Abstract
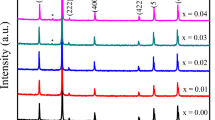
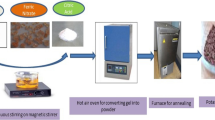
In this study, nanocrystalline Li–Zn ferrites with the chemical composition Li0.5Zn x Fe2.5−x O4 (where x=0, 0.1,0.2,0.3,0.4,0.5) were synthesized by the glycine–nitrate process using glycine as a fuel, nitrate as an oxidizer and microwave oven as a heat source. The combustion reaction was studied by differential thermal analysis and thermogravimetry. The experimentally determined combustion reaction is extremely exothermic and it occurs at 170 ∘C. The as-synthesized powders were characterized by X-ray diffraction technique. X-ray diffraction data shows that nanocrystalline Li–Zn ferrite powders with a spinel structure have been formed successfully in all samples. Morphological studies using scanning electron microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy show agglomerated clusters with a lot of pores attributed to the large amount of gases released during the combustion synthesis with the particle size of 20–40 nm. The magnetic measurements on the as-synthesized powders and compacted samples were carried out using a vibrating sample magnetometer and an inductance/capacitance/resistance meter, respectively. Saturation magnetization increases with the increase in zinc concentration up to x=0.2 and then it decreases with the increase in the zinc content. In addition, maximum magnetic permeability also obtained for the sample with x=0.2 at different frequencies.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hankare, P.P., Patil, R.P., Sankpal, U.B., Garadkar, K.M., Sasikala, R., Tripathi, A.K., Mulla, I.S.: Magnetic, dielectric and complex impedance spectroscopic studies of nanocrystalline Cr substituted Li-ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 2629–2633 (2010)
Mazen, S.A., Dawoud, H.A.: Temperature and composition dependence of dielectric properties in Li–Cu ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 557–566 (2003)
Fu, Y.P., Hsu, C.S.: Li0.5Fe2.5−x Mn x O4 ferrite sintered from microwave-induced combustion. Solid State Commun. 134, 201–206 (2005)
Manjura Hoque, S., Samir Ullah, M., Khan, F.A., Hakim, M.A., Saha, D.K.: Structural and magnetic properties of Li–Cu mixed spinel ferrites. Physica B, Condens. Matter 406, 1799–1804 (2011)
Fu, Y.P.: Microwave-induced combustion synthesis of Li0.5Fe2.5−x Cr x O4 powder and their characterization. Mater. Res. Bull. 41, 809–816 (2006)
Watawe, S.C., Sarwade, B.D., Bellad, S.S., Sutar, B.D., Chougule, B.K.: Microstructure, frequency and temperature-dependent dielectric properties of cobalt-substituted lithium ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 214, 55–60 (2000)
Akhter, S., Hakim, M.A.: Magnetic properties of cadmium substituted lithium ferrites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 120, 399–403 (2010)
Soibam, I., Phanjoubam, S., Sharma, H.B., Sarma, H.N.K., Prakash, C.: Magnetic studies of Li–Zn ferrites prepared by citrate precursor method. Physica B, Condens. Matter 404, 3839–3841 (2009)
Ravinder, D.: Far-infrared spectral studies of mixed lithium–zinc ferrites. Mater. Lett. 40, 205–208 (1999)
Reddy, P.V.B., Reddy, V.R., Gupta, A., Gopalan, R., Reddy, C.G.: Mössbauer study of nano-crystalline Li–Zn ferrites. Hyperfine Interact. 183, 253–258 (2008)
Jiang, X.N., Lan, Z.W., Yu, Z., Liu, P.Y., Chen, D.Z., Liu, C.Y.: Sintering characteristics of Li–Zn ferrites fabricated by a sol–gel process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 52–55 (2009)
Snelling, E.C.: Ferrites for Inductors and Transformers. Research Studies Press, New York (1983)
Gheisari, K., Bhame, S.D., Oh, J.T., Javadpour, S.: Comparative studies on the structure and magnetic properties of Ni–Zn ferrite powders prepared by glycine–nitrate auto-combustion process and solid state reaction method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26, 477–483 (2013)
Patil, K.C., Hegde, M.S.: Chemistry of Nanocrystalline Oxide Materials. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., London (2008)
Chick, L.A., Pederson, L.R., Maupin, G.D., Bates, J.L., Thomas, L.E., Exarhos, G.J.: Glycine–nitrate combustion synthesis of oxide ceramic powders. Mater. Lett. 10, 6–12 (1990)
