Abstract
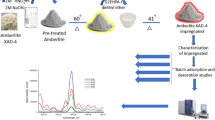
To remove Th(IV) ion from acidic solutions (pH 2.5–2.7), an extractant-impregnated resin (EIR) was fabricated by impregnation of Ambelite XAD-7 resin beads with titan yellow as extractant. Various physicochemical factors such as pH, contact time, temperature, sorbent dose and initial concentration of thorium were investigated. The isotherm data was well interpreted by the Langmuir model. Kinetic experiments data showed that the sorption process could be described by Weber–Morris kinetic model. Thermodynamic studies revealed the feasibility, spontaneity and endothermic nature of sorption process. Desorption experiments showed that the EIR could be reused without significant losses of its initial capacity.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARE:
-
Average relative error (%)
- B :
-
Tempkin constant related to the heat of sorption
- b:
-
Langmuir constant related to the free energy of sorption (L mg−1)
- b M :
-
Langmuir constant related to the free energy of sorption (L mol−1)
- C :
-
Intial concentration of thorium ion in solution
- C e :
-
Equilibrium concentration of the metal ion in the bulk solution (mg L−1)
- C r :
-
Total concentration of the exchangeable ion in resin phase
- D b :
-
Diffusion coefficient in the solution bulk
- D b :
-
Intra-particle diffusion coefficient (m2 s−1)
- E :
-
Mean sorption energy estimated from Dubinin–Radushkevich (J mol−1)
- k 1 :
-
Pseudo-first order rate constant (min−1)
- k 2 :
-
Pseudo-second order rate constant (g mg−1 min−1)
- K d :
-
Distribution coefficient (mL g−1)
- K f :
-
Freundlich constant indicative of the relative sorption capacity of the EIR (mg1−(1/n) L1/n g−1)
- K id :
-
Intra-particle diffusion constant (mg g−1 min−1/2)
- K T :
-
Equilibrium binding constant, Tempkin constant (L g−1)
- I :
-
Intercept in the intraparticle diffusion model (mg g−1)
- m :
-
EIR dose, weight of EIR per liter of solution (g L−1)
- N :
-
Number of measurements
- n :
-
Freundlich constant indicative of the heterogeneity factor
- q 0 :
-
Maximum sorption capacity based on Dubinin–Radushkevich model (mol g−1)
- q e :
-
Amount of metal ion sorbed per unit weight of EIR at equilibrium (mg g−1)
- q e.cal :
-
Theoretical q e values obtained from the kinetic or isotherm models (mg g−1)
- q e.exp :
-
Experimental q e values (mg g−1)
- q max :
-
Maximum sorption capacity; Langmuir constant (mg g−1)
- q max,exp :
-
Maximum experimental sorption capacity (mg g−1)
- q t :
-
Amount of metal ion sorbed at any time t (mg g−1)
- R :
-
Universal gas constant (J mol−1 K−1)
- R 2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- r 0 :
-
Mean radius of the EIR particles (m)
- R%:
-
Removal efficiency (%)
- R L :
-
Dimensionless separation factor
- RMSE:
-
Root mean square error (%)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- t :
-
Time (min)
- V :
-
Solution volume (L or mL)
- W :
-
Weight of EIR (mg)
- X t :
-
Degree of fractional attainment to equilibrium at time t
- ΔG°:
-
Gibb’s free energy change (J mol−1)
- ∆H°:
-
Enthalpy change (J mol−1)
- ∆S°:
-
Entropy change (J mol−1 K−1)
- Δq % :
-
Normalized standard deviation (%)
- α :
-
Elovich constant indicative of the initial sorption rate (mg g−1 min−1)
- β :
-
Elovich constant indicative of the desorption constant (g mg−1)
- δ :
-
Dubinin–Radushkevich constant related to the sorption energy (mol2 J−2)
- ε :
-
Polanyi potential
- ω :
-
Thickness of the liquid film surrounding the sorbent beads
References
Pathak SK, Tripathi SC, Singh KK, Mahtele AK, Kumar M, Gandhi PM (2014) Removal of americium from aqueous nitrate solutions by sorption onto PC88A—Impregnated macroporous polymeric beads. J Hazard Mater 278:464–473
Xu QH, Pan DQ, Wu WS (2015) Effects of pH, ionic strength, humic substances and temperature on Th(IV) sorption onto ZSM-5. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 305:535–541
Akkaya R (2013) Removal of radioactive elements from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto polyacrylamide–expanded perlite: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. Desalination 321:3–8
Ghaedi AM, Ghaedi M, Vafaei A, Iravani N, Keshavarz M, Rad M, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2015) Adsorption of copper (II) using modified activated carbon prepared from Pomegranate wood: optimization by bee algorithm and response surface methodology. J Mol Liq 206:195–206
