Summary
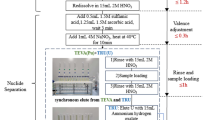
A new high-sensitivity plutonium bioassay program employing thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS) has been developed to monitor Savannah River Site employees for intakes of PuO2. The U.S. Department of Energy requires bioassay laboratories which have the ability to detect a 100 mRem, 50-year committed effective dose equivalent (CEDE) intake of radioactive material. For PuO2, traditional alpha-spectrometry methods are not sensitive enough to meet this specification. To comply with this requirement, a radiochemical TIMS method was developed to determine Pu in urine bioassay samples. Four radiochemical separation steps were used to purify Pu from urine to ensure samples were free from matrix effects that interfere with TIMS analysis. These included precipitation, ion-extraction chromatography, electrodeposition, and ion-exchange chromatography. A batch of reagent blanks determined the detection limit for this method was 0.59 fg 239Pu/l (1.3 µBq 239Pu/l). The 239Pu concentration was also measured in 20 urine blank samples to determine the minimum 239Pu concentration that would indicate an occupational intake. A Probit plot was constructed for the results and the 99 th percentile of the urine blanks showed that the minimum 239Pu concentration that would indicate an uptake was 2.4 fg/l (5.5 µBq/l).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LaMont, S., Shick, C., Cable-Dunlap, P. et al. Plutonium determination in bioassay samples using radiochemical thermal ionization mass spectrometry. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263, 477–481 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0078-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0078-1