Abstract
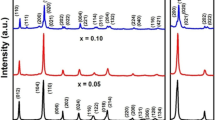
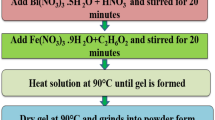
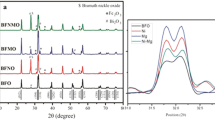
BiFeO3 nanoparticles were prepared via a soft chemical method using citric acid and tartaric acid routes followed by calcination at low temperature. Structural characterization showed remarkably different conditions for pure phase formation from both routes. The tartaric acid route was effective in obtaining pure phase BiFeO3 nanoparticles while citric acid route required leaching in dilute nitric acid to remove impurity phases. Further optical, magnetic, and dielectric characterizations of pure phase BiFeO3 nanoparticles obtained by tartaric acid route were done. X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy confirmed the distorted rhombohedral structure of BiFeO3 nanoparticles. The average crystallite size of BiFeO3 nanoparticles was found to vary in the range 30–50 nm. Fourier Transformed Infrared spectra of BiFeO3 samples calcined at different temperatures were studied in order to analyze various bond formations in the samples. UV-Visible diffuse absorption showed that BFO nanoparticles strongly absorb visible light in the wavelength region of 400–580 nm with absorption cut-off wavelength of 571 nm. The band gap of BiFeO3 nanoparticles was found to be 2.17 eV as calculated from absorption coefficient spectra. Magnetic measurement showed saturated hysteresis loop indicating ferromagnetic behavior of BiFeO3 nanoparticles at room temperature. Temperature dependent dielectric constant showed anomaly well below the antiferromagnetic Néel temperature indicating decrease in antiferromagnetic Néel temperature of BiFeO3 nanoparticles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fiebig, M., Lottermoser, Th., Frohlich, D., Goltsev, A.V., Pisarev, R.V.: Nature 419, 818 (2002)
Hill, N.A.: J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 6694 (2000)
Fischer, P., Polomska, M., Sosnowska, I., Szymanskig, M.: J. Phys. C 13, 1931 (1980)
Wang, Y.P., Zhou, L., Zhang, M.F., Chen, X.Y., Liu, J.M., Liu, Z.G.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 1731 (2004)
Selbach, S.M., Tybell, T., Einarsrud, MA, Grande, T.: Chem. Mater. 19, 6478 (2007)
Dai, H., Li, T., Xue, R., Chen, Z., Xue, Y.: J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25, 109 (2012)
Tang, Y.H., Han, T.C., Liu, H.L., Lin, J.G.: J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. (2011). doi:10.1007/s10948-011-1257-7
Mazumder, R., Ghosh, S., Mondal, P., Bhattacharya, D., Dasgupta, S., Das, N., Sen, A., Tyagi, A.K., Sivakumar, M., Takami, T., Ikuta, H.: J. Appl. Phys. 100, 033908 (2006)
Takahashi, K., Kida, N., Tonouchi, M.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 117402 (2006)
Gao, F., Chen, X., Yin, K., Dong, S., Ren, Z., Yuan, F., Yu, T., Zou, Z., Liu, J.M.: Adv. Mater. 19, 2889 (2007)
Gao, F., Yuan, Y., Wang, K.F., Chen, X.Y., Chen, F., Liu, J.M.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 102506 (2006)
Fukumura, H., Matsui, S., Harima, H., Takahashi, T., Itoh, T., Kisoda, K., Tamada, M., Noguchi, Y., Miyayama, M.: J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19, 365224 (2007)
Singh, M.K., Jang, H.M., Ryu, S., Jo, M.H.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 42907 (2006)
Yang, H., Xian, T., Wei, Z.Q., Dai, J.F., Jiang, J.L., Feng, W.J.: J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 58, 238 (2011)
Bhushan, B., Basumallick, A., Bandopadhyay, S.K., Vasanthacharya, N.Y., Das, D.: J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 42, 065004 (2009)
Jaiswal, A., Das, R., Vivekanand, K., Abraham, P.M., Adyanthaya, S., Poddar, P.: J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 2108 (2010)
Zhang, S.T., Lu, M.H., Wu, D., Chen, Y.F., Ming, N.B.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 262907 (2005)
Chang, D.A., Lin, P., Tseng, T.Y.: J. Appl. Phys. 77, 4445 (1995)
Joshi, U.A., Jang, J.S., Borse, P.H., Lee, J.S.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 242106 (2008)
Maxwell, P.C.: Electricity and Magnetism, vol. 1. Oxford University Press, Oxford. Section 328
Koops, C.G.: Phys. Rev. 83, 121 (1951)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Department of Science and Technology (DST) India through grant No. SR/FTP/PS-91/2009. Manisha Arora is thankful to JIIT Noida for providing Teaching Assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, M., Sati, P.C., Chauhan, S. et al. Structural, Optical and Multiferroic Properties of BiFeO3 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Soft Chemical Route. J Supercond Nov Magn 26, 443–448 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-012-1761-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-012-1761-4