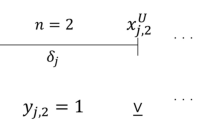Abstract
In this work, we develop an adaptive, multivariate partitioning algorithm for solving nonconvex, Mixed-Integer Nonlinear Programs (MINLPs) with polynomial functions to global optimality. In particular, we present an iterative algorithm that exploits piecewise, convex relaxation approaches via disjunctive formulations to solve MINLPs that is different than conventional spatial branch-and-bound approaches. The algorithm partitions the domains of variables in an adaptive and non-uniform manner at every iteration to focus on productive areas of the search space. Furthermore, domain reduction techniques based on sequential, optimization-based bound-tightening and piecewise relaxation techniques, as a part of a presolve step, are integrated into the main algorithm. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the algorithm on well-known benchmark problems (including Pooling and Blending instances) from MINLPLib and compare our algorithm with state-of-the-art global optimization solvers. With our novel approach, we solve several large-scale instances, some of which are not solvable by state-of-the-art solvers. We also succeed in reducing the best known optimality gap for a hard, generalized pooling problem instance.











Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In the case of a higher order univariate monomial, i.e., \(x_i^5\), apply a reduction of the form \(x_i^2x_i^2x_i \Rightarrow \tilde{x}_i^2x_i \Rightarrow \tilde{\tilde{x}}_ix_i\).
Global optimum is defined numerically by a tolerance, \(\epsilon \).
To keep the algorithm notation simple, this detail is omitted from Algorithm 2.
Exhaustiveness of the partitioning scheme implies AMP will eventually partition all other domains small enough such that AMP will pick an active partition with the global optimal whose length is \(\le \epsilon ^l_i+\epsilon ^u_i\).
See [8] for more details on strategies for choosing the variables for partitioning.
References
Achterberg, T.: SCIP: solving constraint integer programs. Math. Progr. Comput. 1(1), 1–41 (2009)
Al-Khayyal, F.A., Falk, J.E.: Jointly constrained biconvex programming. Math. Oper. Res. 8(2), 273–286 (1983)
Belotti, P.: Bound reduction using pairs of linear inequalities. J. Glob. Optim. 56(3), 787–819 (2013)
Belotti, P., Cafieri, S., Lee, J., Liberti, L.: On feasibility based bounds tightening (2012). https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/file/index/docid/935464/filename/377.pdf
Belotti, P., Lee, J., Liberti, L., Margot, F., Wächter, A.: Branching and bounds tightening techniques for non-convex MINLP. Optim. Methods Softw. 24(4–5), 597–634 (2009)
Bent, R., Nagarajan, H., Sundar, K., Wang, S., Hijazi, H.: A polyhedral outer-approximation, dynamic-discretization optimization solver, 1.x. Tech. rep., Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, NM, USA (2017). https://github.com/lanl-ansi/POD.jl
Bergamini, M.L., Grossmann, I., Scenna, N., Aguirre, P.: An improved piecewise outer-approximation algorithm for the global optimization of MINLP models involving concave and bilinear terms. Comput. Chem. Eng. 32(3), 477–493 (2008)
Boukouvala, F., Misener, R., Floudas, C.A.: Global optimization advances in mixed-integer nonlinear programming, MINLP, and constrained derivative-free optimization, CDFO. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 252(3), 701–727 (2016)
Bussieck, M.R., Drud, A.S., Meeraus, A.: MINLPLib–a collection of test models for mixed-integer nonlinear programming. Inf. J. Comput. 15(1), 114–119 (2003)
Cafieri, S., Lee, J., Liberti, L.: On convex relaxations of quadrilinear terms. J. Glob. Optim. 47(4), 661–685 (2010)
Castro, P.M.: Normalized multiparametric disaggregation: An efficient relaxation for mixed-integer bilinear problems. J. Glob. Optim. 64(4), 765–784 (2016)
Castro, P.M.: Tightening piecewise McCormick relaxations for bilinear problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 72, 300–311 (2015)
Coffrin, C., Hijazi, H.L., Van Hentenryck, P.: Strengthening convex relaxations with bound tightening for power network optimization. In: Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming, pp. 39–57. Springer, Berlin (2015)
Dunning, I., Huchette, J., Lubin, M.: JuMP: A modeling language for mathematical optimization. SIAM Rev. 59(2), 295–320 (2017)
D’Ambrosio, C., Lodi, A., Martello, S.: Piecewise linear approximation of functions of two variables in milp models. Oper. Res. Lett. 38(1), 39–46 (2010)
