Abstract
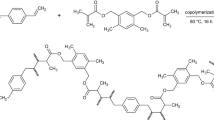
Synthesis of a new partial-alicyclic copolyimide based on bicyclo [2.2.2] oct-7-ene-2,3,5,6-tetracarboxylic dianhydride (BOCA) is presented. This polymer was used to obtain porous microspheres by suspension polymerization method. It is copolymerized with N, N’- 4, 4′- diphenylmethanebismaleimide in the presence of two pairs of porogens: 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone/benzyl alcohol, and 1,4 Dioxane/benzyl alcohol. Influence of different factors, such as diluents composition or crosslinker concentration, on the resulting polymer beads morphology is studied. Various characteristcis including the specific and apparent densities, porosity, pore volume, surface area and mean pore diameter are analyzed. Thermal behavior and tendency to swell in different organic diluents for some chosen samples are also determined. The best polymer beads, obtained in a reaction system with a solubility parameter value of 23.45 MPa ½ and a crosslinker concentration of 40 %, are thermally stable above 400 ºC, having a pore volume of 1.28 mL/g, a surface area of 74.20 m2/g and enhanced swelling properties.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dusek K (1982) Network formation by chain crosslinking (co)polymerization, in Developments in polymerization-3. In: Haward RN (ed) ScD. Publ. Appl. Science publisher in LTD, England
Okay O (2000) Macroporous copolymer networks. Prog Polym Sci 25(6):711–779
Clarisse M, Queirуs Y, Barbosa C, Barbosa L, Lucas E (2012) Synthesis and Characterization of Polymeric Resins Based on Methyl Methacrylate and Divinylbenzene. Chemistry & Chemical Technology, The Journal 6(2):145–152
Gawdzik B, Sobiesiak M (2003) Chemical composition of plasma treated polyimide microspheres. Appl Surf Sci 214:52–55
Gao JG, Zhang Y, Yu YF, Han YC, Zhang BZ, Gao CH (2011) Preparation of chitosan microspheres loading of 3,5-dihydroxy-4-i-propylstilbene and in vitro release. J Polym Res 18:1501–1508
Kun KA, Kunin R (1968) Macroreticular resins. III. Formation of macroreticular styrene–divinylbenzene copolymers. J Polym Sci Part A-1:Polym Chem 6:2689–2701
Sederel WL, De Jong GJ (1973) Styrene–divinylbenzene copolymers. Construction of porosity in styrene divinylbenzene matrices. J App Polym Sci 17(9):2835–2846
Brooks BW (1990) Basis aspects and recent developement in suspension polymerisation. Makromol Chem, Macromol Symp 35/36:121–140
Svec F, Frechet MJ (1996) New design of macroporous polymers and supports from separation to biocatalysis. Science 273:205–21
Bortel E (1965) Porous ion exchangers. I. Porosity of styrene-divinylbenzene copolymers. Przemysl Chem 44:255–270
Nicolescu T-V, Meouche W, Branger C, Margaillan A, Sarbu A, Donescu D (2012) Tailor-made polymer beads for gallic acid recognition and separation. J Polym Res 19:2–13
Flory PJ (1953) Principles of Polymer Chemistry. Press, Cornell University
Chen CW, Chen CY, Lin CL (2011) Preparation of monodisperse poly (methyl methacrylate)microspheres: effect of reaction parameters on particle formation, and optical performances of its diffusive agent application. J Polym Res 18:587–594
Grochowicz M, Bartnicki A, Gawdzik B (2008) Preparation and Characterization of Porous Polymeric Microspheres Obtained from Multifunctional Methacrylate Monomers. J Polym Sci: Part A: Polym Chem 46(18):6165–6174
Sroog CE (1991) Polyimides. Prog Polym Sci 16(4):561–694
Mathews AS, Kim I, Ha CS (2007) Synthesis, characterization, and properties of fully aliphatic polyimides and their derivatives for microelectronics and optoelectronics applications. Macromol Res 15(2):114–128
Wilson D, Stenzenberger HD, Hergenrother PM (1990) Polyimides. Chapman and Hall, New York
Chisca S, Musteata VE, Stoica I, Sava I, Bruma M (2013) Effect of the chemical structure of aromatic-cycloaliphatic copolyimide films on their surface morphology, relaxation behavior and dielectric properties. J Polym Res 20:111–121
