Abstract
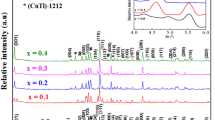
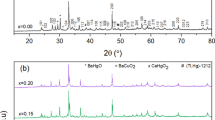
This work reveals the influence of lead fluoride on the physical properties of high-temperature superconductor samples \( \left( {{\text{Cu}}_{0.5 - x} {\text{Tl}}_{0.5} {\text{Pb}}_{x} } \right){\text{Ba}}_{2} {\text{Ca}}_{2} {\text{Cu}}_{3} {\text{O}}_{10 - \delta - y} {\text{F}}_{y} \), with (0.00 ≤ x ≤ 0.10). The samples under investigation were synthesized by solid-state reaction method at normal pressure. Ion beam analysis techniques were employed to determine the elemental content of the starting materials. The fluorine content “y” was estimated using the proton-induced gamma-ray emission technique by the aid of a 3 MeV proton beam. It was correlated to the oxygen content which was obtained using the Rutherford backscattering technique. Moreover, the samples were characterized using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR). The XRD data have indicated that the partial replacement of \( {\text{Cu}}^{2 + } \) ions by Pb2+ ions and oxygen by fluorine in the reservoir layer do not alter the tetragonal structure of the samples. On the other hand, the values of the lattice parameters a and c were found to be varied with x according to the difference in the ionic radii of \( {\text{Pb}}^{2 + } \;{\text{and}}\;{\text{Cu}}^{2 + } \) as well as to the oxygen content. SEM analysis has revealed that lead fluoride substitutions improve the inter-grains connectivity of the prepared samples. FTIR analysis has shown that the apical oxygen, planar and the oxygen in reservoirs layers, modes are observed around 415–524 cm−1, 564–579 cm−1 and 680 cm−1, respectively. Moreover, a shift in all absorption peaks was observed in the pure sample of (CuTl-1223) phase, and new peaks were appeared according to the values of x. The physical properties of the samples were investigated using electrical resistivity and ac magnetic susceptibility measurements at different values of the applied ac magnetic field. The granular response shows both inter-granular and intra-granular contributions. The values of the superconducting transition temperature (\( T_{\text{c}} \)) have shown an increase with x up to 0.06 wt% followed by a decrease with further increase in elements substitution.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Ihara, Y. Sekita, H. Tateai, N.A. Khan, K. Ishida, E. Harashima, T. Kojima, H. Yamamoto, K. Tanaka, Y. Tanaka, N. Terada, IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 9(2), 1551–1554 (1999)
R. Awad, A.A. Aly, M. Kamal, M. Anas, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 24(6), 1947–1956 (2011)
M. Mumtaz, N.A. Khan, S. Abbas, K. Shehzad, Ceram. Int. 40(3), 4187–4191 (2014)
M. Mumtaz, N.A. Khan, F. Ashraf, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 24(5), 1547–1551 (2011)
M. Mumtaz, Z. Iqbal, M.R. Hussain, L. Ali, M. Waqee-ur-Rehman, M. Saqib, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 31(5), 1315–1321 (2018)
N.M. Hamdan, K.A. Ziq, A.S. Al-Harthi, Phys. C Supercond. 314(1–2), 125–132 (1999)
M. Enengl, G. Gritzner, J. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 16(8), 956 (2003)
M. Roumié, B. Nsouli, K. Zahraman, A. Reslan, Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B 219, 389–393 (2004)
A. Srour, R. Awad, W. Malaeb et al., J. Low Temp. Phys. 189, 217–229 (2017)
H. Basma, R. Awad, M. Roumié et al., J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 29, 179–185 (2016)
G.F. Voronin, S.A. Degterov, J. Solid State Chem. 110(1), 50–57 (1994)
N.H. Mohammed, A.I. Abou-Aly, I.H. Ibrahim, R. Awad, M. Rekaby, J. Alloys Compd. 486(1–2), 733–737 (2009)
M. Kühberger, G. Gritzner, J. Phys. C Supercond. 390(3), 263–269 (2003)
N.H. Mohammed, A.I. Abou-Aly, R. Awad, I.H. Ibrahim, M. Roumie, M. Rekaby, J. Low Temp. Phys. 172(3–4), 234–255 (2013)
A. Jabbar, I. Qasim, M. Mumtaz, K. Nadeem, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 25(3), 204–208 (2015)
J.L. Maldonado-Mejía, J.D. Quiz-Celestino, M.E. Botello-Zubiate, S.A. Palomares-Sánchez, J.A. Matutes-Aquino. J. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2013, 5 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/461652
A. Aftabi, M. Mozaffari, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28(8), 2337–2343 (2015)
A. Zelati, A. Amirabadizadeh, A. Kompany, H. Salamati, J. Sonier, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27(6), 1369–1379 (2014)
P. Kameli, H. Salamati, I. Abdolhosseini, J. Alloys Compd. 458(1–2), 61–65 (2008)
H. Salamati, P. Kameli, J. Phys. C Supercond. 403(1–2), 60–66 (2004)
R. Awad, A.I. Abou-Aly, I.H. Ibrahim, M. El-Korek, S. Isber, A. Faraj, J. Alloys Compd. 460(1–2), 500–506 (2008)
X. Liu, H. Liu, J. Xing, Y. Guan, Z. Ma, G. Shan, C. Yang, J. China Particuol. 1(2), 76–79 (2003)
P.G. Radaelli, D.G. Hinks, A.W. Mitchell, B.A. Hunter, J.L. Wagner, B. Dabrowski, K.G. Vandervoort, H.K. Viswanathan, J.D. Jorgensen, J. Phys. Rev. B 49(6), 4163 (1994)
R. Awad, M. Roumié, S. Isber, S. Marhaba, A.I. AbouAly, H. Basma, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 28(2), 535–539 (2015)
R. Awad, N.H. Mohammed, A.A. Aly, S. Isber, H.A. Motaweh, D.E.S. Bakeer, M. Roumié, J. Adv. Ceram. 5(1), 93–101 (2016)
M. Huth, M. Schmitt, H. Adrain, J. Phys. C 178, 203–212 (1991)
S. Celebi, U. Kölemen, A.I. Malik, A. Öztürk, J. Phys. Status Solidi A 194(1), 260–270 (2002)
Acknowledgements
This work was performed in the Materials Science laboratory, Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Beirut Arab University, in cooperation with the Superconductivity and metallic-glass laboratory, Faculty of Science, Alexandria University, Egypt, American University of Beirut (AUB) and Accelerator Laboratory, Lebanese Atomic Energy Commission, CNRS, Beirut, Lebanon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AbuHlaiwa, H., Basma, H., Rekaby, M. et al. Influence of Lead Fluoride Substitution on the Physical Properties of (\( {\text{Cu}}_{0.5} {\text{Tl}}_{0.5} \))-1223 Phase. J Low Temp Phys 198, 26–40 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-019-02245-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-019-02245-z