Faria, D.C., Bagajewicz, M.J.: Novel bound contraction procedure for global optimization of bilinear MINLP problems with applications to water management problems. Comput. Chem. Eng. 35(3), 446–455 (2011)
Faria, D.C., Bagajewicz, M.J.: A new approach for global optimization of a class of MINLP problems with applications to water management and pooling problems. AIChE J. 58(8), 2320–2335 (2012)
Grossmann, I.E., Trespalacios, F.: Systematic modeling of discrete-continuous optimization models through generalized disjunctive programming. AIChE J. 59(9), 3276–3295 (2013)
Hasan, M., Karimi, I.: Piecewise linear relaxation of bilinear programs using bivariate partitioning. AIChE J. 56(7), 1880–1893 (2010)
Hijazi, H., Coffrin, C., Van Hentenryck, P.: Convex quadratic relaxations for mixed-integer nonlinear programs in power systems. Math. Progr. Comput. 9(3), 321–367 (2017)
Hock, W., Schittkowski, K.: Test examples for nonlinear programming codes. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 30(1), 127–129 (1980)
Horst, R., Pardalos, P.M.: Handbook of global optimization, vol. 2. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Horst, R., Tuy, H.: Global optimization: deterministic approaches. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Karuppiah, R., Grossmann, I.E.: Global optimization for the synthesis of integrated water systems in chemical processes. Comput. Chem. Eng. 30(4), 650–673 (2006)
Kocuk, B., Dey, S.S., Sun, X.A.: Strong SOCP relaxations for the optimal power flow problem. Oper. Res. 64(6), 1177–1196 (2016)
Kolodziej, S.P., Grossmann, I.E., Furman, K.C., Sawaya, N.W.: A discretization-based approach for the optimization of the multiperiod blend scheduling problem. Comput. Chem. Eng. 53, 122–142 (2013)
Li, H.L., Huang, Y.H., Fang, S.C.: A logarithmic method for reducing binary variables and inequality constraints in solving task assignment problems. Inf. J. Comput. 25(4), 643–653 (2012)
Liberti, L., Lavor, C., Maculan, N.: A branch-and-prune algorithm for the molecular distance geometry problem. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 15(1), 1–17 (2008)
Lu, M., Nagarajan, H., Bent, R., Eksioglu, S., Mason, S.: Tight piecewise convex relaxations for global optimization of optimal power flow. In: Power Systems Computation Conference (PSCC), pp. 1–7. IEEE (2018)
Lu, M., Nagarajan, H., Yamangil, E., Bent, R., Backhaus, S., Barnes, A.: Optimal transmission line switching under geomagnetic disturbances. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 33(3), 2539–2550 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2017.2761178
Luedtke, J., Namazifar, M., Linderoth, J.: Some results on the strength of relaxations of multilinear functions. Math. Progr. 136(2), 325–351 (2012)
McCormick, G.P.: Computability of global solutions to factorable nonconvex programs: Part i–convex underestimating problems. Math. Progr. 10(1), 147–175 (1976)
Meyer, C.A., Floudas, C.A.: Global optimization of a combinatorially complex generalized pooling problem. AIChE J. 52(3), 1027–1037 (2006)
Misener, R., Floudas, C.: Generalized pooling problem (2011). Available from Cyber-Infrastructure for MINLP [www.minlp.org, a collaboration of Carnegie Mellon University and IBM Research] at: www.minlp.org/library/problem/index.php?i=123
Misener, R., Floudas, C.A.: GloMIQO: Global mixed-integer quadratic optimizer. J. Glob. Optim. 57(1), 3–50 (2013)
Misener, R., Thompson, J.P., Floudas, C.A.: APOGEE: Global optimization of standard, generalized, and extended pooling problems via linear and logarithmic partitioning schemes. Comput. Chem. Eng. 35(5), 876–892 (2011)
Mouret, S., Grossmann, I.E., Pestiaux, P.: Tightening the linear relaxation of a mixed integer nonlinear program using constraint programming. In: Integration of AI and OR Techniques in Constraint Programming for Combinatorial Optimization Problems, pp. 208–222. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Nagarajan, H., Lu, M., Yamangil, E., Bent, R.: Tightening McCormick relaxations for nonlinear programs via dynamic multivariate partitioning. In: International Conference on Principles and Practice of Constraint Programming, pp. 369–387. Springer, Berlin (2016)
Nagarajan, H., Pagilla, P., Darbha, S., Bent, R., Khargonekar, P.: Optimal configurations to minimize disturbance propagation in manufacturing networks. In: American Control Conference (ACC), 2017, pp. 2213–2218. IEEE (2017)
