Abstract
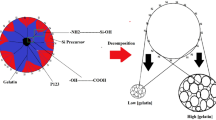
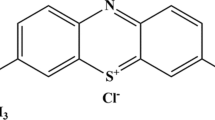
Silicon dioxide xerogels with controlled mesoporosity were produced by sol–gel technique. The mesoporosity and adsorption behavior of methylene blue (MB) were evaluated for the fabricated silica materials. This study is supported by several characterizations, including FTIR, TEM, SEM, and N2 sorption. The adsorption kinetics of MB on the prepared samples was evaluated at room temperature over time. It was demonstrated that the pore structure and adsorption performance of silica are closely dependent on the pH of the sol–gel solution, H2O:TEOS molar ratio, the addition of F127 template, and heat treatment performed. The present study shows that for the adsorption parameters used in this work, the control of sol–gel parameters can give rise to silica xerogels with higher adsorption capacities than SBA-16 silica molecular sieve used as the reference and already recognized as an efficient dye adsorbent. The highest adsorption capacities were measured for silica structures obtained without the use of acidic catalyst, heat treatment or F127 template. As the pore volume of the studied materials is much larger than the amount of MB captured in the adsorption tests, such results seem to be related to the specific surface area and pore size obtained in the sol–gel synthesis. Therefore, it appears that large surface areas and pore sizes accelerate the adsorption kinetic and increase the amount of MB able to stay in equilibrium in the pore structure of silica. As a matter of fact, the work developed here underlines the advantages regarding the simplicity, safety, environmental preservation and cost saving of the synthesis methodology developed herein when compared with the other methodologies commonly used to fabricate silica adsorbents.

Highlights
-
Silicon dioxide xerogel structures with controlled mesoporosity produced by sol–gel technique
-
Mesoporosity tailored by varying the solution pH, H2O:TEOS molar ratio, addition of F127 and heat treatment
-
Synthesis of silica xerogel adsorbents with higher adsorption capacity than SBA-16 silica used as the reference
-
Development of a simple, safe and green procedure to fabricate silica adsorbents with a high adsorption capacity










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hench LL, West JK (1990) The sol-gel process. Chem Rev 90:33–72. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00099a003
Hanuhov T, Asulin E, Gvishi R (2017) Evaluation of opto-mechanical properties of UV-cured and thermally-cured sol-gel hybrids monoliths as a function of organic content and curing process. J Non Cryst Solids 471:301–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.05.043
Voicu G, Ene V-L, Sava D-F, Surdu V-A, Busuioc C (2016) Sol-gel derived vitroceramic materials for biomedical applications. J Non Cryst Solids 449:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.07.021
Bouck RM, Anderson AM, Prasad C, Hagerman ME, Carroll MK (2016) Cobalt-alumina sol gels: effects of heat treatment on structure and catalytic ability. J Non Cryst Solids 453:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.09.013
Girgis BS, El-Sherif IY, Attia AA, Fathy NA (2012) Textural and adsorption characteristics of carbon xerogel adsorbents for removal of Cu (II) ions from aqueous solution. J Non Cryst Solids 358:741–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2011.12.004
Ernawati L, Balgis R, Ogi T, Okuyama K (2017) Tunable synthesis of mesoporous silica particles with unique radially oriented pore structures from Tetramethyl Orthosilicate via oil–water emulsion process. Langmuir 33:783–790. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b04023
Barua NK, Ragini T, Subasri R (2017) Sol-gel derived single-layer zeolite-based coatings on glass for broadband antireflection properties. J Non Cryst Solids 469:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.04.016
Rigacci A, Einarsrud M-A, Nilsen E, Pirard R, Ehrburger-Dolle F, Chevalier B (2004) Improvement of the silica aerogel strengthening process for scaling-up monolithic tile production. J Non Cryst Solids 350:196–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2004.06.042
Nassif N, Livage J (2011) From diatoms to silica-based biohybrids. Chem Soc Rev 40:849–859. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0CS00122H
Jafarzadeh M, Rahman IA, Sipaut CS (2009) Synthesis of silica nanoparticles by modified sol-gel process: the effect of mixing modes of the reactants and drying techniques. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 50:328–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-009-1958-6
Houmard M, Nunes EHM, Vasconcelos DCL, Berthomé G, Joud JC, Langlet M, Vasconcelos WL (2014) Correlation between sol-gel reactivity and wettability of silica films deposited on stainless steel. Appl Surf Sci 289:218–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.137
Rodrigues Mota TL, Marques de Oliveira AP, Nunes EHM, Houmard M (2017) Simple process for preparing mesoporous sol-gel silica adsorbents with high water adsorption capacities. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.07.010
Tsai WT, Chang CY, Ing CH, Chang CF (2004) Adsorption of acid dyes from aqueous solution on activated bleaching earth. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.01.072
