Abstract
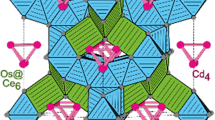
Polycrystalline samples of rare-earths molybdates and tungstates, i.e., CdRE4Mo3O16 (RE = Eu, Gd, Y, Ho) and Pb1–3x□xEu2xWO4 (0 < x ≤ 0.1296 and □ denotes cationic vacancies) have been successfully prepared by high-temperature annealing of adequate CdMoO4/RE2MoO6 and PbWO4/Eu2(WO4)3 mixtures, respectively. According to the X-ray diffraction analysis, the CdRE4Mo3O16 compounds crystallize in a cubic, fluorite-related-type structure with space group \(Pn\bar{3}n\). In turn, new Pb1–3x□xEu2xWO4 phases crystallize in the scheelite-type, tetragonal symmetry, space group I41/a. Cadmium and rare-earth molybdates decompose in the solid state and the solid products of their decomposition are two RE molybdates, i.e., RE2MoO6 and RE2(MoO4)3. Thermal stability of CdRE4Mo3O16 decreases with decreasing of RE3+ radius. The melting point of each sample of Pb1–3x□xEu2xWO4 solid solution is lower than melting point of pure matrix, i.e., PbWO4 (1116 °C), and it decreases with increasing in Eu content. Both CdRE4Mo3O16 as well as Pb1–3x□xEu2xWO4 samples are insulators, and their optical band gap (E g) is bigger than 3 eV.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Öztürk E, Kalaycioglu Ozpozan N. Mn4+-, Tb3+,4+-, and Er3+- activated red phosphors in the MgAl2Si2O8 system. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:573–7.
Öztürk E, Karacaoglu E. Luminescence properties of M2TiO4:Eu3+, Li+, (M:Mg, Ca) and MgAl2O4:RE3+ (RE3+:Ho3+, Sm3+, and Yb3+). J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:1063–71.
Öztürk E, Karacaoglu E. Investigation of phase formation dependency of photoluminescence properties of Eu3+ in Mg4Al2O7:Eu3+, Dy3+, and Ca4Al2O7:Eu3+, Dy3+ red-emitting phosphors. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120:1139–43.
Öztürk E. The effect of Ba/Mg impurities on the phase formation and photoluminescence properties of (Sr3-xMx)Al2O6:Eu3+, Ho3+ (M = Ba, Mg) phosphors. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:365–9.
Guzik M, Cybińska J, Tomaszewicz E, Guyot Y, Legendziewicz J, Boulon G, Stręk W. Spectroscopic behavior of Nd3+ in a new microcrystalline ZnY4W3O16 tungstate. Opt Mater. 2011;34:487–95.
Tomaszewicz E, Guzik M, Cybińska J, Legendziewicz J. Spectroscopic investigation of the Eu(3+) ion in a new ZnY4W3O16 matrix. Helv Chim Acta. 2009;92:2274–90.
Guzik M, Tomaszewicz E, Kaczmarek SM, Cybińska J, Fuks H. Spectroscopic investigations of Cd0.25Gd0.50□0.25WO4:Eu3+—a new promising red phosphor. J Non Cryst Solids. 2010;356:1902–7.
Guzik M, Tomaszewicz E, Guyot Y, Legendziewicz J, Boulon J. Spectroscopic properties, concentration quenching and Yb3+ site occupations in a vacancied scheelite-type molybdates. J Lumin. 2016;169:755–64.
Shivakumara C, Saraf R. Eu3+-activated SrMoO4 phosphors for white LEDs applications: synthesis and structural characterization. Opt Mater. 2015;42:178–86.
Aghamalyan NR, Demirkhanyan GG, Hovsepyan RK, Kostanyan RB, Zargaryan DG. Room-temperature near infrared emission and green up-conversion in PbMoO4:Er3+ crystals. Opt Mater. 2010;32:1046–9.
Tu C, Qiu M, Li J, Liao H. The study of 1.06 μm laser characteristics of Nd3+:KGd(WO4)2 crystal. Opt Mater. 2001;16:431–6.
Kato A, Oishi S, Shishido T, Yamazaki M, Iida S. Evaluation of stoichiometric rare-earth molybdate and tungstate compounds as laser materials. J Phys Chem Solids. 2005;66:2079–81.
Grabtchikov AS, Kuzmin AN, Lisinwtskii VA, Orlovich VA, Demidovich AA, Yumashev KV, Kuleshov NV, Eichler HJ, Danailov MB. Passively Q-switched 1.35 μm diode pumped Nd:KGW laser with V:YAG saturable absorber. Opt Mater. 2001;16:349–52.
