-in-water emulsions formed with highly hydrolysed whey proteins as influenced by starch. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 38:1–9
Guo-xiu, X., Shu-fen, Z., Ben-zhi, J., Jin-zong, Y. (2005). Recent advances in modified starch as Flocculant, the proceedings of the 3rd Internation13al conference on functional molecules, China.
Van der kooji D, Hijnen WAM (1985) Determination of the concentration of maltose-and starch-like compounds in drinking water by growth measurement with a well-defined strain of a elavobacterium species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49:765–771
Sene M, Thévenot C, Prioul JL (1997) Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of amylose amylopectin in starch from maize kernel by multiwavelength analysis. J. Cereal Sci. 26:211–221
Boley NP, Burn MJS (1990) The determination of starch in composite food stuffs by high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 36:45–51
Lim LH, Macdonald DG, Gordon A, Hill GA (2003) Hydrolysis of starch particles using immobilized barley alpha-amylase. Biochem. Eng. J. 13:53–62
Hu T, Zhang X, Zhang Z (1999) Disposable screen-printed enzyme sensor for simultaneous determination of starch and glucose. Biotechnol. Tech. 13:359–362
Sakac N, Sak-Bosnar M, Horvat M (2013) Direct potentiometric determination of starch using a platinum redox sensor. Food Chem. 138:9–12
McCleary BV, Solah V, Gibson TS (1994) Quantitative measurement of total starch in cereal flours and products. J. Cereal Sci. 20:51–58
Mitchell GA (1990) Methods of starch analysis. Starch-Starke 42:131–134
Tayebi M, Tavakkoli Yaraki M, Ahmadieh M, Tahriri M, Vashaee D, Tayebi L (2016) Determination of total aflatoxin using cysteamine-capped CdS quantum dots as a fluorescence probe. Colloid Polym Sci 1–10. doi:10.1007/s00396-016-3903-x
Karimi M, Rabiee M, Moztarzadeh F, Bodaghi M, Tahriri M (2009) Ammonia-free method for synthesis of CdS nanocrystalline thin films through chemical bath deposition technique. Solid State Commun 149:1765–1768
Mozafari M, Moztarzadeh F, Tahriri M (2013) Green synthesis and characterisation of spherical PbS luminescent micro- and nanoparticles via wet chemical technique. Adv Appl Ceram 110:30–34
Sahai S, Husain M, Shanker V, Singh N, Haranath D (2011) Facile synthesis and step by step enhancement of blue photoluminescence from Ag-doped ZnS quantum dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 357:379–383
Verma RK, Kumar K, Rai SB (2013) Near infrared induced optical heating in laser ablated Bi quantum dots. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 390:11–16
Kim JJU, Kim YK, Yang H (2010) Reverse micelle-derived Cu-doped Zn1_xCdxS quantum dots and their core/shell structure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 341:59–63
Barglik-Chory C, Buchold D, Schmitt M, Kiefer W, Heske C, Kumpf C, Fuchs O, Weinhardt L, Stahl A, Umbach E, Lentze M, Geurts J, Muuller G (2003) Synthesis, structure and spectroscopic characterization of water-soluble CdS nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 379:443–451
Spoerke ED, Voigt JA (2007) Influence of engineered peptides on the formation and properties of cadmium sulfide nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 17:2031–2037
Kim D, Miyamoto M, Mishima T, Nakayama M (2005) Strong enhancement of band-edge photoluminescence in CdS quantum dots prepared by a reverse-micelle method. J. Appl. Phys. 98:083514–083517
Brichkin S, Chernykh E (2011) Hydrophilic semiconductor quantum dots. High Energy Chem 45:1–12
Van der Maarel MJEC, van der Veen B, Uitdehaag JCM, Leemhuis H, Dijkhuizen L (2002) Properties and applications of starch-converting enzymes of the alpha-amylase family. J. Biotechnol. 94:137–155
Xiao Q, Xiao C (2008) Synthesis and photoluminescence of water-soluble Mn2 + −doped ZnS quantum dots. Appl. Surf. Sci. 254:6432–6435
Hardzei M, Artemyev M (2012) Nfluence of pH on luminescence from water-soluble colloidal Mn-doped ZnSe quantum dots capped with different mercaptoacids. J. Lumin. 132:425–428
Murray CB, Norris DJ, Bawendi MG (1993) Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115:8706–8715
Spanhel L, Anderson MA (1990) Synthesis of porous quantum-size cadmium sulfide membranes: photoluminescence phase shift and demodulation measurements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 112:2278–2284
Zhan JH, Yang XG, Wang DW, Li SD, Xie Y, Xia Y, Qian Y (2000) Polymer-controlled growth of CdS nanowires. Adv. Mater. 12:1348–1351
Kuczynski J, Kerry Thomas J (1985) Photochemical behavior of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide stabilized colloidal cadmium sulfide: effect of surface charge on electron transfer across the colloid-water interface. Langmuir 1:158–161
El-Tayeb O, Mohammad F, Hashem A, Aboulwafa M (2007) Optimization of the industrial production of bacterial alpha amylase in Egypt. IV Fermentor production and characterization of the enzyme of two strains of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 7:4521–4536
Varavinit S, Chaokasem N (2002) Immobilization of a thermosTable alpha-amylase. Sci. Asia 28:247–251
Dhyani H, Azahar Ali M, Pandey MK, Malhotra BD, Sen P (2012) Electrophoretically deposited CdS quantum dots based electrode for biosensor application. J. Mater. Chem. 22:4970–4976
Hamilton LM, Kelly CT, Fogarty WM (1998) Raw starch degradation by the non-raw starch-adsorbing bacterial alpha amylase of bacillus sp. IMD 434. Carbohydr. Res. 314:251–257
Gangadharan D, Nampoothiri KM, Sivaramakrishnan S, Pandey A (2009) Biochemical characterization of raw-starch-digesting alpha amylase purified from bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 158:653–662
Goyal N, Sindhu GS, Chakraburti ST, Gupta JK (1995) Thermostability of alpha amylase produced by bacillus sp., E2-a thermophilic mutant. J. Microb. Biotechnol. 11:593–594
Ul-Haq I, Javed MM, Hameed U, Adnan F (2010) Kinetics and thermodynamic studies of alpha amylase from BACILLUS LICHENIFORMIS MUTANT. Pakistan J Biotechnol 42:3507–3516
Long GL, Winefordner JD (1983) Limit of detection a closer look at the IUPAC definition. Anal. Chem. 55:712–724
Acknowledgments
The authors hereby gratefully acknowledge Professor Farzaneh Vahabzadeh; all the laboratory facilities were provided under the aegis of her.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
M. Tayebi and M. Tavakkoli Yaraki contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tayebi, M., Tavakkoli Yaraki, M., Mogharei, A. et al. Thioglycolic Acid-Capped CdS Quantum Dots Conjugated to α-Amylase as a Fluorescence Probe for Determination of Starch at Low Concentration. J Fluoresc 26, 1787–1794 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-016-1870-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-016-1870-8