Hajarpour, S., Gheisari, Kh., Honarbakhsh Raouf, A.: Characterization of nanocrystalline Mg0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 soft ferrites synthesized by glycine–nitrate combustion process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 329, 165–169 (2013)
Mirshekari, G.R., Daee, S., Mohseni, H., Torkian, S., Ghasemi, M., Ameriannejad, M., Hoseinizade, M., Pirnia, M., Pourjafar, D., Pourmahdavi, M., Gheisari, K.: Structure and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrite synthesized by glycine–nitrate auto-combustion process. Adv. Mater. Res. 409, 520–525 (2012)
Mohseni, H., Shokrollahi, H., Sharifi, I., Gheisari, Kh.: Magnetic and structural studies of the Mn-doped Mg–Zn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by the glycine–nitrate process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3741–3747 (2012)
Sertkol, M., Köseoglu, Y., Baykal, A., Kavas, H., Bozkurt, A., Toprak, M.S.: Microwave synthesis and characterization of Zn-doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 486, 325–329 (2009)
Costa, A.C.F.M., Vieira, D.A., Silva, V.J., Diniz, V.C.S., Kiminami, R.H.G.A., Gama, L.: Synthesis of the Ni–Zn–Sm ferrites using microwaves energy. J. Alloys Compd. 483, 37–39 (2009)
Halliday, D., Resnick, R., Walker, J.: Fundamentals of Physics, 9th edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Yue, Z., Zhou, J., Wang, X., Gui, Z., Li, L.: Preparation and magnetic properties of titanium-substituted LiZn ferrites via a sol–gel auto-combustion process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 23, 189–193 (2003)
Yue, Z., Zhou, J., Li, L., Zhang, H., Gui, Z.: Synthesis of nanocrystalline NiCuZn ferrite powders by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 208, 55–60 (2000)
Graef, M.D., McHenry, M.E.: Structure of Materials: an Introduction to Crystallography, Diffraction, and Symmetry. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2007)
Hankare, P.P., Kadam, M.R., Patil, R.P., Garadkar, K.M., Sasikala, R., Tripathi, A.K.: Effect of zinc substitution on structural and magnetic properties of copper ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 501, 37–41 (2010)
Tjong, S.C., Chen, H.: Nanocrystalline materials and coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng., R Rep. 45, 1–88 (2004)
Sharma, S., Verma, K., Chaubey, U., Singh, V., Mehta, B.R.: Influence of Zn substitution on structural, microstructural and dielectric properties of nanocrystalline nickel ferrites. Mater. Sci. Eng. B, Solid-State Mater. Adv. Technol. 167, 187–192 (2010)
Goldman, A.: Modern Ferrite Technology, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Shen, Y., Hng, H.H., Oh, J.T.: Synthesis and characterization of high-energy ball milled Ni–15%Fe–5%Mo. J. Alloys Compd. 379, 266–271 (2004)
Kumar, G., Chand, J., Dogra, A., Kotnal, R.K., Singh, M.: Improvement in electrical and magnetic properties of mixed Mg–Al–Mn ferrite system synthesized by citrate precursor technique. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 71, 375–380 (2010)
Haque, M.M., Huq, M., Hakim, M.A.: Influence of CuO and sintering temperature on the microstructure and magnetic properties of Mg–Cu–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 2792–2799 (2008)
Akther Hossain, A.K.M., Mahmud, S.T., Seki, M., Kawai, T., Tabata, H.: Structural, electrical transport, and magnetic properties of Ni1−x Zn x Fe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 312, 210–219 (2007)
Gutiérrez-López, J., Rodriguez-Senín, E., Pastor, J.Y., Paris, M.A., Martín, A., Levenfeld, B., Várez, A.: Microstructure, magnetic and mechanical properties of Ni–Zn ferrites prepared by powder injection moulding. Powder Technol. 210, 29–35 (2011)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the Shahid Chamran University for providing support to this research through the Grant 91-4-06-636410. The authors are indebted to Dr. Ranjbar, Dr. Saemi and S. Tahanzadeh for their great assistance. We also would like to thank H. Mohseni and S. Hajarpour who gave us excellent advices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borhan, N., Gheisari, K. Structural and Magnetic Properties of Nanocrystalline Lithium–Zinc Ferrite Synthesized by Microwave-Induced Glycine–Nitrate Process. J Supercond Nov Magn 27, 1483–1490 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-013-2450-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-013-2450-7