Abstract
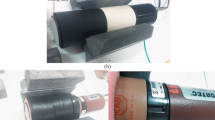
In this work, a well-type phoswich detector with three scintillation layers has been designed and tested for measuring atmospheric xenon radioisotopes in order to monitor nuclear explosions. The detector was made by optically coupling three concentric cylindrical scintillation layers (BC-400, CsI(Tl) and BGO) to a single photomultiplier tube. Beta-gamma coincidence technique was used to detect beta particles and gamma rays. Other important features of this detector are its Compton suppression capability and simple, compact and cost effective design. Our calculations and measurements with the well-type phoswich detector show that the minimum detectable concentrations are close to or below 1 mBq/m3 for the four xenon radioisotopes.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjurman B, De Geer L-E, Vintersved I, Rudjord AL, Ugletveit F, Aaltonen H, Sinkko K, Rantavaara A, Nielsen SP, Aarkrog A (1990) The detection of radioactive material from a venting underground nuclear explosion. J Environ Radioact 11(1):1–14
England TR, Rider BF (1993) Evaluation and compilation of fission product yields. Los Alamos National Laboratory, LA-UR-94-3106, ENDF-349
Preparatory commission for the comprehensive nuclear-test-ban treaty organization (2013). http://www.ctbto.org/verification-regime/monitoring-technologies-how-they-work/radionuclide monitoring. Accessed 29 Aug 2013
Auer M, Kumberg T, Sartorius H, Wernsperger B, Schlosser C (2010) Ten years of development of equipment for measurement of atmospheric radioactive xenon for the verification of the CTBT. Pure Appl Geophys 167(4–5):471–486
Hoffmann W, Kebeasy R, Firbas P (1999) Introduction to the verification regime of the comprehensive nuclear-test-ban treaty. Phys Earth Planet Inter 113(1):5–9
Saey PRJ, De Geer L-E (2005) Notes on radioxenon measurements for CTBT verification purposes. Appl Radiat Isot 63(5–6):765–773
Ringbom A, Larson T, Axelsson A, Elmgren K, Johansson C (2003) SAUNA—a system for automatic sampling, processing, and analysis of radioactive xenon. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect Accel Spectrometers Detect Assoc Equip 508(3):542–553
Bowyer TW, Schlosser C, Abel KH, Auer M, Hayes JC, Heimbigner TR, McIntyre JI, Panisko ME, Reeder PL, Satorius H (2002) Detection and analysis of xenon isotopes for the comprehensive nuclear-test-ban treaty international monitoring system. J Environ Radioact 59(2):139–151
Prelovskii VV, Kazarinov NM, Donets AY, Popov VY, Popov IY, Skirda NV (2007) The ARIX-03F mobile semiautomatic facility for measuring low concentrations of radioactive xenon isotopes in air and subsoil gas. Instruments Exp Tech 50(3):393–397
Fontaine J-P, Pointurier F, Blanchard X, Taffary T (2004) Atmospheric xenon radioactive isotope monitoring. J Environ Radioact 72(1–2):29–135
Ely JH, Aalseth CE, McIntyre JI (2005) Novel beta-gamma coincidence measurements using phoswich detectors. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 263(1):245–250
Hennig W, Tan Hui, Warburton WK, McIntyre JI (2006) Single-channel beta-gamma coincidence detection of radioactive xenon using digital pulse shape analysis of phoswich detector signals. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 53(2):620–624
Farsoni AT, Alemayehu B, Alhawsawi A, Becker EM (2013) A phoswich detector with compton suppression capability for radioxenon measurements. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 60(1):456–464
Farsoni AT, Alemayehu B, Alhawsawi A, Becker EM (2013) Real-time pulse-shape discrimination and beta-gamma coincidence detection in field-programmable gate array. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect Accel Spectrometers Detect Assoc Equip 712:75–82
De Voigt MJA, Bacelar JC, Micek SL, Schotanus P, Verhoef BAW, Wintraecken YJE, Vermeulen P (1995) A novel compact Ge-BGO Compton-suppression spectrometer. Nucl Instruments Methods Phys Res Sect Accel Spectrometers Detect Assoc Equip 356(2):362–375
