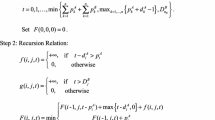Abstract
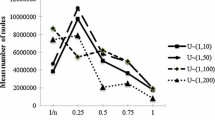
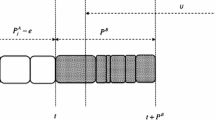
In this paper, we develop branch-and-bound algorithms for several hard, two-agent scheduling problems, i.e., problems in which each agent has an objective function which depends on the completion times of its jobs only. Our bounding approach is based on the fact that, for all problems considered, the Lagrangian dual gives a good bound and can be solved exactly in strongly polynomial time. The problems addressed here consist in minimizing the total weighted completion time of the jobs of agent A, subject to a bound on the cost function of agent B, which may be: (i) total weighted completion time, (ii) maximum lateness, (iii) maximum completion time. An extensive computational experience shows the effectiveness of the approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albino, V., Carbonara, N., & Giannoccaro, I. (2006). Innovation in industrial districts: an agent-based simulation model. International Journal of Production Economics, 104, 30–45.
Arbib, C., Servilio, M., & Smriglio, S. (2004). A competitive scheduling problem and its relevance to UMTS channel assignment. Networks, 44(2), 132–141.
Agnetis, A., Mirchandani, P. B., Pacciarelli, D., & Pacifici, A. (2000). Nondominated schedules for a job-shop with two competing agents. Computational and Mathematical Organization Theory, 6(2), 191–217.
Agnetis, A., Mirchandani, P. B., Pacciarelli, D., & Pacifici, A. (2004). Scheduling problems with two competing agents. Operations Research, 52(2), 229–242.
Baker, K. R., & Cole Smith, J. (2003). A multiple-criterion model for machine scheduling. Journal of Scheduling, 6(1), 7–16.
Cheng, T. C. E., Ng, C. T., & Yuan, J. J. (2006). Multi-agent scheduling on a single machine to minimize total weighted number of tardy jobs. Theoretical Computer Science, 362, 273–281.
Cheng, T. C. E., Ng, C. T., & Yuan, J. J. (2008). Multi-agent scheduling on a single machine with max-form criteria. European Journal of Operational Research, 188, 603–609.
Ng, C. T., Cheng, T. C. E., & Yuan, J. J. (2006). A note on the complexity of the problem of two-agent scheduling on a single machine. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 12(4), 387–394.
Pan, Y. (2003). An improved branch and bound algorithm for single machine scheduling with deadlines to minimize total weighted completion time. Operations Research Letters, 31, 492–496.
Peha, J. M. (1995). Heterogeneous-criteria scheduling: minimizing weighted number of tardy jobs and weighted completion time. Journal of Computers and Operations Research, 22(10), 1089–1100.
Posner, M. E. (1985). Minimizing weighted completion times with deadlines. Operations Research, 33(3), 562–574.
Smith, W. E. (1956). Various optimizers for single-stage production. Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 3(1), 59–66.
Sourd, F. (2008). Private communication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agnetis, A., de Pascale, G. & Pacciarelli, D. A Lagrangian approach to single-machine scheduling problems with two competing agents. J Sched 12, 401–415 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-008-0098-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10951-008-0098-0