Abstract
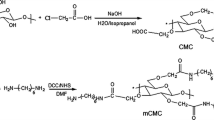
In this paper, pH-sensitive magnetic hydrogels were prepared from carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) and chitosan (CS) without a toxic agent by a simple method as a new carrier for a controlled drug release. Magnetic (Fe3O4) nanoparticles were synthesized by chemical co-precipitation via in situ method under the presence of N2 gas. The effect of magnetic (Fe3O4) nanoparticles amounts on CMC, β-CD and CS hydrogel for drug delivery of Methotrexate (MTX) was investigated. The stability of hydrogel was evaluated using TGA, XRD, VSM, FT-IR, and FE-SEM measurements. The SEM images demonstrated the Fe3O4 distribution in the hydrogel, while XRD patterns confirmed the cubic crystalline phase of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. The hysteresis loop of low magnetic CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogel and high magnetic CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogel is 6.32 and 11.6 emug−1, respectively. The swelling manner of the CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogels was studied at a varied pH range 2–11. CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogel demonstrated slightly higher swelling amount as compared to magnetic CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogel. The prepared hydrogel showed a pH-sensitive swelling manner with great water-absorbing at pH 9. The maximum capacity of swelling in CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogel, low and high magnetic CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogels were obtained 8.8, 6.7 and 4.6 g g−1 respectively. In vitro, MTX release experiment was performed to attain the success of this new method of magnetic CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogel for drug delivery progress. The results showed that the release percent of CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogel was more significant than the other prepared hydrogel. The maximum drug release in CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogel, low and high magnetic CMC/β-CD/CS hydrogels were obtained 92.7, 80.4 and 58.3% at pH 7.4, respectively. Also, the MTX release investigated under an external alternating magnetic field (AMF). The studies illustrated that the response of hydrogel nanocomposite to external stimulants could be used for novel drug delivery systems.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.R. Hoare, D.S. Kohane, Hydrogels in drug delivery: progress and challenges. Polymer 49(8), 1993–2007 (2008)
S. Pandey, K.K. Nanda, Au nanocomposite based chemiresistive ammonia sensor for health monitoring. ACS Sens. 1(1), 55–62 (2015)
S. Pandey, S.B. Mishra, Microwave synthesized xanthan gum-g-poly (ethylacrylate): an efficient Pb2+ ion binder. Carbohydr. Polym. 90(1), 370–379 (2012)
M. Yadollahi, S. Farhoudian, S. Barkhordari, I. Gholamali, H. Farhadnejad, H. Motasadizadeh, Facile synthesis of chitosan/ZnO bio-nanocomposite hydrogelbeads as drug delivery systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 82, 273–278 (2016)
S. Barkhordari, M. Yadollahi, H. Namazi, pH sensitive nanocomposite hydrogel beads based on carboxymethyl cellulose/layered double hydroxide as drug delivery systems. J. Polym. Res. 21(6), 1–9 (2014)
H. Hezaveh, I.I. Muhamad, Impact of metal oxide nanoparticles on oral release properties of pH-sensitive hydrogel nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 50(5), 1334–1340 (2012)
L. Liu, S. Zhu, A study on the supramolecular structure of inclusion complex of β-cyclodextrin with prazosin hydrochloride. Carbohydr. Polym. 68(3), 472–476 (2007)
A. Abou-Okeil, M. Rehan, S.M. El-Sawy, M.K. El-bisi, O.A. Ahmed-Farid, F.A. Abdel-Mohdy, Lidocaine/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex as drug delivery system. Eur. Polym. J. 108, 304–310 (2018)
C. Chang, B. Duan, J. Cai, L. Zhang, Superabsorbent hydrogels based on cellulose for smart swelling and controllable delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 46, 92–100 (2010)
A. de Sousa Leal, R. de Araújo, G.R. Souza, G.L.N. Lopes, L.C.C. Nunes, In vitro bioactivity and cytotoxicity of films based on mesocarp of Orbignya sp. and carboxymethylcellulose as a tannic acid release matrix. Carbohydr. Polym. 201, 113–121 (2018)
