Abstract
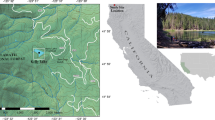
We investigated relationships among modern diatom species composition and physical and chemical characteristics of high-elevation lakes of the Sierra Nevada (California), to develop transfer functions that can be used to infer historic lake conditions. Data were collected from 50 lakes in National Parks and Forests of the central and southern Sierra Nevada. Multivariate statistical methods revealed that acid neutralizing capacity (ANC) and nitrate accounted for significant variation in diatom taxa. A training set with 242 modern diatom taxa from a subset of 41 lakes was used to develop transfer functions for ANC and nitrate using weighted averaging techniques. ANC and nitrate calibration ranges were 23.0–137 μEq/L and 0.18–9.5 μM, respectively. Coefficients of determination for the models were: ANC: R2 = 0.76, and R 2jackknife = 0.44; NO3: R2 = 0.67, and R 2jackknife = 0.27. The ANC model was applied to the top 50 cm of sediments in Moat Lake to reconstruct ANC from ca. AD 350 to 2005. The reconstruction suggests that ANC declined by about 40 % (101–60 μEq/L) between the 1920s and the 1960s and then recovered to pre-1920s levels during 1980–2000. The magnitude of this ANC excursion was the largest observed during the past 1,600 years. We hypothesize that temporal variations in ANC were influenced by: (1) changes in rates of acid deposition, especially nitric acid and (2) variations in the timing and magnitude of snowmelt runoff.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson NJ (2000) Diatoms, temperature and climate change. J Phycol 35:307–314
Appleby PG, Oldfield F (1983) The assessment of 210Pb data from sites with varying sediment accumulation rates. Hydrobiologia 103:29–35
Arnett HA, Saros JE, Mast MA (2012) A caveat regarding diatom-inferred nitrogen concentrations in oligotrophic lakes. J Paleolimnol. doi:10.1007/s10933-011-9576-z
Baron JS (2006) Hindcasting nitrogen deposition to determine an ecological critical load. Ecol Appl 16:433–439
Battarbee RW, Charles DF, Dixit SS, Renberg I (1999) Diatoms as indicators of surface water acidity. In: Stoermer EF, Smol JP (eds) The diatoms: applications for the environmental and earth sciences. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 85–127
Binford MW (1990) Calculation and uncertainty of 210Pb dates for PIRLA project sediment cores. J Paleolimnol 3:253–267
Birks HJB (1998) Numerical tools in palaeolimnology—progress, potentialities, and problems. J Paleolimnol 20:307–332
Birks HJB, Juggins S, Line JM (1990) Lake surface-water chemistry reconstructions from palaeolimnological data. In: Mason BJ (ed) The surface waters acidification program. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 301–313
Bloom AM, Moser KA, Porinchu DF, MacDonald GM (2003) Diatom-inference models for surface-water temperature and salinity developed from a 57-lake calibration set from the Sierra Nevada, California, USA. J Paleolimnol 29:235–255
Box GEP, Cox DR (1964) Analysis of transformations. J R Stat Soc Ser B 26:211–243
Bradford DF, Cooper SD, Brown AD, Jenkins TM, Kratz K, Sarnelle O (1994) Geological controls on natural acidification of alpine lakes in the Eastern Sierra Nevada. Final report, Contract #A132-192, California Air Resources Board, 176 pp
Cameron NG, Birks HJB, Jones VJ, Berges F, Catalan J, Flower RJ, Garcia J, Kawecka B, Koinig KA, Marchetto A, Sánchez-Castillo P, Schmidt R, Šiško M, Solovieva N, Štefková E, Toro M (1999) Surface-sediment and epilithic diatom pH calibration sets for remote European mountain lakes (AL: PE Project) and their comparison with the Surface Waters Acidification Programme (SWAP) calibration set. J Paleolimnol 22:291–317
Catalan J, Barbieri MG, Bartumeus F, Bitušík P, Botev I, Brancelj A, Cogălniceanu DAN, Manca M, Marchetto A, Ognjanova-Rumenova N, Pla S, Rieradevall M, Sorvari S, Štefková E, Stuchlík E, Ventura M (2009) Ecological thresholds in European alpine lakes. Freshw Biol 54:2494–2517
Chen G, Dalton C, Leira M, Taylor D (2008) Diatom-based total phosphorus (TP) and pH transfer functions for the Irish ecoregion. J Paleolimnol 40:143–163
Clerk S, Hall RI, Quinlan R, Smol JP (2000) Quantitative indicators of past hypolimnetic anoxia and nutrient levels from a Canadian Precambrian Shield lake. J Paleolimnol 23:319–336
Clow DW, Nanus L, Huggett B (2010) Use of regression -based models to map sensitivity of aquatic resources to atmospheric deposition in Yosemite National Park, USA. Water Resour Res 46:W09529. doi:10.1029/2009WR008316
Cooper OR, Parrish DD, Stohl A, Trainer M, Nédélec P, Thouret V, Cammas JP, Oltmans SJ, Johnson BJ, Tarasick D, Leblanc T, McDermid IS, Jaffe D, Gao R, Stith J, Ryerson T, Aikin K, Campos T, Weinheimer A, Avery MA (2010) Increasing springtime ozone mixing ratios in the free troposphere over western North America. Nature. doi:10.1038/nature08708