Turkten N, Cinar Z (2017) Photocatalytic decolorization of azo dyes on TiO2: prediction of mechanism via conceptual DFT. Catal Today 287:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.01.019
Marçal L, De Faria EH, Saltarelli M, Calefi PS, Nassar EJ, Ciuffi KJ, Trujillano R, Vicente MA, Korili SA, Gil A (2011) Amine-functionalized titanosilicates prepared by the sol-gel process as adsorbents of the Azo-Dye orange II. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:239–246. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie101650h
Parshetti GK, Telke AA, Kalyani DC, Govindwar SP (2010) Decolorization and detoxification of sulfonated azo dye methyl orange by Kocuria rosea MTCC 1532. J Hazard Mater 176:503–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.058
Gupta VK, Sharma G, Pathania D, Kothiyal NC (2015) Nanocomposite pectin Zr(IV) selenotungstophosphate for adsorptional/photocatalytic remediation of methylene blue and malachite green dyes from aqueous system. J Ind Eng Chem 21:957–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.05.001
Santiago G, De Salas F, Lucas MF, Monza E, Acebes S, Martinez ÁT, Camarero S, Guallar V (2016) Computer-aided laccase engineering: toward biological oxidation of arylamines. ACS Catal 6:5415–5423. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.6b01460
Vijayaraghavan G, Vignesh Kumar P, Chandrakanthan K, Selvakumar S (2017) Acanthocereus tetragonus an effective natural coagulant for decolorization of synthetic dye wastewater. J Mater Environ Sci 8:3028–3033
Oun A, Tahri N, Mahouche-Chergui S, Carbonnier B, Majumdar S, Sarkar S, Sahoo GC, Ben Amar R (2017) Tubular ultrafiltration ceramic membrane based on titania nanoparticles immobilized on macroporous clay-alumina support: elaboration, characterization and application to dye removal. Sep Purif Technol 188:126–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.07.005
Shaban M, Abukhadra MR, Hamd A (2017) Recycling of glass in synthesis of MCM-48 mesoporous silica as catalyst support for Ni2O3 photocatalyst for Congo red dye removal. Clean Technol Environ Policy 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1447-5
Crini G (2006) Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour Technol 97:1061–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.05.001
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.047
Liu G, Yang R, Li M (2010) Liquid adsorption of basic dye using silica aerogels with different textural properties. J Non Cryst Solids 356:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2009.11.019
Chaudhuri H, Dash S, Ghorai S, Pal S, Sarkar A (2016) SBA-16: application for the removal of neutral, cationic, and anionic dyes from aqueous medium. J Environ Chem Eng 4:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.11.020
Rao AV, Hegde ND, Hirashima H (2007) Absorption and desorption of organic liquids in elastic superhydrophobic silica aerogels. J Colloid Interface Sci 305:124–132
Zong S, Wei W, Jiang Z, Yan Z, Zhua J, Xie J (2015) Characterization and comparison of uniform hydrophilic/hydrophobic transparent silica aerogel beads: skeleton strength and surface modification. RSC Adv 5(68):55579–55587
Estella J, Echeverría JC, Laguna M, Garrido JJ (2007) Effects of aging and drying conditions on the structural and textural properties of silica gels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 102:274–282
Brinker C, Scherer G (1990) Sol-gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. Academic Press, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-8-444
Senthilkumaar S, Varadarajan PR, Porkodi K, Subbhuraam CV (2005) Adsorption of methylene blue onto jute fiber carbon: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.09.027
Castricum HL, Qureshi HF, Nijmeijer A, Winnubst L (2015) Hybrid silica membranes with enhanced hydrogen and CO2 separation properties. J Memb Sci 488:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2015.03.084
Uddin MT, Islam MA, Mahmud S, Rukanuzzaman M (2009) Adsorptive removal of methylene blue by tea waste. J Hazard Mater 164:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.07.131
Sing KSW (1982) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl Chem 54:2201–2218. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603
Feliczak-Guzik A, Jadach B, Piotrowska H, Murias M, Lulek J, Nowak I (2016) Synthesis and characterization of SBA-16 type mesoporous materials containing amine groups. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 220:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.09.006
Huirache-Acuña R, Pawelec B, Rivera-Muñoz EM, Guil-López R, Fierro JLG (2017) Characterization and HDS activity of sulfided CoMoW/SBA-16 catalysts: effects of P addition and Mo/(Mo+W) ratio. Fuel 198:145–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.09.042
Kavian S, Azizi SN, Ghasemi S (2017) Novel bimetallic nanoporous Pd-Cu-SBA-16/CPE as a highly sensitive sensor for determination of formaldehyde. J Electroanal Chem 799:308–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2017.06.006
Tsai C-H, Chang W-C, Saikia D, Wu C-E, Kao H-M (2016) Functionalization of cubic mesoporous silica SBA-16 with carboxylic acid via one-pot synthesis route for effective removal of cationic dyes. J Hazard Mater 309:236–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.08.051
