Abstract
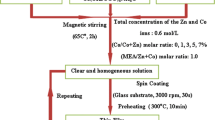
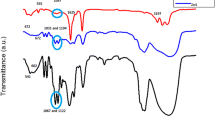
ZnO thin films were synthesized using sol–gel method at 0.25 and 0.5 M molarity concentration. Moreover, the obtained thin films were Calcium-doped with 1 and 5 at% concentration. In order to investigate the structural changes in the molecular binding between ZnO and Ca, Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD) were performed. The surface morphology and the chemical constituents distribution of the films were studied through Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) and Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), respectively. The optical and electrical properties were studied by UV–Vis spectroscopy, Spectral ellipsometry and electrical I–V measurements. The results show that the properties of prepared ZnO thin films were strongly influenced by the molarity concentration and Ca-dopant. The band shape obtained at FTIR is a band attributable to metal oxide bonds and can be attributed to the vibrational assignment of Zn–O bond. SEM-EDX and AFM investigations reveal an enlarged surface area due to the porous nature of the thin films and confirm the presence of Ca in the ZnO matrix. The XRD and Raman analyses indicate the achievement of the high crystalline quality and confirm the wurtzite phase of the synthesized thin films. The films transmittance spectra indicate values between 81 and 93% in the 350–800 nm wavelength region. We further performed I–V characteristics, resulting that Ca has a different impact of the electrical performances.

Highlights
-
Effect of Ca doping on morphological, structural, and opto-electrical properties of ZnO thin films synthesized by sol–gel at 0.25 and 0.5 M is studied.
-
The films has a porous nature and a strong preferred orientation of (002) reflex when the concentration of Ca is greater.
-
EDX study reveals the substitution of Ca atoms into ZnO lattice.
-
Ca-doped ZnO thin films at 0.5 M exhibit superior properties when compared with 0.25 M.
-
The 5 at%-Ca:ZnO, 0.5 M present the lowest resistivity value of 4.70 Ω cm.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nimbalkar AR, Patil NB, Ganbavle VV, Mohite SV, Madhale KV, Patil MG (2019) Sol-gel derived aluminium doped zinc oxide thin films: a view of aluminium doping effect on physicochemical and NO2 sensing properties. J Alloy Compd 775:466–473
Yu W, Han D, Cui G, Cong Y, Dong J, Zhang X, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang S (2016) High-performance calcium-doped zinc oxide thin-film transistors fabricated on glass at low temperature. Jpn J Appl Phys 55:1–4
Yu W, Han D, Shi P, Cong Y, Zhang Y, Dong J, Zhou X, Huang L, Cui G, Zhang S, Zhang X, Wang Y (2015) Effects of substrate temperature on performance of calcium-doped zinc oxide TFTs. Electron Lett 51:1286–1288
Wong LLP, Na S, Chen AI, Li Z, Macecek M, Yeow JTW (2016) A feasibility study of piezoelectric micromachined ultrasonic transducers fabrication using a multi-user MEMS process. Sens Actuat A—Phys 247:430–439
Bhatia D, Sharma H, Meena RS, Palkar VR (2016) A novel ZnO piezoelectric microcantilever energy scavenger: Fabrication and characterization. Sens Biosensing Res 9:45–52
A Ghosh, C Zhang, S Shi, H Zhang (2019) High temperature CO2 sensing and its cross-sensitivity towards H2 and CO gas using calcium doped ZnO thin film coated langasite SAW sensor. Sensor Actuat. B-Chem https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.126958
Salim ZT, Hashim U, Md. Arshad MK, Fakhri MA, Salim ET (2017) Zinc oxide flakes-corolla lobes like nano combined structure for SAW applications. Mater Res Bull 86:215–219
Nazir Kayani Z, Sahar S, Riaz S, Naseem S (2019) Tuning of optical and antibacterial characteristics of ZnO thin films: role of Ce content. Ceram Int 45:3930–3939
Water W, Wang S-F, Chen Y-P, Pu J-C (2005) Calcium and strontium doped ZnO films for love wave sensor applications. Integr Ferroelectr 72:13–22
Dhahri R, Hjiri M, El Mir L, Fazio E, Neri F, Barreca F, Donato N, Bonavita A, Leonardi SG, Neri G (2015) ZnO:Ca nanopowders with enhanced CO2 sensing properties. J Phys D: Appl Phys 48:1–7
Hjiri M, Zahmouli N, Dhahri R, Leonardi SG, El Mir L, Neri G (2017) Doped-ZnO nanoparticles for selective gas sensors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28:9667–9674