Elser JJ, Andersen T, Baron JS, Bergstrom A-K, Jansson M, Kyle M, Nydick KR, Steger L, Hessen DO (2009) Shifts in lake N:P stoichiometry and nutrient limitation driven by atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Science 326:835–837
Fenn ME, Haeuber R, Tonnesen GS, Baron JS, Grossman-Clarke S, Hope D, Jaffe DE, Copeland S, Geiser L, Rueth HM, Sickman JM (2003) Nitrogen emissions, deposition, and monitoring in the western United States. Bioscience 53:1–13
Gauch HG (1982) Multivariate analysis in community structure. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hastie T, Tibshirani R (1990) Generalized additive models. Chapman & Hall, London. Mathematical Reviews (MathSciNet). MR92e:62117
Hill MO, Gauch HG (1980) Detrended correspondence analysis: an improved ordination technique. Vegetation 42:47–58
Hobbs WO, Telford RJ, Birks HJB, Saros JE, Hazewinkel RRO, Perren BB, Saulnier-Talbot A, Wolfe AP (2010) Quantifying recent ecological changes in remote lakes of North America and Greenland using sediment diatom assemblages. PLoS ONE 5:e10026
Holmes RW, Whiting MC, Stoddard JL (1989) Changes in diatom-inferred pH and add neutralizing capacity in a dilute, high elevation, Sierra Nevada lake since AD 1825. Freshw Biol 21:295–310
Hustedt F (1930) Die Susswasserflora Mitteleuropas. Heft 10, 2nd edn. Bacillariophyta (Diatomeae). Verlag von Gustav Fischer, Germany
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. In: Parry ML, Canziani OF, Palutikof JP, van der Linden PJ, Hanson CE (eds) Contribution of working group II to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 976 pp
Juggins S (2007) C2 version 1.5 user guide. Software for ecological and palaeoecological data analysis and visualisation. Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 73 pp
Kociolek JP, Stoermer EF (1993) Freshwater gomphonemoid diatom phylogeny: preliminary results. Hydrobiologia 269(270):31–38
Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1986) Bacillariophyceae. 1. Teil: Naviculaceae. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart
Leahy PJ, Tibby J, Kershaw AP, Heijnis H, Kershaw JS (2005) The impact of European settlement on Bolin Billabong, a Yarra River floodplain lake, Melbourne, Australia. River Res Appl 21:131–149
Leydecker A, Sickman JO, Melack JM (1999) Episodic lake acidification in the Sierra Nevada, California. Water Resour Res 35:2793–2804
Lien L, Raddum GG, Fjellheim A, Henriksen A (1996) A critical limit for acid neutralizing capacity in Norwegian surface waters, based on new analyses of fish and invertebrate responses. Sci Total Environ 177:173–193
Miller RG (1974) The jackknife—a review. Biometrika 61:1–15
Oldfield F, Appleby PG (1984) Empirical testing of 210Pb-dating models for lake sediments. In: Haworth EY, Lund JWG (eds) Lake sediments and environmental history. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, pp 93–124
Olsson I (1986) Radiometric methods. In: Berglund B (ed) Handbook of Holocene palaeoecology and palaeohydrology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 273–312
Patrick R, Reimer CW (1966) The diatoms of United States, exclusive of Alaska and Hawaii: Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae, Achnanthaceae, Naviculaceae. The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Monograph no. 13, Lititz, Pennsylvania, 688 pp
Philibert A, Gell P, Newall P, Chessman B, Bate N (2006) Development of diatom-based tools for assessing stream water quality in south-eastern Australia: assessment of environmental transfer functions. Hydrobiologia 572:103–114
Porinchu DF, Potito AP, MacDonald GM, Bloom AM (2007) Subfossil chironomids as indicators of recent climate change in Sierra Nevada, California, lakes. Arct Antarct Alp Res 39:286–296
Potapova M, Hamilton PB (2007) Morphological and ecological variation within the Achnanthidium minutissimum (Bacillariophyceae) species complex. J Phycol 43:561–575
Reavie ED, Axler RP, Sgro GV, Danz N, Kingston JC, Kireta AR, Brown TN, Hollenhorst TP, Ferguson MJ (2009) Diatom-based weighted-averaging transfer functions for Great Lakes coastal water quality: relationships to watershed characteristics. J Great Lakes Res 32:321–347
Reimer PJ, Baillie MGL, Bard E, Bayliss A, Beck JW, Blackwell PG, Bronk Ramsey C, Buck CE, Burr GS, Edwards RL, Friedrich M, Grootes PM, Guilderson TP, Hajdas I, Heaton TJ, Hogg AG, Hughen KA, Kaiser KF, Kromer B, McCormac FG, Manning SW, Reimer RW, Richards DA, Southon JR, Talamo S, Turney CSM, van der Plicht J, Weyhenmeyer CE (2010) IntCal09 and Marine09 radiocarbon age calibration curves, 0–50,000 years cal BP. Radiocarbon 51:1111–1150
Rose N, Juggins S, Watt J, Battarbee R (1994) Fuel-type characterization of spheroidal carbonaceous particles using surface chemistry. Ambio 23:296–299