Z. Shariatinia, A. Mazloom-Jalali, Chitosan nanocomposite drug delivery systems designed for the ifosfamide anticancer drug using molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 273, 346–367 (2019)
A.V. Samrot, U. Burman, S.A. Philip, N. Shobana, K. Chandrasekaran, Synthesis of curcumin loaded polymeric nanoparticles from crab shell derived chitosan for drug delivery. Inform. Med. Unlocked 10, 159–182 (2018)
Y. Liang, X. Zhao, P.X. Ma, B. Guo, X. Han, pH-responsive injectable hydrogels with mucosal adhesiveness based on chitosan-grafted-dihydrocaffeic acid and oxidized pullulan for localized drug delivery. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 536, 224–234 (2019)
T. Vermonden, R. Censi, W.E. Hennink, Hydrogels for protein delivery. Chem. Rev. 112, 2853–2888 (2012)
G.R. Mahdavinia, Z. Rahmani, S. Karami, A. Pourjavadi, Magnetic/pH-sensitive κ-carrageenan/sodium alginate hydrogel nanocomposite beads: preparation, swelling behavior, and drug delivery. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 25, 1891–1906 (2014)
M.C. Koetting, J.T. Peters, S.D. Steichen, N.A. Peppas, Stimulus-responsive hydrogels: theory, modern advances, and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 93, 1–49 (2015)
S.J. Buwalda, K.W.M. Boere, P.J. Dijkstra, J. Feijen, T. Vermonden, W.E. Hennink, Hydrogels in a historical perspective: from simple networks to smart materials. J. Control. Release 190, 254–273 (2014)
L. Klouda, A.G. Mikos, Thermoresponsive hydrogels in biomedical applications—a review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 68, 34–45 (2008)
N. Sood, A. Bhardwaj, S. Mehta, A. Mehta, Stimuli-responsive hydrogels in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Drug Deliv. 23, 748–770 (2016)
H. Hong, F. Chen, W. Cai, Pharmacokinetic issues of imaging with nanoparticles: focusing on carbon nanotubes and quantum dots. Mol. Imaging Biol. 15, 507–520 (2013)
Z. Li, J.C. Barnes, A. Bosoy, J.F. Stoddart, J.I. Zink, Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 2590–2605 (2012)
S.J. Soenen, W.J. Parak, J. Rejman, B. Manshian, (Intra)cellular stability of inorganic nanoparticles: effects on cytotoxicity, particle functionality, and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev. 115, 2109–2135 (2015)
Y. Min, J. Li, F. Liu, P. Padmanabhan, E. Yeow, B. Xing, Recent advance of biological molecular imaging based on lanthanide-doped upconversion-luminescent nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 4, 129–154 (2014)
D. Ling, T. Hyeon, Chemical design of biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Small 9, 1450–1466 (2013)
R.H. Muller, C. Jacobs, O. Kayser, Nanosuspensions as particulate drug formulations in therapy: rationale for development and what we can expect for the future. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 47, 3–19 (2001)
D.H. Hanna, G.R. Saad, Encapsulation of ciprofloxacin within modified xanthan gum- chitosan based hydrogel for drug delivery. Bioorg. Chem. 84, 115–124 (2019)
A.M. Craciun, L.M. Tartau, M. Pinteala, L. Marin, Nitrosalicyl-imine-chitosan hydrogels based drug delivery systems for long term sustained release in local therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 536, 196–207 (2019)
M. Zhang, J. Wang, Z. Jin, Supramolecular hydrogel formation between chitosan and hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin via Diels-Alder reaction and its drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 114, 381–391 (2018)
S. Javanbakht, M. Pooresmaeil, H. Hashemi, H. Namazi, Carboxymethylcellulose capsulated Cu-based metal-organic framework-drug nanohybrid as a pH-sensitive nanocomposite for ibuprofen oral delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 119, 588–596 (2018)
S.M. Carvalho, A.A.P. Mansur, N.S.V. Capanema, I.C. Carvalho, P. Chagas, L.C.A. de Oliveira, H.S. Mansur, Synthesis and in vitro assessment of anticancer hydrogels composed by carboxymethylcellulose-doxorubicin as potential transdermal delivery systems for treatment of skin cancer. J. Mol. Liq. 266, 425–440 (2018)