Hosseini MS, Abedi F (2015) Comparison of adsorption behavior of Th(IV) and U(VI) on mixed-ligands impregnated resin containing antraquinones with that conventional one. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303:2173–2183
Kaynar ÜH, Ayvacıklı M, Hiçsönmez Ü, Kaynar SÇ (2015) Removal of thorium (IV) ions from aqueous solution by a novel nanoporous ZnO: isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Radioact 150:145–151
Kim JO, Lee SM, Jeon C (2014) Adsorption characteristics of sericite for cesium ions from an aqueous solution. Chem Eng Res Des 92:367–384
Lin P, Chen M, Guo L (2015) Effect of natural organic matter on the adsorption and fractionation of thorium and protactinium on nanoparticles in seawater. Mar Chem 173:291–301
Zeng Y, Liao X, He Q, Shi B (2009) Recovery of Th(IV) from aqueous solution by reassembled collagen-tannin fiber adsorbent. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 280:91–98
Shehata FA, Attallah MF, Borai EH, Hilal MA, Abo-Aly MM (2010) Sorption reaction mechanism of some hazardous radionuclides from mixed waste by impregnated crown ether onto polymeric resin. Appl Radiat Isot 68:239–249
Ilaiyaraja P, Singha Deb AK, Sivasubramanian K, Ponraju D, Venkatraman B (2013) Removal of thorium from aqueous solution by adsorption using PAMAM dendron-functionalized styrene divinyl benzene. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 297:59–69
Cortina JL, Arad-Yelling R, Miralles N, Saster AM, Warshawsky A (1998) Kinetics studies on heavy metal ions extraction by Amberlite XAD2 impregnated resins containing a bifunctional organophosphorous extractant. React Funct Polym 38:269–278
Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Hosseini MS, Sarw-Ghadi M, Zowghi S, Hosseini E, Hosseini-Bandegharaei H (2010) Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic study of Cr(VI) sorption into toluidine blue o-impregnated XAD-7 resin beads and its application for the treatment of wastewaters containing Cr(VI). Chem Eng J 160:190–198
Ali A, Shahida Sh, Haleem Kha M, Mufazzal Saeed M (2011) Online thorium determination after preconcentration in a minicolumn having XAD-4 resin impregnated with N-benzoylphenylhydroxylamine by FI-spectrophotometry. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 288:735–743
Hosseini SH, Rahmani-Sani A, Jalalabadi Y, Karimzadeh M, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Kharghani K, Allahabadi A (2015) Preconcentration and determination of ultra-trace amounts of U(VI) and Th(IV) using titan yellow-impregnated Amberlite XAD-7 resin. Intern J Environ Anal Chem 95:277–290
Ghasemi JB, Zolfonoun E (2010) Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of trace amounts of uranium, thorium, and zirconium using the partial least squares method after their preconcentration by α-benzoin oxime modified Amberlite XAD-2000 resin. Talanta 80:1191–1197
Saha B, Gill RJ, Bailey DG, Kabay N, Arda M (2004) Sorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by Amberlite XAD-7 resin impregnated with Aliquat 336. React Funct Polym 60:223–244
Negrea A, Popa A, Ciopec M, Lupa L, Negrea P, Davidescu CM, Motoc M, Mînzatu V (2014) Phosphonium grafted styrene–divinylbenzene resins impregnated with iron(III) and crown ethers for arsenic removal. Pure Appl Chem 86:1729–1740
Erdogan S, Merdivan M, Hamamci C, Akba O, Baysal A (2004) Polymer supported humic acid for separation and preconcentration of Th(IV). Anal Lett 37:2565–2575
Metilda P, Sanghamitra K, Gladis JM, Naidu GRK, Lao TP (2005) Amberlite XAD-4 functionalized with succinic acid for the solid phase extractive preconcentration and separation of U(VI). Talanta 65:192–200
Rahmani-Sani A, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Hosseini SH, Kharghani K, Zarei H, Rastegar A (2015) Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies on sorption of uranium and thorium from aqueous solutions by a selective impregnated resin containing carminic acid. J Hazard Mater 286:152–163
Ciopec M, Davidescu CM, Negrea A, Grozav I, Lupa L, Negrea P, Popa A (2012) Adsorption studies of Cr(III) ions from aqueous solutions by DEHPA impregnated onto Amberlite XAD7—factorial design analysis. Chem Eng Res Des 90:1660–1670
Ghaedi M, Niknam K, Taheri K, Hossainian H, Soylak M (2010) Flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination of copper, zinc and manganese after solid-phase extraction using 2,6-dichlorophenyl-3,3-bis(indolyl)methane loaded on Amberlite XAD-16. Food Chem Toxicol 48:891–897
Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Sarwghadi M, Heydarbeigi A, Hosseini SH, Nedaie M (2013) Solid-phase extraction of trace amounts of Uranium(VI) in environmental water samples using an extractant-impregnated resin followed by detection with UV–Vis Spectrophotometry. J Chem 2013:1–10
Draa MT, Belaid T, Benamor M (2004) Extraction of Pb(II) by XAD7 impregnated resins with organophosphorus extractants (DEHPA, IONQUEST 801, CYANEX 272). Sep Purif Technol 40:77–86
Hosseini MS, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A (2010) Selective extraction of Th(IV) over U(VI) and other co-existing ions using eosin B-impregnated Amberlite IRA-410 resin beads. J Radional Nucl Chem 283:23–30
Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Karimzadeh M, Sarwghadi M, Heydarbeigi A, Hosseini SH, Nedaie M, Shoghi H (2014) Use of a selective extractant-impregnated resin for removal of Pb(II) ion from waters and wastewaters: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Chem Eng Res Des 92:581–591
Rao GPC, Veni SS, Pratap K, Rao YK, Seshaiah K (2006) Solid phase extraction of trace metals in seawater using morpholine dithiocarbamate-loaded Amberlite XAD-4 and determination by ICP-AES. Anal Lett 39:1009–1021
Kabay N, Cortina JL, Trochimczuk A, Streat M (2010) Solvent-impregnated resins (SIRs)—methods of preparation and their applications. React Funct Polym 70:484–496
Otto EB, Otto CE (1941) Titan yellow qualitative test for magnesium. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 13:65–66
El-Kamash AM, Zaki AA, Abdel M, Geleel E (2005) Modeling batch kinetics and thermodynamics of zinc and cadmium ions removal from waste solutions using synthetic zeolite. J Hazard Mater B 127:211–220
Allen SJ, Mckay G, Porter JF (2004) Adsorption isotherm models for basic dye adsorption by peat in single and binary component systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 280:322–333
Kumar M, Rathore DPS, Singh AK (2000) Metal ion enrichment with Amberlite XAD-2 functionalized with Tiron: analytical applications. Analyst 125:1221–1226
Negrea A, Ciopec M, Lupa L, Davidescu CM, Popa A, Ilia G, Negrea P (2011) Removal of AsV by FeIII-Loaded XAD7 Impregnated Resin Containing Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phosphoric Acid (DEHPA): equilibrium, Kinetic, and thermodynamic modeling studies. J Chem Eng Data 56:3830–3838
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295
Freundlich H (1906) Adsorption in solution. Phys Chem Soc 40:1361–1368
Tempkin MJ, Pyzhev V (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physiochim URSS 12:217–222
Hutson ND, Yang RT (1997) Theoretical basis for the Dubinin–Radushkevitch (D–R) adsorption isotherm equation. Adsorption 3:189–195
Zhao Y, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang S, Huang Y, Wu X, Wang X (2014) Synthesis of amidoxime-functionalized Fe3O4@ SiO2 core–shell magnetic microspheres for highly efficient sorption of U (VI). Chem Eng J 235:275–283
Nilchi A, Shariati Dehaghan T, Rasouli Garmarodi S (2013) Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics for uranium and thorium ions adsorption from aqueous solutions by crystalline tin oxide nanoparticles. Desalination 321:67–71
Humelnicu D, Drochioiu G, Sturza MI, Cecal A, Popa K (2006) Kinetic and thermodynamic aspects of U(VI) and Th(IV) sorption on a zeolitic volcanic tuff. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 270:637–640
Shao D, Hou G, Li J, Wen T, Ren X, Wang X (2014) PANI/GO as a super adsorbent for the selective adsorption of uranium(VI). Chem Eng J 255:604–612
Khazaei Y, Faghihian H, Kamali M (2011) Removal of thorium from aqueous solutions by sodium clinoptilolite. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 289:529–536
Zhang Z-B, Zhou Y-D, Liu YH, Cao X-H, Zhou Z-W, Han B, Liang P, Xiong G-X (2015) Removal of thorium from aqueous solution by ordered mesoporous carbon CMK-3. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 302:9–16
Talip Z, Eral M, Hiçsönmez Ü (2009) Adsorption of thorium from aqueous solutions by perlite. J Environ Radioact 100:139–143
Chandramouleeswaran S, Ramkumar J (2014) n-Benzoyl-n-phenylhydroxylamine impregnated Amberlite XAD-4 beads for selective removal of thorium. J Hazard Mater 280:514–523
