Abstract
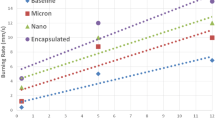
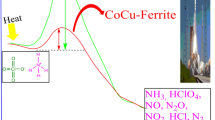
Ammonium perchlorate (APC) is the most common oxidizer in use for solid rocket propulsion systems. However its initial thermal decomposition is an endothermic process that requires 102.5 J/g. This behavior involves high activation energy and could render high burning rate regime. This study reports on the sustainable fabrication of barium ferrite nanoparticles as a novel catalyzing agent for APC oxidizer. Colloidal BaFe12O19 nanoparticles with consistent product quality were fabricated using hydrothermal processing. TEM micrographs demonstrated mono-dispersed particles of 10 nm particle size. XRD diffractogram demonstrated highly crystalline material. The synthesized colloidal BaFe12O19 particles were effectively coated with APC particles via co-precipitation using fast-crash solvent–antisolvent technique. The impact of ferrite particles on APC thermal behavior has been investigated using DSC and TGA techniques. APC demonstrated an initial endothermic decomposition stage at 142 °C with subsequent two exothermic decomposition stages at 297.8 and 452.8 °C respectively. At 1 wt%, barium ferrite offered decrease in initial endothermic decomposition stage by 42.5%. The main outcome of this study is that the two main exothermic decomposition peaks were merged into one single peak with an increase in total heat release by 19.7%. These novel features can inherit ferrite particles unique catalyzing ability for advanced highly energetic systems.













Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
31 March 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-020-01825-x
References
S. Jain, M. Mehilal, S. Nandagopal, P. Singh, K. Radhakrishnan, B. Bhattacharya, Size and shape of ammonium perchlorate and their influence on properties of composite propellant. Def. Sci. J. 59(3), 294 (2009)
A. Kumari, S. Mehilal, M. Jain, B. Jain, Bhattacharya, Nano-ammonium perchlorate: preparation, characterization, and evaluation in composite propellant formulation. J. Energ. Mater. 31(3), 192–202 (2013)
G.P. Li, L.H. Shen, B.M. Zheng, M. Xia, Y.J. Luo, The preparation and properties of AP-based nano-limit growth energetic materials, in Advanced Materials Research (Trans Tech Publ, Zurich, 2014), vol. 924, pp. 105–109
M. Zou, X. Jiang, L. Lu, X. Wang, Nano or micro? A mechanism on thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate catalyzed by cobalt oxalate. J. Hazard. Mater. 225, 124–130 (2012)
J.A. Conkling, C. Mocella, Chemistry of pyrotechnics: basic principles and theory (CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2010)
G.P. Sutton, O. Biblarz, Rocket propulsion elements (2001)
N. Kubota, Propellants and explosives: thermochemical aspects of combustion (Wiley, Hoboken, 2015)
R.A. Chandru, S. Patra, C. Oommen, N. Munichandraiah, B. Raghunandan, Exceptional activity of mesoporous β-MnO2 in the catalytic thermal sensitization of ammonium perchlorate. J. Mater. Chem. 22(14), 6536–6538 (2012)
S. Chaturvedi, P.N. Dave, Nano-metal oxide: potential catalyst on thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J. Exp. Nanosci. 7(2), 205–231 (2012)
M.J. Turner, Rocket and spacecraft propulsion: principles, practice and new developments (Springer, New York, 2008)
N.R. Council, Advanced energetic materials (National Academies Press, Washington, DC, 2004)
S.G. Hosseini, R. Abazari, A. Gavi, Pure CuCr2O4 nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and their morphological and size effects on the catalytic thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Solid State Sci. 37, 72–79 (2014)
S. Wang, R. Shen, Y. Ye, Y. Hu, An investigation into the fabrication and combustion performance of porous silicon nanoenergetic array chips. Nanotechnology 23(43), 435701 (2012)
P.R. Patil, V.E.N. Krishnamurthy, S.S. Joshi, Differential scanning calorimetric study of HTPB based composite propellants in presence of nano ferric oxide. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 31(6), 442–446 (2006)
N. Li et al., Well-dispersed ultrafine Mn3O4 nanoparticles on graphene as a promising catalyst for the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Carbon 54, 124–132 (2013)
S.R. Chakravarthy, E.W. Price, R.K. Sigman, Mechanism of burning rate enhancement of composite solid propellants by ferric oxide. J. Propuls. Power 13(4), 471–480 (1997)
S.-M. Shen, S.-I. Chen, B.-H. Wu, The thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate (AP) containing a burning-rate modifier. Thermochim. Acta 223, 135–143 (1993)
A. Nema, S. Jain, S. Sharma, S. Nema, S. Verma, Mechanistic aspect of thermal decomposition and burn rate of binder and oxidiser of AP/HTPB composite propellants comprising HYASIS-CAT. Int. J. Plastics Technol. 8, 344–354 (2004)
L. Liu, F. Li, L. Tan, L. Ming, Y. Yi, Effects of nanometer Ni, Cu, Al and NiCu powders on the thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 29(1), 34–38 (2004)
R. Rastogi, G. Singh, R.R. Singh, Burning rate catalysts for composite solid propellants Combust. Flame. 30, 117–124 (1977)
W. Pang et al, Effects of different nano-sized metal oxide catalysts on the properties of composite solid propellants. Combust. Sci. Technol. 188(3), 315–328 (2016)
P.W.M. Jacobs, H. Whitehead, Decomposition and combustion of ammonium perchlorate. Chem. Rev. 69(4), 551–590 (1969)