Farsoni AT, Alemayehu B, Alhawsawi A, Becker EM (2012) A compton-suppressed phoswich detector for gamma spectroscopy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 296(1):63–68
Saint-Gobain crystals (2013). http://www.detectors.saint-gobain.com. Accessed 29 Aug 2013
Grupen C, Buvat I (2012) Handbook of particle detection and imaging, vol 2. Springer, Heidelberg
Farsoni AT, Hamby DM (2010), Characterizing a two channel phoswich detector using radioxenon isotopes produced in the Oregon State University TRIGA reactor. In: Proceedings of the 2010 monitoring research review: ground-based nuclear explosion monitoring technologies, LA-UR-10-05578, vol 2. pp 585–594
Schulze J, Auer M, Werzi R (2000) Low level radioactivity measurement in support of the CTBTO. Appl Radiat Isot 53(1):23–30
Currie LA (1968) Limits for qualitative detection and quantitative determination. Appl Radiochem Anal Chem 40(3):586–593
McIntyre JI, Bowyer TW, Reeder PL (2006) Calculation of minimum detectable concentration levels of radioxenon isotopes using the PNNL ARSA system. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, PNNL-13102
McIntyre JI, Able KH, Bower TW, Hayes JC, Heimbigner TR, Panisko ME, Reeder PL, Thompson RC (2001) Measurements of ambient radioxenon levels using the automated radioxenon sampler/analyzer (ARSA). J Radioanal Nucl Chem 248(3):629–635
Hennig W, Cox CE, Asztalos SJ, Tan H, Franz PJ, Grudberg PM, Warburton WK (2011) Study of silicon detectors for high-resolution radioxenon measurements. In: Proceedings of the 2011 monitoring research review: ground-based nuclear explosion monitoring technologies, LA-UR-11-04823, vol 2. pp 695–707
Foltz Biegalski KM, Biegalski SR (2001) Determining detection limits and minimum detectable concentrations for noble gas detectors utilizing beta-gamma coincidence systems. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 248(3):673–682
Goha H, Auer M (2010) 1st IMS noble gas system certification—review of certification requirements. In: Proceedings of 2010 INGE workshop (day 2, session 5)
Petit G, Armand P, Brachet G, Taffary T, Fontaine JP, Achim P, Blanchard X, Piwowarczyk JC, Pointurier F (2008) Contribution to the development of atmospheric radioxenon monitoring. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 276(2):391–398
Hennig W, Warburton WK, Fallu-Labruyere A, Sabourov K, Cooper MW, McIntyre JI, Gleyzer A, Bean M, Korpach P, Ungar K (2009) Radioxenon measurements with the Phoswatch detector system. In: Proceedings of the 2009 monitoring research review: ground-based nuclear explosion monitoring technologies, LA-UR-09-05276, vol 2. pp 641–652
Reeder PL, Bowyer TW, McIntyre JI, Pitts WK, Ringbom A, Johansson C (2004) Gain calibration of coincidence spectrometer for automated radioxenon analysis. Nucl Instr and Meth in Phys Res A 521:586
Cooper MW, McIntyre JI, Bowyer TW, Carman AJ, Hayes JC, Heimbigner TR, Hubbard CW, Lidey L, Litke KE, Morris SJ, Ripplinger MD, Suarez R, Thompson R (2007) Redesigned β-γ radioxenon detector. Nucl Instr Meth Phys Res A 579:426
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, National Nuclear Security Administration under Award No. DE-AC52-09NA29324. The authors would like to thank A. Alhawsawi from Department of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Health physics and S. Smith from the Radiation Center of the Oregon State University for their contributions to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alemayehu, B., Farsoni, A.T., Ranjbar, L. et al. A well-type phoswich detector for nuclear explosion monitoring. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 301, 323–332 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3182-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3182-2