Dhahri R, Leonardi SG, Hjiri M, El Mir L, Bonavita A, Donato N, Iannazzo D, Neri G (2017) Enhanced performance of novel calcium/aluminum co-doped zinc oxide for CO2 sensors. Sens Actuators B 239:36–44
Mahdhi H, Djessas K, Ben Ayadi Z (2018) Synthesis and characteristics of Ca-doped ZnO thin films by rf magnetron sputtering at low temperature. Mater Lett 214:10–14
Samuel EP, Bhadane H, Chandra U, Gautam DK (2014) Sol gel Spin coated ZnO thin films for biosensing applications. Int J Eng Technol Res 2:42–44
Znaidi L (2010) Sol–gel-deposited ZnO thin films: a review. Mater Sci Eng B 174:18–30
Ammaih Y, Lfakir A, Hartiti B, Ridah A, Thevenin P, Siadat M (2014) Structural, optical and electrical properties of ZnO:Al thin films for optoelectronic applications. Opt Quant Electron 46:229–234
Water W, Yang Y-S (2006) The influence of calcium doped ZnO films on Love wave sensor characteristics. Sens Actuators A 127:360–365
Cao L, Jiang J, Zhu L (2013) Realization of band-gap engineering of ZnO thin films via Ca alloying. Mater Lett 100:201–203
Santangelo S, Patanè S, Frontera P, Pantò F, Triolo C, Stelitano S, Antonucci P (2017) Effect of calcium- and/or aluminum-incorporation on morphological, structural and photoluminescence properties of electro-spun zinc oxide fibers. Mater Res Bull 92:9–18
Ghiloufi I, El Ghoul J, Modwi A, El Mir L (2016) Preparation and characterization of Ca-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution. MRS Adv 1:3607–3612
Karthikeyan B, Pandiyarajan T, Mangaiyarkarasi K (2011) Optical properties of sol–gel synthesized calcium doped ZnO nanostructures. Spectrochim Acta A: Mol Biomol Spectrosc 82:97–101
Ivanova T, Harizanova A, Koutzarova T, Vertruyen B (2010) Study of ZnO sol–gel films: effect of annealing. Mater Lett 64:1147–1149
Nimbalkar AR, Patil MG (2017) Synthesis of ZnO thin film by sol-gel spin coating technique for H2S gas sensing application. Physica B 527:7–15
Ganbavle VV, Patil SK, Inamdar SI, Shinde SS, Rajpure KY (2014) Effect of Co doping on structural, morphological and LPG sensing properties of nanocrystalline ZnO thin films. Sens Actuators A 216:328–334
Nimbalkar AR, Patil MG (2017) Synthesis of highly selective and sensitive Cu-doped ZnO thin film sensor for detection of H2S gas. Mater Sci Semicond Process 71:332–341
Deng H, Russell JJ, Lamb RN, Jiang B, Li Y, Zhou XY (2004) Microstructure control of ZnO thin films prepared by single source chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films 458:43–46
Xu Z, Deng H, Li Y, Guo QH (2006) Characteristics of Al-doped c-axis orientation ZnO thin films prepared by the sol–gel method. Mater Res Bull 41:354–358
Bao D, Gu H, Kuang A (1998) Sol-gel-derived c-axis oriented ZnO thin films. Thin Solid Films 312:37–39
Amirhaghi S, Craciun V, Craciun D, Elders J, Boyd IW (1994) Low temperature growth of highly transparent c-axis oriented ZnO thin films by pulsed laser deposition. Microelectron Eng 25:321–326
Raoufi D, Raoufi T (2009) The effect of heat treatment on the physical properties of sol-gel derived ZnO thin films. Appl Surf Sci 255:5812–5817
Ravichandran C, Srinivasan G, Lennon C, Sivananthan S, Kumar J (2011) Influence of post-deposition annealing on the structural, optical and electrical properties of Li and Mg co-doped ZnO thin films deposited by sol–gel technique. Superlattice Microstruct 49:527–536
Shaban M, El Sayed AM (2016) Effects of lanthanum and sodium on the structural, optical and hydrophilic properties of sol–gel derived ZnO films: a comparative study. Mater Sci Semicond Process 41:323–334
Musat V, Fortunato E, Purica M, Mazilu M, Botelho do Rego AM, Diaconu B, Busani T (2012) Multifunctional zinc oxide nanostructures for a new generation of devices. Mater Chem Phys 132:339–346
Kalyanaraman S, Vettumperumal R (2013) Study of multiple phonon behavior in Li-doped ZnO thin films fabricated using the sol-gel spin-coating technique. J Korean Phys Soc 62:804–808
Chai GY, Chow L, Lupan O, Rusu E, Stratan GI, Heinrich H, Ursaki VV, Tiginyanu IM (2011) Fabrication and characterization of an individual ZnO microwire-based UV photodetector. Solid State Sci 13:1205–1210
Vettumperumal R, Kalyanaraman S, Santoshkumar B, Thangavel R (2016) Estimation of electron–phonon coupling and Urbach energy in group-I elements doped ZnO nanoparticles and thin films by sol–gel method. Mater Res Bull 77:101–110
Chen LC, Tien C-H, Fu C-S (2012) Magneto-optical characteristics of Mn-doped ZnO films deposited by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Mater Sci Semicond Process 15:80–85