Nagarajan, H., Sundar, K., Hijazi, H., Bent, R.: Convex hull formulations for mixed-integer multilinear functions. In: Proceedings of the XIV International Global Optimization Workshop (LEGO 18) (2018)
Nagarajan, H., Yamangil, E., Bent, R., Van Hentenryck, P., Backhaus, S.: Optimal resilient transmission grid design. In: Power Systems Computation Conference (PSCC), 2016, pp. 1–7. IEEE (2016)
Puranik, Y., Sahinidis, N.V.: Domain reduction techniques for global NLP and MINLP optimization. Constraints 22(3), 338–376 (2017)
Rikun, A.D.: A convex envelope formula for multilinear functions. J. Glob. Optim. 10, 425–437 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008217604285
Ruiz, J.P., Grossmann, I.E.: Global optimization of non-convex generalized disjunctive programs: a review on reformulations and relaxation techniques. J. Glob. Optim. 67(1–2), 43–58 (2017)
Ryoo, H.S., Sahinidis, N.V.: Global optimization of nonconvex nlps and MINLPs with applications in process design. Comput. Chem. Eng. 19(5), 551–566 (1995)
Ryoo, H.S., Sahinidis, N.V.: Analysis of bounds for multilinear functions. J. Glob. Optim. 19(4), 403–424 (2001)
Sahinidis, N.V.: Baron: A general purpose global optimization software package. J. Glob. Optim. 8(2), 201–205 (1996)
Speakman, E.E.: Volumetric Guidance for Handling Triple Products in Spatial Branch-and-Bound by. Ph.D. thesis, University of Michigan (2017)
Tawarmalani, M., Sahinidis, N.V.: A polyhedral branch-and-cut approach to global optimization. Math. Program. 103(2), 225–249 (2005)
Teles, J.P., Castro, P.M., Matos, H.A.: Univariate parameterization for global optimization of mixed-integer polynomial problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 229(3), 613–625 (2013)
Trespalacios, F., Grossmann, I.E.: Cutting plane algorithm for convex generalized disjunctive programs. Inf. J. Comput. 28(2), 209–222 (2016)
Vielma, J.P., Nemhauser, G.L.: Modeling disjunctive constraints with a logarithmic number of binary variables and constraints. Math. Progr. 128(1), 49–72 (2011)
Wicaksono, D.S., Karimi, I.: Piecewise MILP under-and overestimators for global optimization of bilinear programs. AIChE J. 54(4), 991–1008 (2008)
Wu, F., Nagarajan, H., Zlotnik, A., Sioshansi, R., Rudkevich, A.: Adaptive convex relaxations for gas pipeline network optimization. In: American Control Conference (ACC), 2017, pp. 4710–4716. IEEE (2017)
Acknowledgements
The work was funded by the Center for Nonlinear Studies (CNLS) at LANL and the LANL’s directed research and development project “POD: A Polyhedral Outer-approximation, Dynamic-discretization optimization solver”. Work was carried out under the auspices of the U.S. DOE under Contract No. DE-AC52-06NA25396.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
A: Appendix
A: Appendix
1.1 A.1: Sensitivity analysis of \(\Delta \)
One of the important details of MINLP algorithms and approaches is their parameterization. As seen in the earlier sections, AMP is no different. The quality of the solutions depend heavily on the choice of \(\Delta \). However, in spite of this problem specific dependence, it is often interesting to identify reasonable default values. Table 8 presents computational results on all instances for different choices of \(\Delta \). From these results, AMP is most effective when \(\Delta \) is between 4 and 10.
1.2 A.2: Logarithmic and linear encodings of partition variables
In Sect. 2, the discussion on piecewise convex relaxations described formulations that encoded the partition variables with a linear number of variables and a logarithmic number of variables [52]. Table 9 compares the performance of AMP using both formulations. Despite fewer variables in the logarithmic formulation, this encoding is only effective on a few problems, generally on problems that require a significant number of partitions. These results suggest that when the logarithmic encoding has nearly the same number of partition variables as the linear encoding, the linear encoding is more effective.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagarajan, H., Lu, M., Wang, S. et al. An adaptive, multivariate partitioning algorithm for global optimization of nonconvex programs. J Glob Optim 74, 639–675 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-018-00734-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-018-00734-1