V.S. Ghorpade, A.V. Yadav, R.J. Dias, Citric acid crosslinked β-cyclodextrin/carboxymethylcellulose hydrogel films for controlled delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 164, 339–348 (2017)
D. Jeong, S.W. Joo, Y. Hu, V.V. Shinde, E. Cho, S. Jung, Carboxymethyl cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels containing carboxymehtyl β-cyclodextrin for enhanced mechanical strength and effective drug delivery. Eur. Polym. J. 105, 17–25 (2018)
K. Nakagawa, N. Sowasod, W. Tanthapanichakoon, T. Charinpanitkul, Hydrogel based oil encapsulation for controlled release of curcumin by usinga ternary system of chitosan kappa-carrageenan, and carboxymethylcellulosesodium salt. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 54, 600–605 (2013)
R. Machín, J.R. Isasi, I. Vélaz, β-Cyclodextrin hydrogels as potential drug delivery systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 87, 2024–2030 (2012)
Z. Naderi, J. Azizian, Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan/Fe3O4 and MnFe2O4 nanocomposites hydrogels for loading and release of curcumin. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 185, 206–214 (2018)
E.S. Dragan, A.I. Cocarta, Smart macroporous IPN hydrogels responsive to pH, temperature, and ionic strength: synthesis, characterization, and evaluation of controlled release of drugs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 12018–12030 (2016)
E.S. Dragan, A.I. Cocarta, M. Gierszewska, Designing novel macroporous composite hydrogels based on methacrylic acid copolymers and chitosan and in vitro assessment oflysozyme controlled delivery. Colloids Surf. B 139, 33–41 (2016)
A. Fakhri, M. Naji, P. Afshar Nejad, Adsorption and photocatalysis efficiency of magnetite quantum dots anchored tin dioxide nanofibers for removal of mutagenic compound: toxicity evaluation and antibacterial activity. J. Photochem. Photobiol., B 173, 204–209 (2017)
W. Gao, R. Razavi, A. Fakhri, Preparation and development of FeS2 Quantum Dots on SiO2 nanostructures immobilized in biopolymers and synthetic polymers as nanoparticles and nanofibers catalyst for antibiotic degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 114, 357–362 (2018)
M. Hosseini, M. Sarafbidabad, A. Fakhri, Z. Noor Mohammadi, S. Tahami, Preparation and characterization of MnS2/chitosan–sodium alginate and calcium alginate nanocomposites for degradation of analgesic drug: photocorrosion, mechanical, antimicrobial and antioxidant properties studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 118, 1494–1500 (2018)
X. Li, Z. Zhang, A. Fakhri, V.K. Gupta, S. Agarwal, Adsorption and photocatalysis assisted optimization for drug removal by chitosan-glyoxal/Polyvinylpyrrolidone/MoS2 nanocomposites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 136, 469–475 (2019)
A.M.K. Pasha, M. Hosseini, A. Fakhri, V.K. Gupta, S. Agarwal, Investigation of photocatalytic process for iron disulfide-bismuth oxide nanocomposites by using response surface methodology: structural and antibacterial properties. J. Mol. Liq. 289, 110950 (2019)
M.A. Ashraf, W.-X. Peng, A. Fakhri, M. Hosseini, S. Chelliapan, Manganese disulfide-silicon dioxide nano-material: synthesis, characterization, photocatalytic, antioxidant and antimicrobial studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 198, 111579 (2019)
A. Fakhri, V.K. Gupta, H. Rabizadeh, S. Agarwal, S. Tahami, Preparation and characterization of WS2 decorated and immobilized on chitosan and polycaprolactone as biodegradable polymers nanofibers: photocatalysis study and antibiotic-conjugated for antibacterial evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 120, 1789–1793 (2018)
M. Hosseini, A. Pourabadeh, A. Fakhri, J. Hallajzadeh, S. Tahami, Synthesis and characterization of Sb2S3-CeO2/chitosan-starch as a heterojunction catalyst for photo-degradation of toxic herbicide compound: optical, photo-reusable, antibacterial and antifungal performances. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 118, 2108–2112 (2018)
V.K. Gupta, A. Fakhri, S. Agarwal, M. Azad, Synthesis and characterization of Ag2S decorated chitosan nanocomposites and chitosan nanofibers for removal of lincosamides antibiotic. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 103, 1–7 (2017)