Orozco S, Riascos H, Duque S (2016) Raman spectroscopy of ZnMnO thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition. J Phys: Conf Ser 687:1–4
Ben Yahia S, Znaidi L, Kanaev A, Petitet JP (2008) Raman study of oriented ZnO thin films deposited by sol–gel method. Spectrochim Acta A 71:1234–1238
Bedia A, Bedia FZ, Aillerie M, Maloufi N, Benyoucef B (2015) Morphological and optical properties of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis on glass substrates at various temperatures for integration in solar cell. Energy Proced 74:529–538
Girma T, Siraj K, Yifru A (2016) Defect induced band gap narrowing of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Li+, Na+ and K+ metal ions as a dopant. Elixir Mater Sci 91:38058–38062
Hasabeldaim E, Ntwaeaborwa OM, Kroon RE, Swart HC (2019) Structural, optical and photoluminescence properties of Eu doped ZnO thin films prepared by spin coating. J Mol Struct 1192:105–114
Islam MR, Podder J, Islam MM, Chowdhury RI, Farhad SFU, Saha DK (2011) Effect of annealing on the structural and optical properties of nano fiber ZnO films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Sens Transducers 134:170–176
Slama R, El Ghoul J, Omri K, Houas A, El Mir L, Launay F (2016) Effect of Ca-doping on microstructure and photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by sol gel method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27:7939–7946
Santoshkumar B, Kalyanaraman S, Vettumperumal R, Thangavel R, Kityk IV, Velumani S (2016) Structure-dependent anisotropy of the photoinduced optical nonlinearity in calcium doped ZnO nanorods grown by low cost hydrothermal method for photonic device applications. J Alloy Compd 658:435–439
Che Ani N, Kamaruddin SA, Nayan N, Tawil SNM, Sahdan MZ (2015) Effects of ageing time of ZnO sol on properties of ZnO films by sol gel spin coating. Int J Nanoelectron Mater 8:15–21
Aydın H, Yakuphanoglu F, Aydın C (2019) Al-doped ZnO as a multifunctional nanomaterial: structural, morphological, optical and low-temperature gas sensing properties. J Alloy Compd 773:802–811
Ahmed MAM, Meyer WE, Nel JM (2019) Structural, optical and electrical properties of the fabricated Schottky diodes based on ZnO, Ce and Sm doped ZnO films prepared via wet chemical technique. Mater Res Bull 115:12–18
Shakti N, Gupta PS (2010) Structural and optical properties of sol-gel prepared ZnO thin film. Appl Phys Res 2:19–28
Dutta M, Mridha S, Basak D (2008) Effect of sol concentration on the properties of ZnO thin films prepared by sol–gel technique. Appl Surf Sci 254:2743–2747
Bhat JS, Patil AS, Swami N, Mulimani BG, Gayathri BR, Deshpande NG, Kim GH, Seo MS, Lee YP (2010) Electron irradiation effects on electrical and optical properties of sol-gel prepared ZnO films J Appl Phys 108:043513-1–043513-8
Dahoudi NA (2014) Comparative study of highly dense aluminium and gallium doped zinc oxide transparent conducting sol–gel thin films. Bull Mater Sci 37:1243–1248
Mahdhi H, Ben Ayadi Z, Gauffier JL, Djessas K, Alaya S (2015) Effect of sputtering power on the electrical and optical properties of Ca-doped ZnO thin films sputtered from nanopowders compacted target. Opt Mater 45:97–103
Natsume Y, Sakata H (2000) Zinc oxide films prepared by sol–gel spin-coating. Thin Solid Films 372:30–36
Talukder A-A, Pokharel J, Shrestha M, Fan QH (2016) Improving electrical properties of sol-gel derived zinc oxide thin films by plasma treatment J Appl Phys 120:155303-1–155303-7
Davis K, Yarbrough R, Froeschle M, White J, Rathnayake H (2019) Band gap engineered zinc oxide nanostructures via a sol–gel synthesis of solvent driven shape-controlled crystal growth. RSC Adv 9:14638–14648
Nakrela A, Benramdane N, Bouzidi A, Kebbab Z, Medles M, Mathieu C (2016) Site location of Al-dopant in ZnO lattice by exploiting the structural and optical characterisation of ZnO:Al thin films. Results Phys 6:133–138
Acknowledgements
The work has been funded by the Core Project MICRO-NANO-SIS PLUS no. 14N/2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Istrate, AI., Nastase, F., Mihalache, I. et al. Synthesis and characterization of Ca doped ZnO thin films by sol–gel method. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 92, 585–597 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05144-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05144-7