Rivera-Muñoz EM, Huirache-Acuña R (2010) Sol gel-derived SBA-16 mesoporous material. Int J Mol Sci 11:3069–3086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11093069
Thielemann J, Girgsdies F, Schlögl R, Hess C (2011) Pore structure and surface area of silica SBA-15: influence of washing and scale-up. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 2:110–118. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.2.13
Castricum HL, Paradis GG, Mittelmeijer-Hazeleger MC, Bras W, Eeckhaut G, Vente JF, Rothenberg G, Ten Elshof JE (2014) Tuning the nanopore structure and separation behavior of hybrid organosilica membranes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 185:224–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.11.005
Tomita T, Kawasaki S, Okada K (2004) A novel preparation method for foamed silica ceramics by sol-gel reaction and mechanical foaming. J Porous Mater 11:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JOPO.0000027366.90408.1f
McDonagh C, Sheridan F, Butler T, MacCraith BD (1996) Characterisation of sol-gel-derived silica films. J Non Cryst Solids 194:72–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(95)00488-2
Jung HY, Gupta RK, Oh EO, Kim YH, Whang CM (2005) Vibrational spectroscopic studies of sol-gel derived physical and chemical bonded ORMOSILs. J Non Cryst Solids 351:372–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2005.01.004
Yoshino H, Kamiya K, Nasu H (1990) IR study on the structural evolution of sol-gel derived SiO2 gels in the early stage of conversion to glasses. J Non Cryst Solids 126:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3093(90)91024-L
Almeida RM, Pantano CG (1990) Structural investigation of silica gel films by infrared spectroscopy. J Appl Phys 68:4225–4232. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.346213
Wood DL, Rabinovich EM, Johnson DW, MacChesney JB, Vogel EM (1983) Preparation of high-silica glasses from colloidal gels: III, Infrared spectrophotometric studies. J Am Ceram Soc 66:693–699. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1983.tb10531.x
Sen PN, Thorpe MF (1977) Phonons in AX2 glasses: from molecular to band-like modes. Phys Rev B 15:4030–4038. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.15.4030
Galeener FL (1979) Band limits and the vibrational spectra of tetrahedral glasses. Phys Rev B 19:4292–4297. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.19.4292
Alexandridis P, Holzwarth JF, Hatton TA (1994) Micellization of poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) triblock copolymers in aqueous solutions: Thermodynamics of copolymer association. Macromolecules 27:2414–2425. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00087a009
De Paz-Simon H (2013) Sol-gel photopolymerization of inorganic precursors and application for mesoporous silica films elaboration. Université de Haute Alsace, Mulhouse
Rosen MJ, Kunjappu JT (2012) Surfactants and interfacial phenomena. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Hoboken. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118228920
Lu Y, Ganguli R, Drewien CA, Anderson MT, Jeffrey Brinker C, Gong W, Guo Y, Soyez H, Dunn B, Huang MH, Zink JI (1997) Continuous formation of supported cubic and hexagonal mesoporous films by sol-gel dip-coating. Nature 389:364–368. https://doi.org/10.1038/38699
Da Costa JCD, Lu GQ, Zhu HY, Rudolph V (1999) Novel composite membranes for gas separation: Preparation and performance. J Porous Mater 6:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009635506549
Lagergren S (1898) Zur Theorie der Sogenannten Adsorption Gelöster Stoffe, K. Sven. Vetenskapsakademiens, Handl 24: 1–39
Yuh-Shan H (2004) Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics 59:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:SCIE.0000013305.99473.cf
Ho Y, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Wu F-C, Tseng R-L, Juang R-S (2009) Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem Eng J 153:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.04.042
Oliveira LS, Franca AS, Alves TM, Rocha SDF (2008) Evaluation of untreated coffee husks as potential biosorbents for treatment of dye contaminated waters. J Hazard Mater 155:507–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.093
Hameed BH, Rahman AA (2008) Removal of phenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from biomass material. J Hazard Mater 160:576–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.028
Acknowledgements
FAPEMIG (APQ-00792-17 and APQ-01881-18), CNPq (305013/2017-3 and 301423/2018-0), and PRPq-UFMG (05/2016) are acknowledged for the financial support. The authors kindly thank INCT-Acqua Institute, Prof. Paulo Brandão, Ilda Batista and Isabel Batista for the help about FTIR and Nitrogen sorption characterizations. We also greatly thank Professors Adriana França and Leandro Soares from DEMEC-UFMG (Laboratório de Biocombustíveis) for the helpful discussions and support given to this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mota, T.L.R., Gomes, A.L.M., Palhares, H.G. et al. Influence of the synthesis parameters on the mesoporous structure and adsorption behavior of silica xerogels fabricated by sol–gel technique. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 92, 681–694 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05131-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05131-y