Rosén P, Hall R, Korsman T, Renberg I (2000) Diatom transfer-functions for quantifying past air temperature, pH and total organic carbon concentration from lakes in northern Sweden. J Paleolimnol 24:109–123
Saros JE, Michel TJ, Interlandi SJ, Wolfe AP (2005) Resource requirements of Asterionella formosa and Fragilaria crotonensis in oligotrophic alpine lakes: implications for recent phytoplankton community reorganizations. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62:1681–1689
Saros JE, Clow DW, Blett T, Wolfe AP (2011) Critical nitrogen deposition loads in high-elevation Lakes of the western US inferred from paleolimnological records. Water Air Soil Pollut. doi:10.1007/s11270-010-0526-6
Schelske CL, Peplow A, Brenner M, Spencer CN (1994) Low-background gammacounting: applications for 210Pb dating of sediments. J Paleolimnol 10:115–128
Sickman JO, Leydecker A, Melack JM (2001) Nitrogen mass balances and abiotic controls on N retention and yield in high-elevation catchments of the Sierra Nevada, California, USA. Water Resour Res 37:1445–1461
Sickman JO, Leydecker A, Chang CCY, Kendall C, Melack JM, Lucero DM, Schimel JP (2003) Mechanisms underlying export of N from high-elevation catchments during seasonal transitions. Biogeochemistry 64:1–32
Siver PA (1999) Development of paleolimnological inference models for pH, total nitrogen and specific conductivity based on planktonic diatoms. J Paleolimnol 21:45–60
Smol JP (2010) The power of the past: using sediments to track the effects of multiple stressors on lake ecosystems. Freshw Biol 55:43–59
Steffen W, Sanderson A, Tyson PD, Jager J, Matson PM et al (2004) Global change and the earth system: a planet under pressure. Springer, New York
Telford R, Birks H (2011) Effect of uneven sampling along an environmental gradient on transfer-function performance. J Paleolimnol 46:99–106
ter Braak CJF (1986) Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67:1167–1179
ter Braak CJF (1995) Non-linear methods for multivariate statistical calibration and their use in palaeoecology: a comparison of inverse (k-Nearest Neighbours, PLS and WA-PLS) and classical approaches. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 28:165–180
ter Braak CJF, Juggins S (1993) Weighted averaging partial least squares regression (WA-PLS): an improved method for reconstructing environmental variables from species assemblages. Hydrobiologia 269–270:485–502
ter Braak CJF, Looman CWN (1986) Weighted averaging, logistic regression and the Gaussian response model. Plant Ecol 65:3–11
ter Braak CJF, Smilauer P (1998) CANOCO reference manual and user’s guide to CANOCO for Windows: software for canonical community ordination (version 4). Microcomputer Power, Ithaca
Weckstrom J, Korhola A, Blom T (1997) Diatoms as quantitative indicators of pH and water temperature in subarctic Fennoscandian lakes. Hydrobiologia 347:171–184
Whiting MC, Whitehead DR, Holmes RW, Norton SA (1989) Paleolimnological reconstruction of recent acidity changes in four Sierra Nevada lakes. J Paleolimnol 2:285–304
Wilander A (2001) How are results from critical load calculations reflected in lake water chemistry? Water Air Soil Pollut Focus 1:525–532
Wolfe AP, Cooke CA, Hobbs WO (2007) Are current rates of atmospheric nitrogen deposition influencing lakes in the eastern Canadian arctic? Arct Antarct Alp Res 38:465–476
Acknowledgments
The first two authors contributed equally to the research and preparation of the manuscript. We are grateful to Jason Curtis and Jaime Escobar for their generous assistance collecting the long core from Moat Lake and guidance on sediment processing. We thank Kevin Skeen, Steve Sadro, Andrea Heard, Peter Homyak, Tor Skeen, William Vicars, Samuel Lucero-Sickman, Kaitlyn Lucero-Sickman, Paul Sternberg, Katherine Kendrick, Nicole Reid and personnel from Sequoia and Kings Canyon National Parks for assistance with calibration lake sampling. We thank Annie Esperanza and Lee Tarnay of the U.S. National Park Service and Joe Gurrieri, and Jeffrey Weise of the U.S. Forest Service for their logistical support of the project. Assistance with the sampling design and 210Pb analyses was provided by Mark Brenner of the Land Use and Environmental Change Institute (LUECI) at the University of Florida. Project funding was provided by the National Park Service, U.S. Forest Service and the University of California, Riverside.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sickman, J.O., Bennett, D.M., Lucero, D.M. et al. Diatom-inference models for acid neutralizing capacity and nitrate based on 41 calibration lakes in the Sierra Nevada, California, USA. J Paleolimnol 50, 159–174 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-013-9711-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-013-9711-0