Abstract
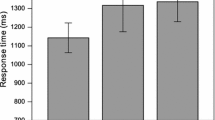
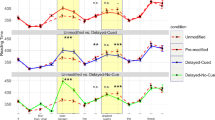
The present study examines whether children reactivate a moved constituent at its gap position and how children’s more limited working memory span affects the way they process filler-gap dependencies. 46 5–7 year-old children and 54 adult controls participated in a cross-modal picture priming experiment and underwent a standardized working memory test. The results revealed a statistically significant interaction between the participants’ working memory span and antecedent reactivation: High-span children (n = 19) and high-span adults (n = 22) showed evidence of antecedent priming at the gap site, while for low-span children and adults, there was no such effect. The antecedent priming effect in the high-span participants indicates that in both children and adults, dislocated arguments access their antecedents at gap positions. The absence of an antecedent reactivation effect in the low-span participants could mean that these participants required more time to integrate the dislocated constituent and reactivated the filler later during the sentence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann H., Nagengast J., & Klaas G. (1993). Nijmegen: New experimental setup (NESU) Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics.
Booth J., Perfetti C., MacWhinney B. (1999). Quick, automatic and general activation of orthographic and phonological representation in young readers. Developmental Psychology 35, 3–19
Booth J., MacWhinney B., Harasaki Y. (2000). Developmental differences in visual and auditory processing of complex sentences. Child Development 71(4): 981–1003
Chomsky N. (1981). Lectures on government and binding. Dordrecht, Foris
Chomsky N. (1995). The minimalist program. Cambridge, MA, MIT Press
Clahsen H., Featherston S. (1999). Antecedent-priming at tracepositions: Evidence from German scrambling. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 28(4): 415–437
Crain S., Wexler K. (1999). Methodology in the study of language acquisition: A modular approach. In: Richie W., Bhatia T., (eds) Handbook of child language acquisition. SanDiego, Academic Press, pp. 387–425
Daneman M., Carpenter P. (1980). Individual differences in working memory and reading. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behaviur 19, 450–466
Felser C., Marinis T., Clahsen H. (2003). Children’s processing of ambiguous sentence: a study of relative clause attachment. Language Acquisition 11, 127–163
Francis N., Kucera H. (1982). Frequency analysis of English usage: Lexicon and grammar. Boston, Houghton Mifflin
Friederici A., Hahne A. (2001). Development patterns of brain activity. In: Weissenborn J., Höhle B. (eds), Approaches to bootstrapping: Phonological, lexical, syntactic and neurophysiological aspects of early language acquisition, Vol.2. Amsterdam & Philadelphia, John Benjamins, pp. 231–246
Gathercole S., Baddeley A. (1989). Evaluation of the role of phonological STM in the development of vocabulary in children: A longitudinal study. Journal of Memory and Language 28, 200–213
Gathercole S., Baddeley A. (1990). Phonological memory deficits in language disordered children: Is there a causal connection?. Journal of Memory and Language 29, 336–360
Gaulin C., Campbell T. (1994). Procedure for assessing verbal working memory in normal school-age children: Some preliminary data. Perceptual and Motor Skills 79, 55–64
Gibson E. (1998). Syntactic complexity: Locality of syntactic dependencies. Cognition 68, 1–75
Gibson E., Warren T. (2004). Reading-time evidence for intermediate linguistic structure in long-distance dependencies. Syntax 7, 55–78
King J., Just M. (1991). Individual differences in syntactic processing: The role of working memory. Journal of Memory and Language 30, 580–602
King J., Kutas M. (1995). Who did what and when? Using word- and clause-level ERPs to monitor working memory usage in reading. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 7, 376–395
Kluender R., Kutas M. (1993). Bridging the gap: Evidence from ERPs on the processing of unbounded dependencies. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 5, 196–214
Kluender R., & Münte T. (1998). Subject/Object asymmetries: ERPs to grammatical and ungrammatical wh-questions. Poster presented at the 11th Annual CUNY Conference on Human Sentence Processing, Rutgers University.
Love T., Swinney D. (1996). Coreference processing and levels of analysis in object-relative constructions: Demonstration of antecedent reactivation with the cross-modal priming paradigm. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 20(1): 5–24
Love T., & Swinney D. (1997). Real time processing of object relative constructions by pre-school children. Poster presented at the 10th Annual CUNY Conference on Human Language Processing, Santa Monica.
Love T., & Swinney D. (2007) The processing of non-canonically ordered constituents in long distance dependencies by pre-school children: a real-time investigation. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research.
McKee C., Nicol J., McDaniel D. (1993). Children’s application of binding during sentence processing. Language and Cognitive Processes 8, 265–290
Miyamoto E., Takahashi S. (2001). Antecedent reactivation in the processing of scrambling in Japanese. MIT Working Papers in Linguistics 43, 127–142
Nakano Y., Felser C., Clahsen H. (2002). Antecedent priming at trace positions in Japanese long-distance scrambling. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 31, 531–571
Nicol J. (1993). Reconsidering reactivation. In: Altmann G., Shillcock R. (eds) Cognitive models of speech processing: The second Sperlonga meeting. Hove, Erlbaum, pp. 321–350
Pickering M. (1993). Direct Association and sentence processing: A reply to Gibson, and Hickok. Language and Cognitive Processes 8, 163–196
Sekerina I, Stromswold K., Hestvik A. (2004). How do adults and children process referentially ambiguous pronouns?. Journal of Child Language 31, 123–152
Snodgrass J., Vanderwart M. (1980). A standardized set of 260 pictures: Norms for name agreement, image agreement, familiarity and visual complexity. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Learning, & Memory 6: 174–215
Traxler M. (2002). Plausibility and subcategorization preference inchildren’s processing of temporarily ambiguous sentences: Evidence fromself-paced reading. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 55A(1): 75–96
Traxler M., Pickering M. (1996). Plausibility and the processing of unbounded dependencies: An eye-tracking study. Journal of Memory and Language 35, 454–475
Trueswell J., Sekerina I., Hill N., Logrip M. (1999). Thekindergarden-path effect: Studying on-line sentence processing in young children. Cognition 73, 89–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, L., Marinis, T., Felser, C. et al. Antecedent Priming at Trace Positions in Children’s Sentence Processing. J Psycholinguist Res 36, 175–188 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-006-9038-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-006-9038-3