Ree M (2006) High performance polyimides for applications in microelectronics and flat panel displays. Macromol Res 14(1):1–33
Ando S (2004) Optical Properties of Fluorinated Polyimides and Their Applications to Optical Components and Waveguide Circuits. J Photopolym Sci Technol 17(2):219–232
Cosutchi AI, Hulubei C, Stoica I, Ioan S (2011) A new approach for patterning epiclon-based polyimide precursor films using a lyotropic liquid crystal template. J Polym Res 18(6):2389–2402
Mittal KL (1984) Polyimides: synthesis, characterization and applications, vol 1 & 2. Springer (Plenum Press), New York
Ismail AF, Aziz F (2012) Chemical Cross-Linking Modifications of Polymeric Membranes for Gas Separation Applications, Chap. 11. In: Hilal N, Khayet M, Wright CJ (eds) Membrane Modification Technology and Applications. CRC Press, US
Takekoshi T (1996) In: Ghosh MK, Mittal KL (eds) Polyimides: Fundamentals and Applications, vol 1, 1st edn. Marcel Dekker, New York
Chen JC, Tseng WY, Tseng IH, Tsai MH (2011) High transparency and thermal stability of alicyclic polyimide with crosslinking structure by triallylamine. Adv Mater Res 287–290:1388–1396
Ioan S, Hulubei C, Popovici D, Musteata VE (2013) Origin of dielectric response and conductivity of some alicyclic polyimides. Polym Eng Sci 53(7):1430–1447
Kumar SV, Yu HC, Choi J, Kudo K, Jang YH, Chung CM (2011) Structure–property relationships for partially aliphatic polyimides. J Polym Res 18:1111–1117
Chen G, Pei X, Liu J, Fang X (2013) Synthesis and properties of transparent polyimides derived from trans- and cis-1,4-bis(3,4-dicarboxyphenoxy)cyclohexane Dianhydrides. J Polym Res 20:159–169
Hou Y, Chen G, Pei X, Fang X (2012) Synthesis and characterization of novel optically transparent and organosoluble polyimides based on diamines containing cyclohexane moiety. J Polym Res 19:9955–9963
Barzic AI, Stoica I, Fifere N, Vlad CD, Hulubei C (2013) Morphological effects on transparency and absorption edges of some semi-alicyclic polyimides. J Polym Res 20:130–137
Brock T, Sherrington DC, Swindell J (1994) Synthesis and characterisation of porous particulate polyimides. J Mater Chem 4(2):229–236
Sherrington D (1998) Preparation, structure and morphology of polymer supports. Chem Commun 21:2275–2286
Fu GD, Li GL, Neoh KG, Kang ET (2011) Hollow polymeric nanostructures—Synthesis, morphology and function. Prog Polym Sci 36(1):127–167
Ishizaka T, Kasai H (2012) In: Abadie MJM (ed) High Performance Polymers - Polyimides Based - From Chemistry to Applications, Fabrication of Polyimide Porous Nanostructures for Low-k Materials. Novi Sad, InTech
Hren J, Polanc S, Kočevar M (2008) The synthesis and transformations of fused bicyclo[2.2.2]octenes. Special Issue Reviews and Accounts ARKIVOC 209–231 ISSN 1551–7012
Ioan S, Cosutchi AI, Hulubei C, Macocinschi D, Ioanid G (2007) Surface and interfacial properties of poly(amic acid)s and polyimides. Polym Eng Sci 47(4):381–389
Dix LR, Ebdon JR, Flint NJ, Hodge P, O’Dell R (1995) Chain extension and crosslinking of telechelic oligomers—I. Michael additions of bisamines to bismaleimides and bis(acetylene ketone)s. Eur Polym J 31(7):647–652
Freeman ES, Carroll B (1958) The Application of Thermoanalytical Techniques to Reaction Kinetics: The Thermogravimetric Evaluation of the Kinetics of the Decomposition of Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate. J Phys Chem 62(4):394–397
Brunauer S (1957) Adsorption of Gases and Vapors Princeton University Press. New Jersey Press, New York
Choi YS, Hong SR, Lee YM, Song KW, Park MH, Nam YS (1999) Study on gelatin-containing artificial skin: I. Preparation and characteristics of novel gelatin-alginate sponge Biomaterials 20(5):409–417
Park HY, Song IH, Kim JH, Kim WS (1998) Preparation of thermally denatured albumin gel and its pH-sensitive swelling. Int J Pharm 175(2):231–236
ISO 25178–2:2012, Geometrical product specifications (GPS) - Surface texture: Areal - Part 2: Terms, definitions and surface texture parameters