Abbasizadeh S, Keshtkar AR, Mousavian MA (2013) Preparation of a novel electrospun polyvinyl alcohol/titanium oxide nanofiber adsorbent modified with mercapto groups for uranium(VI) and thorium(IV) removal from aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 220:161–171
Anirudhan TS, Rijith S, Tharun AR (2010) Adsorptive removal of thorium(IV) from aqueous solutions using poly(methacrylic acid)-grafted chitosan/bentonite composite matrix: process design and equilibrium studies. Colloid Surf A 368:13–22
Anirudhan TS, Sreekumari SS, Jalajamony S (2013) An investigation into the adsorption of thorium(IV) from aqueous solutions by a carboxylate-functionalised graft copolymer derived from titanium dioxide-densified cellulose. J Environ Radioact 116:141–147
Anirudhan TS, Rejeena SR (2011) Thorium(IV) temoval and recovery from aqueous solutions using Tannin-modified poly(glycidylmethacrylate)-grafted zirconium oxide densified cellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:13288–13298
Riazi Ma Keshtkar AR, Moosavian MA (2014) Batch and continuous fixed-bed column biosorption of thorium(IV) from aqueous solutions: equilibrium and dynamic modeling. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 301:493–503
Sharma S, Balasubramanian K (2015) Molecularly imprinted and nanoengineered camphor soot functionalized PAN-nanofibers for effluent treatment. RSC Adv 5:31732–31741
Lagergren S, Svenska BK (1989) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption geloester stoffe. Veternskapsakad Handlingar 24:1–39
Ho YS, Ng JCY, McKay G (2000) Kinetics of pollutant sorption by biosorbents: review. Sep Purif Method 29:189–232
Yang X, Al-Duri B (2005) Kinetic modeling of liquid-phase adsorption of reactive dyes on activated carbon. J Colloid Interface Sci 287:25–34
Juang RS, Chen ML (1997) Application of the Elovich equation to the kinetics of metal sorption with solvent-impregnated resins. Ind Eng Chem Res 36:813–820
Chein SH, Clayton WR (1980) Application of elovich equation to the biomass of phosphate release and sorption on soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 44:265–268
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div Am Soc Civ Eng 89:31–60
Malash GF, El-Khaiary MI (2010) Piecewise linear regression: a statistical method for the analysis of experimental adsorption data by the intraparticle-diffusion models. Chem Eng J 163:256–263
Weber TW, Chakraborti RK (1974) Pore and solid diffusion models for fixed bed adsorbents. J Am Inst Chem Eng 20:228–238
Akkaya R (2012) Separation of uranium and thorium in aqueous solution using polyhydroxyethylmethacrylate-hydroxyapatite novel composite. Desalin Water Treat 50:180–188
Yusan S, Gok C, Erenturk S, Aytas S (2012) Adsorptive removal of thorium (IV) using calcined and flux calcined diatomite from Turkey: evaluation of equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic data. Appl Clay Sci 67–68:106–116
Abdel Raouf MW, El-Kamash AM (2005) Kinetic and thermodynamic studies for sorption of uranium and thorium ions from nitric acid solutions on to a TBP-impregnated sorbent. Arab J Nucl Sci Appl 38:85–96
Banerjee GL, Amy M, Prevost S, Nour M, Jekel PM, Blumenschein CD (2008) Kinetic and thermodynamic aspects of adsorption of arsenic onto granular ferric hydroxide. Water Res 42:3371–3378
Michelson LD, Gideon PG, Pace EG, Kutal LH (1975) Removal of soluble mercury from wastewater by complexing technique. In: Bull. No. 74. US Department Industry, Office of Water Research and Technology. Blacksburg
Ghodbane I, Hamdaoui O (2008) Removal of mercury(II) from aqueous media using eucalyptus bark: kinetic and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 160:301–309
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support of the present work from the Central Research Council of Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences (Grant 3930101102). In addition, the authors wish to take this opportunity to express their sincere thanks to Prof. Mohammad Mohammad–Zadeh, the research council president of Sabzevar University of medical Science, for his great helps and supports during the experimental works.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A., Allahabadi, A., Rahmani-Sani, A. et al. Thorium removal from weakly acidic solutions using titan yellow-impregnated XAD-7 resin beads: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 309, 761–776 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4689-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4689-x