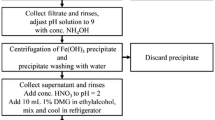
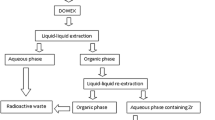
Abstract
A comparative study using liquid scintillation counting was performed to measure 63Ni in low and intermediate level radioactive waste. Three dimethylglyoxime (DMG)-based radiochemical procedures (solvent extraction, precipitation, extraction chromatography) were investigated, the solvent extraction method being considered as the reference method. Theoretical speciation calculations enabled to better understand the chemical reactions involved in the three protocols and to optimize them. In comparison to the method based on DMG precipitation, the method based on extraction chromatography allowed to achieve the best results in one single step in term of recovery yield and accuracy for various samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANDRA, National Radioactive Waste Management Agency (2014) ACO.SP.ASRE.99.0002D ANDRA specifications. Accessed 5 June 2015
Hou X, Roos P (2008) Critical comparison of radiometric and mass spectrometric methods for the determination of radionuclides in environmental, biological and nuclear waste samples. Anal Chim Acta 608:105–139
Hoeppener-Kramar U, Pimpl M, Willmann F (1997) Application of procedures for low level radionuclide analysis in environmental monitoring for the purpose of clearance measurements of materials from decommissioning of nuclear facilities. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 226:99–103
Lee CH, Lee MH, Ha YK, Song KS (2011) Systematic radiochemical separation for the determination of 99Tc, 90Sr, 94Nb, 55Fe and 59,63Ni in low and intermediate radioactive waste samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288:319–325
Lee CH, Choi KS, Song BC, Ha YK, Song K (2013) Rapid separation of nickel for 59Ni and 63Ni activity measurement in radioactive waste samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298:1221–1226
Hou X, Østergaard LF, Nielsen SP (2005) Determination of 63Ni and 55Fe in nuclear waste samples using radiochemical separation and liquid scintillation counting. Anal Chim Acta 535:297–307
Hou X (2007) Radiochemical analysis of radionuclides difficult to measure for waste characterization in decommissioning of nuclear facilities. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273:43–48
Poletiko C (1988) Determination of nickel-63. Environ Int 14:387–390
Numajiri M, Oki Y, Suzuki T, Miura T, Taira M, Kanda Y, Kondo K (1994) Estimation of nickel-63 in steel and copper activated at high-energy accelerator facilities. Appl Radiat Isot 45:509–514
Scheuerer C, Schupfner R, Schottelkopf H (1995) A very sensitive LSC procedure to determine Ni-63 in environmental samples, steel and concrete. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 193:127–131
Shizuma K, Iwatani K, Hasai H, Oka T, Hoshi M, Shibata S, Imamura M, Shibata T (1997) Identification of 63Ni and 60Co produced in a steel sample by thermal neutrons from the Hiroshima atomic bomb. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A 384:375–379
Rosskopfova O, Galambo M, Rajec P (2011) Determination of 63Ni in low level solid radioactive waste. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 289:251–256
Taddei MHT, Macacini JF, Vicente R, Marumo JT, Sakata SK, Terremoto LAA (2013) Determination of 63Ni and 59Ni in spent ion-exchange resin and activated charcoal from the IEA-R1 nuclear research reactor. Appl Radiat Isot 77:50–55
Kaye JH, Strebin RS, Nevissi AE (1994) Measurement of 63Ni in highly radioactive Hanford waste by liquid scintillation couting. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 180:197–200
Warwick PE, Croudace IW (2006) Isolation and quantification of 55Fe and 63Ni in reactor effluents using extraction chromatography and liquid scintillation analysis. Anal Chim Acta 567:277–285
Jordan N, Michel H, Barci-Funel G, Barci V (2008) Radiochemical procedure and quantitative determination of the activation product, 63Ni, in environmental soft water samples with high Ca and Mg phosphate concentration. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 275:253–256