Nic M, Jirat J, Kosata B updates compiled by Jenkins A (1997) IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the “Gold Book”). Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. XML on-line corrected version: http://goldbook.iupac.org
Ishida H, Wellinghoff ST, Baer E, Koenig JL (1980) Spectroscopic Studies of Poly [N, N’-bis(phenoxyphenyl)pyromellitimide]. 1. Structures of the Polyimide and Three Model Compounds. Macromolecules 13(4):826–834
Kotoulas C, Kiparissides C (2006) A generalized population balance model for the prediction of particle size distribution in suspension polymerization reactors. Chem Eng Sci 61(2):332–346
Chatzi EG, Kiparissides C (1994) Drop size distributions in high holdup fraction dispersion systems: effect of the degree of hydrolysis of PVA stabilizer. Chem Eng Sci 49(24, Part 2):5039–5052
Jalili K, Abbasi F, Nasiri M, Ghasemi M, Haddadi NDE (2009) Preparation and Characterization of Expandable St/MMA Copolymers Produced by Suspension Polymerization. J Cell Plast 45:197–224
Ioan S, Filimon A, Hulubei C, Stoica I, Dunca S (2013) Origin of rheological behavior and surface/interfacial properties of some semi-alicyclic polyimides for biomedical applications. Polym Bull 70(10):2873–2893
Jahanzad F, Sajjadi S, Brooks BW (2005) Comparative Study of Particle Size in Suspension Polymerization and Corresponding Monomer − Water Dispersion. Ind Eng Chem Res 44(11):4112–4119
Svec F, Frechet JMJ (1995) Temperature, a Simple and Efficient Tool for the Control of Pore Size Distribution in Macroporous Polymers. Macromolecules 28(22):7580–7582
Koenhen DM, Smolders CA (1975) The determination of solubility parameters of solvents and polymers by means of correlations with other physical quantities. J Appl Polym Sci 19(4):1163–1179
van Krevelen DW, te Nijenhuis K (2009) Properties of Polymers: Their Correlation with Chemical Structure; their Numerical Estimation and Prediction from Additive Group Contributions. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Allan F, Barton M (1983) Handbook of Solubility Parameters, Ph.D. Thesis. CRC Press, 153–157
Chompff A J, Newman S, Society A C (1971) Polymer networks: structure and mechanical properties: proceedings. Press, Plenum
Small PA (1953) Some factors affecting the solubility of polymers. J Appl Chem 3(2):71–80
Stoica I, Barzic AI, Hulubei C, Timpu T (2013) Statistical Analysis on Morphology Development of Some Semi-alicyclic Polyimides Using Atomic Force Microscopy Microsc. Res Techn 76:503–513
Marcu Puscas T, Signorini M, Molinari A, Straffelini G (2003) Image analysis investigation of the effect of the process variables on the porosity of sintered chromium steels. Mater Character 50(1):1–10
Dickie RA, Labana SS, Bauer RS, Science ACSDoPM, Engineering (1988) Cross-Linked Polymers: Chemistry, Properties, and Applications. American Chemical Society
Silverstein MS, Cameron NR, Hillmyer MA (2011) Porous Polymers. Wiley
Calvino-Casilda V, Lopez-Peinado AJ, Vaganova E, Yitzchaik S, Pacios IE, Pierola IF (2008) Porosity Inherent to Chemically Crosslinked Polymers. Poly(N-vinylimidazole) Hydrogels. J Phys Chem B 112(10):2809–2817
Poinescu I, Vlad C, Carpov A, Ioanid A (1988) On the structure of macroreticular styrene-divinylbenzene copolymers. Die Angewandte Makromolekulare Chemie 156(1):105–121
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported from PN-II-ID-PCE-2011-3-0937 Project No. 302/5.10.2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Paper dedicated to the 65th anniversary of “Petru Poni” Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry of Romanian Academy, Iasi, Romania.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hulubei, C., Vlad, C.D., Stoica, I. et al. New polyimide-based porous crosslinked beads by suspension polymerization: physical and chemical factors affecting their morphology. J Polym Res 21, 514 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0514-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-014-0514-4