Abstract
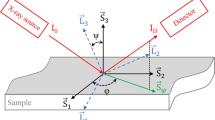
The effects of lamellar duplex microstructure within grains that contain alternating phases of cementite and ferrite on ultrasonic scattering in railroad wheel steel are evaluated using a diffuse ultrasonic backscatter technique. A new singly scattered response (SSR) model that considers the lamellar duplex microstructure within grains is developed based on a previous SSR model. The results show that the amplitude of ultrasonic scattering decreases with decreasing lamellar space. Corresponding experiments are performed with 10 MHz and 15 MHz focused transducers by scanning both unquenched and quenched wheels. The experimental results show that the ultrasonic scattering amplitudes drop dramatically near the quenched tread surface, a result which is attributed to the creation of duplex microstructure (pearlite phase) within grains due to the quenching process. The lamellar spacing within grains increases progressively from the tread surface to the deeper locations due to the non-uniform cooling rate. The distribution of lamellar spacing within grains as a function of depth is quantified with the modified SSR model. Good agreement with optical microscopy is observed. The diffuse ultrasonic backscatter technique exhibits strong sensitivity to microstructure changes, an outcome that may be applicable for quality control during manufacturing.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghoshal, G., Turner, J.A., Weaver, R.L.: Wigner distribution of a transducer beam pattern within a multiple scattering formalism for heterogeneous solids. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 122, 2009–2021 (2007)
Thompson, R.B., Margetan, F., Haldipur, P., Yu, L., Li, A., Panetta, P., Wasan, H.: Scattering of elastic waves in simple and complex polycrystals. Wave Motion 45, 655–674 (2008)
Mamou, J., Oelze, M.L., O’Brien, W.D. Jr, Zachary, J.F.: Identifying ultrasonic scattering sites from three-dimensional and complex polycrystals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 117, 413–423 (2005)
Thompson, R.B., Gray, T.A.: A model relating ultrasonic scattering measurement through liquid–solid interfaces to unbounded medium scattering amplitudes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 74, 1279–1290 (1983)
Weaver, R.L.: Diffusivity of ultrasound in polycrystals. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 38, 55–86 (1990)
Papadakis, E.P.: Ultrasonic attenuation caused by scattering in polycrystalline media. In: Mason, W. (ed.) Physical Acoustics, vol. IV, Part B, pp. 269–328. Academic Press, New York (1968)
Merkulov, L.G.: Investigation of ultrasonic scattering in metals. Sov. Phys. Tech. Phys. 26, 59–69 (1956)
Hirsekorn, S.: The scattering of ultrasonic waves by polycrystals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 72, 1021–1031 (1982)
Hirsekorn, S.: The scattering of ultrasonic waves by polycrystals, II. Shear waves. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 73, 1160–1163 (1982)
Stanke, F.E., Kino, G.S.: A unified theory for elastic wave propagation in polycrystalline materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 75, 665–681 (1984)
Ahmed, S., Thompson, R.B.: Attenuation of ultrasonic waves in cubic metals having elongated, oriented grains. Nondestruct. Test. Eval. 8–9, 525–531 (1992)
Rokhlin, S.I., Bolland, T.K., Adler, L.: High frequency ultrasonic wave propagation in polycrystalline materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 91, 151–165 (1992)
Yang, L., Lobkis, O.I., Rokhlin, S.I.: Shape effect of elongated grains on ultrasonic attenuation in polycrystalline materials. Ultrasonics 51, 697–708 (2011)
Ghoshal, G., Turner, J.A.: Diffuse ultrasonic backscatter at normal incidence through a curved interface. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 128, 3449–3458 (2010)
Rose, J.H.: Ultrasonic backscattering from polycrystalline aggregates using time-domain linear response theory. In: Thompson, D.O., Chimenti, D.E. (eds.) Review of Progress in QNDE, vol. 10, pp. 1715–1720. Plenum, New York (1991)
Rose, J.H.: Ultrasonic backscatter from microstructure. In: Thompson, D.O., Chimenti, D.E. (eds.) Review of Progress in QNDE, vol. 11, pp. 1677–1684. Plenum, New York (1992)
Han, Y.K., Thompson, R.B.: Ultrasonic backscattering in duplex microstructures: theory and application to titanium alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 28A, 91–104 (1997)
Lobkis, O.I., Yang, L., Li, J., Rokhlin, S.I.: Ultrasonic backscattering in polycrystals with elongated single phase and duplex microstructures. Ultrasonics 52, 694–705 (2012)
Lobkis, O.I., Rokhlin, S.I.: Characterization of polycrystals with elongated duplex microstructure by inversion of ultrasonic backscattering data. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 161905 (2010)
Yang, L., Li, J., Lobkis, O.I., Rokhlin, S.I.: Ultrasonic propagation and scattering in duplex microstructures with application to titanium alloys. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 31, 270–283 (2012)
Rodgers, P.H., Van Buren, A.L.: An exact expression for the Lommel diffraction correction integral. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 55, 724–728 (1974)
Schmerr, L.W., Song, S.J.: Ultrasonic Nondestructive Evaluation System. Springer, New York (2007). Chaps. 5, 6, and 8
Schmerr, L.W.: A multigaussian ultrasonic beam model for high performance simulation on a personal computer. Mater. Eval. 58, 882–888 (2000)
Schmerr, L.W.: Fundamentals of Ultrasonic Nondestructive Evaluation, a Modeling Approach. Plenum, New York (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, H., Lonsdale, C., Oliver, J. et al. Evaluation of Railroad Wheel Steel with Lamellar Duplex Microstructures Using Diffuse Ultrasonic Backscatter. J Nondestruct Eval 32, 331–340 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-013-0186-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-013-0186-8