Remenec B, Dulanska S, Matel L (2013) Determination of difficult to measure radionuclides in primary circuit facilities of NPP V1 Jaslovske Bohunice. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 298:1879–1884
Holm E, Rots P, Skwarzec B (1992) Radioanalytical Studies of Fallout 63Ni. Appl Radiat Isot 43:371–376
Laboratoire National Henri Becquerel (2005) Table de radionucléides—63Ni
Yonezawa C, Sagawa T, Hoshi M, Tachikama E (1983) Rapid determination of specific activity of nickel-63. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 78:7–14
AFNOR Standard NF M60-317 (2001) Nuclear energy—nuclear fuel technology—waste—determination of nickel 63 in effluents and waste by liquid scintillation after a preliminary chemical extraction. Association Française de Normalisation, Paris, France
European Chemicals Agency (2012) Guidance for the implementation of REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals). Accessed 5 June 2015
Rajkovich S, Cahill D, Peedin L, Wheland S, Lardy M (1996) 2 case studies using Eichrom’s Nickel resin: a nuclear power plant and a commercial laboratory. Eichrom Cincinnati Users’ Seminar, USA. Accessed 5 June 2015
Horwitz EP, Dietz ML, Chiarizia R, Diamond H, Maxwell SL, Nelson MR (1995) Separation and preconcentration of actinides by extraction chromatography using a supported liquid anion exchanger: application to the characterization of high-level nuclear waste solutions. Anal Chim Acta 310:63–78
Gautier C, Coppo M, Caussignac C, Fichet P, Goutelard F (2013) Zr and U determination at trace level in simulated deep groundwater by Q ICP-MS using extraction chromatography. Talanta 106:1–7
Eichrom Technologies, Inc. (2003) Analytical procedures NIW01, nickel 63/59 in water, Feb 25
Fisera O, Sebesta F (2010) Determination of 59Ni in radioactive waste. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 286:713–717
Smith RM, Martell AE (1973) In critical stability constants, Plenum Press, New York
International Atomic Energy Agency (2009) Determination and use of scaling factors for waste characterization in nuclear power plants. AIEA, Nuclear Energy Series NW-T-1.18
Fréchou C, Degros JP (2006) Radiological inventory of irradiated graphite samples. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273:677–681
Banford AW, Eccles H, Graves MJ, von Lensa W, Norris S (2008) Carbowaste—an integrated approach to irradiated graphite. Nucl Future 4:1–5
AFNOR Standard NF M60-323 (2011) Nuclear energy—nuclear fuel cycle technology—waste—guide for pre-analysis dissolution of effluents, waste and embedding matrices. Association Française de Normalisation, Paris, France
AFNOR Standard NF M60-322 (2005) Nuclear energy—nuclear fuel cycle technology—waste—determination of iron 55 activity in effluents and waste by liquid scintillation after prior chemical separation
Marczenko Z, Balcerzak M (2000) In: separation, preconcentration and spectrophotometry in inorganic analysis. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Zelenin OY (2007) Interaction of the Ni2+ ion with citric acid in an aqueous solution. Russ J Coord Chem 33:346–350
Dyrssen D, Krašovek F, Sillén LG (1959) On the complex formation of nickel with dimethylglyoxime. Acta Chem Scand 13:50–59
Standard NF EN ISO/CEI 17043 (2010) General requirements for proficiency testing. Association Française de Normalisation, Paris, France
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the organizing committees of 17th RadChem and ERA12 conferences for allowing the oral presentations of this work. They also thank Thomas Grangeon and Julien Roger for the measurements by gamma spectrometry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Cécile Garcia its on leave for AREVA, Demantelement et Services/MSIS Assistance, 91196 Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gautier, C., Colin, C. & Garcia, C. A comparative study using liquid scintillation counting to determine 63Ni in low and intermediate level radioactive waste. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 308, 261–270 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4301-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4301-4