V.K. Gupta, A. Fakhri, S. Agarwal, N. Sadeghi, Synthesis of MnO2/cellulose fiber nanocomposites for rapid adsorption of insecticide compound and optimization by response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 102, 840–846 (2017)
Y. Gao, B. Mahmoudi, A. Fakhri, H. Aghazadeh, M. Hosseini, H.A. Ebrahimi, Synthesis of MnO2/CdTiO3 nano-structure for high performance photocatalysis and antimicrobial application. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 33, e5051 (2019)
M. Yadollahi, H. Namazi, Synthesis and characterization of carboxymethyl cellulose/layered double hydroxide nanocomposites. J. Nanopart. Res. 15, 1–9 (2013)
M. Yadollahi, H. Namazi, S. Barkhordari, Preparation and properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/layered double hydroxide bionanocomposite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 108, 83–90 (2014)
N. Shamshad Malik, M. Ahmad, M.U. Minhas, Cross-linked β-cyclodextrin and carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels for controlled drug delivery of acyclovir. PLoS ONE 12, 172727 (2017)
J. Smit, H.P.J. Wijn, Ferrites (Phil. Tech. Lib, Netherland, 1959)
P. Sivakumar, R. Ramesh, A. Ramanand, S. Ponnusamy, C. Muthamizhchelvan, Preparation of sheet like polycrystalline NiFe2O4 nanostructure with PVA matrices and their properties. Mater. Lett. 65(9), 1438–1440 (2011)
P.P. Dhawade, R.N. Jagtap, Characterization of the glass transition temperature of chitosan and its oligomers by temperature modulated differential scanning calorimetry. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 3, 1372–1382 (2012)
M.F. Canbolat, A. Celebioglu, T. Uyar, Drug delivery system based on cyclodextrin-naproxen inclusion complex incorporated in electrospun polycaprolactone nanofibers. Colloids Surf. B 115, 15–21 (2014)
S. Barkhordari, M. Yadollahi, H. Namazi, pH sensitive nanocomposite hydrogel beads based on carboxymethyl cellulose/layered double hydroxide as drug delivery systems. J. Polym. Res. 21(6), 1–9 (2014)
H. Omidian, K. Park, U. Kandalam, J.G. Rocca, Swelling and Mechanical Properties of Modified HEMA-based Superporous Hydrogels. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 25, 483–497 (2010)
O. Philippova, A. Barabanova, V. Molchanov, A. Khokhlov, Magnetic polymer beads: recent trends and developments in synthetic design and applications. Eur. Polym. J 47, 542–559 (2011)
S. Barkhordari, M. Yadollahi, Carboxymethyl cellulose capsulated layered double hydroxides/drug nanohybrids for Cephalexin oral delivery. Appl. Clay Sci. 121–122, 77–85 (2016)
F. Marquez, G.M. Herrera, T. Campo, M. Cotto, J. Duconge, J.M. Sanz, E. Elizalde, O. Perales, C. Morant, Preparation of hollow magnetite microspheres and their applications as drugs carriers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 1–11 (2012)
S. Guerrero, C. Teijón, M. Enriqueta, M.T. José, M.D. Blanco, Characterization and in vivo evaluation of ketotifen-loaded chitosan microspheres. Carbohydr. Polym. 79, 1006–1013 (2010)
S. Rasouli, S. Davaran, F. Rasouli, M. Mahkam, R. Salehi, Synthesis, characterization and pH-controllable methotrexate release from biocompatible polymer/silica nanocomposite for anticancer drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 21, 155–163 (2014)
S. Likhitkar, A.K. Bajpai, Magnetically controlled release of cis-platin from superparamagnetic starch nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 87, 300–308 (2012)
R. Gupta, A.K. Bajpai, Magnetically guided release of ciprofloxacin from superparamagnetic polymer nanocomposites. J. Biomater. Sci. 22, 893–918 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The author thanks from Science and Research Branch, IAU for accomplishment support of the project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naderi, Z., Azizian, J., Moniri, E. et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Carboxymethyl Cellulose/β-Cyclodextrin/Chitosan Hydrogels and Investigating the Effect of Magnetic Nanoparticles (Fe3O4) on a Novel Carrier for a Controlled Release of Methotrexate as Drug Delivery. J Inorg Organomet Polym 30, 1339–1351 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01301-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-019-01301-1