T. Daou et al, Hydrothermal synthesis of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 18(18), 4399–4404 (2006)
X. Wang, Y. Li, Selected-control hydrothermal synthesis of α-and β-MnO2 single crystal nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124(12), 2880–2881 (2002)
A. Cabanas, M. Poliakoff, The continuous hydrothermal synthesis of nano-particulate ferrites in near critical and supercritical water. J. Mater. Chem. 11(5), 1408–1416 (2001)
J.W. Lee, A.S. Hall, J.-D. Kim, T.E. Mallouk, A facile and template-free hydrothermal synthesis of Mn3O4 nanorods on graphene sheets for supercapacitor electrodes with long cycle stability. Chem. Mater. 24(6), 1158–1164 (2012)
J. Li, Engineering Nanoparticles in Near-critical and Supercritical Water, Ph.D. (University of Nottingham, Nottingham, 2008)
M. Yoshimura, K. Byrappa, Hydrothermal processing of materials: past, present and future. J. Mater. Sci. 43(7), 2085–2103 (2008)
K. Byrappa, M. Yoshimura, Handbook of hydrothermal technology (William Andrew, Norwich, 2001)
P. Savage, S. Gopalan, T. Mizan, C. Martino, Reactions at supercritical conditions: applications and fundamentals. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. (AIChE) J. 41(7), 1723–1778 (1995)
K.S. Morley et al, Clean preparation on nanoparticulate metals in porous supports: a supercritical route. J. Chem. Mater. 12, 1898–1905 (2002)
J.A. Darr, M. Poliakoff, New directions in inorganic and metal-organic coordination chemistry in supercritical fluids. Chem. Rev. 99(2), 495–541 (1999)
S. Elbasuney, Dispersion characteristics of dry and colloidal nano-titania into epoxy resin. Powder Technol. 268, 158–164 (2014)
S. Elbasuney, Surface engineering of layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanoparticles for polymer flame retardancy. Powder Technol. 277, 63–73 (2015)
S. Elbasuney, Continuous hydrothermal synthesis of AlO(OH) nanorods as a clean flame retardant agent. Particuology 22, 66–71 (2015)
S. Elbasuney, Sustainable steric stabilization of colloidal titania nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 409, 438–447 (2017)
S. Elbasuney, Novel multi-component flame retardant system based on nanoscopic aluminium-trihydroxide (ATH). Powder Technol. 305, 538–545 (2017)
S. Elbasuney, Novel colloidal molybdenum hydrogen bronze (MHB) for instant detection and neutralization of hazardous peroxides. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 102, 272–279 (2018)
T. Adschiri, Y. Hakuta, K. Arai, Hydrothermal synthesis of metal oxide fine particles at supercritical conditions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 39(12), 4901–4907 (2000)
T. Adschiri, K. Kanazawa, K. Arai, Rapid and continuous hydrothermal synthesis of boehmite particles in subcritical and supercritical water. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75(9), 2615–2618 (1992)
S. Elbasuney, Novel colloidal nanothermite particles (MnO2/Al) for advanced highly energetic systems. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28(5), 1793–1800 (2018)
S. Elbasuney, A. Elsaidy, M. Kassem, H. Tantawy, “Infrared signature of novel super-thermite (Fe2O3/Mg) fluorocarbon nanocomposite for effective countermeasures of infrared seekers. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28(5), 1718–1727 (2018)
S. Elbasuney et al., Super-thermite (Al/Fe2O3) fluorocarbon nanocomposite with stimulated infrared thermal signature via extended primary combustion zones for effective countermeasures of infrared seekers. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 28(6), 2231–2240 (2018)
S. Elbasuney, M. Gaber Zaky, M. Radwan, S.F. Mostafa, Stabilized super-thermite colloids: a new generation of advanced highly energetic materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 419, 328–336 (2017)
S. Elbasuney, H.E. Mostafa, Synthesis and surface modification of nanophosphorous-based flame retardant agent by continuous flow hydrothermal synthesis. Particuology 22, 82–88 (2015)
S. Elbasuney, S.F. Mostafa, Continuous flow formulation and functionalization of magnesium di-hydroxide nanorods as a clean nano-fire extinguisher. Powder Technol. 278, 72–83 (2015)
T. Tillotson, L. Hrubesh, R. Simpson, R. Lee, R. Swansiger, L. Simpson, Sol–gel processing of energetic materials. J. Non-cryst. Solids 225, 358–363 (1998)
M. Mahinroosta, Catalytic effect of commercial nano-CuO and nano-Fe2O3 on thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 3(1), 47 (2013)
V. Boldyrev, Thermal decomposition of ammonium perchlorate. Thermochim. Acta 443(1), 1–36 (2006)
L. Li, Y. Zhou, Z. Li, Y. Ma, C. Pei, One step fabrication of Mn3O4/carbonated bacterial cellulose with excellent catalytic performance upon ammonium perchlorate decomposition. Mater. Res. Bull. 60, 802–807 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work has been conducted at nanotechnology research center in collaboration with department of chemical engineering, School of chemical engineering, Military Technical College, Cairo, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elbasuney, S., Gobara, M. & Yehia, M. Ferrite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Catalytic Activity Evaluation for Solid Rocket Propulsion Systems. J Inorg Organomet Polym 29, 721–729 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-1046-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-1046-x