Cano-Torres JM, Han X, García-Cortés A, Serrano MD, Zaldo C, Valle FJ, Mateos X, Rivier S, Griebner U, Petrov V. Infrared spectroscopic and laser characterization of Tm in disordered double tungstates. Mat Sci Eng B. 2008;146:22–8.
Bourdet JB, Chevalier R, Fournier JP, Kohlmuller R, Omaly J. A structural study of cadmium yttrium molybdate CdY4Mo3O16. Acta Crystallogr B. 1982;38:2371–4.
Faurie JP, Kohlmuller R. Étude des phases MLn4Mo3O16 et M’Ln6Mo4O22 (M = Cd; M’ = Ca, Sr) de structure dérivée de la fluorine par magnétochemie, luminescence cristalline, spectroscopic infrarouge, et radiocristallographie. Hypothèse structurale pour la phase CdTm4Mo3O16. Rev Chim Miner. 1971;8:241–76.
Sleight AW. Accurate cell dimensions for ABO4 molybdates and tungstates. Acta Crystallogr B. 1972;28:2899–902.
Bomio MRD, Cavalcante LS, Almeida MAP, Tranquilin RL, Batista NC, Pizani PS, Siu Li M, Andrés J, Longo E. Structural refinement, growth mechanism, infrared/Raman spectroscopies and photoluminescence properties of PbMoO4 crystals. Polyhedron. 2013;50:532–45.
Piątkowska M, Tomaszewicz E. Solid-state synthesis, thermal stability and optical properties of new scheelite-type Pb1–3x□xPr2xWO4 ceramics where □ denotes cationic vacancies. Mat Lett. 2016;182:332–5.
Tomaszewicz E, Filipek E, Fuks H, Typek J. Thermal and magnetic properties of new scheelite type Cd1–3x□xGd2xMoO4 ceramic materials. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2014;34:1511–22.
Guzik M, Tomaszewicz E, Guyot Y, Legendziewicz J, Boulon G. Structural and spectroscopic characterizations of new vacancied Cd1–3xNd2x□xMoO4 scheelite-type molybdates as potential optical materials. J Mater Chem C. 2015;3:4057–69.
Tomaszewicz E, Dąbrowska G, Filipek E, Fuks H, Typek J. Structure, thermal and magnetic properties of new scheelite-type Cd1–3x□xGd2x(MoO4)1–3x(WO4)3x ceramics. Ceram Int. 2016;42:6673–81.
Kukuła Z, Tomaszewicz E, Mazur S, Groń T, Pawlus S, Duda H, Mydlarz T. Electrical and magnetic properties of CdRE2W2O10 tungstates (RE = Y, Nd, Sm, Gd-Er). J Phys Chem Solids. 2013;74:86–93.
Tomaszewicz E, Fuks H, Typek J, Sawicki B, Oboz M, Groń T, Mydlarz T. Preparation, thermal stability and magnetic properties of new AgY1–xGdx(WO4)2 ceramic materials. Ceram Int. 2015;41:5734–48.
Tomaszewicz E, Dąbrowska G. Reactivity in the solid state between ZnWO4 and some rare-earth metal molybdates RE 2MoO6, (RE = Y, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Er and Lu). J Therm Anal Cal. 2008;94:189–94.
Tomaszewicz E, Worsztynowicz A, Kaczmarek SM. Subsolidus phase relations in CuWO4-–Gd2WO6 system. Solid State Sci. 2007;9:43–51.
Keskar M, Krishnan K, Phatak R, Dash S, Sali SK, Kannan S. Studies on thermophysical properties of ThW2O8 and UWO6. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:659–70.
Taupin D. A powder—diagram automatic—indexing routine. J Appl Crystallogr. 1973;6:380–5.
Shannon RD. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr A. 1976;32(5):751–67.
Jeitschko W. A comprehensive X-ray study of the ferroelectric–ferroelastic and paraelectric–paraelastic phase of Gd2(MoO4)3. Acta Crystallogr B. 1972;28:60–76.
Sleight AW, Brixner LH. A new ferroelastic transition in some A2(MO4)3 molybdates and tungstates. J Solid State Chem. 1973;7:172–4.
Brixner LH, Bierstedt PE, Sleight AW, Licis MS. Precision parameters of some Ln2(MoO4)3-type rare earth molybdates. Mat Res Bull. 1971;6:545–54.
Alonso JA, Rivillas F, Martínez-Lope MJ, Pomjakushin V. Preparation and structural study from neutron diffraction data of R2MoO6 (R = Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Y). J Solid State Chem. 2004;177:2470–6.
Brixner LH, Sleight AW, Licis MS. Ln2MoO6-type rare earth molybdates—preparation and lattice parameters. J Solid State Chem. 1972;5:186–90.
Kubelka P, Munk F. Ein Beitrag zur Optic der Farbanstriche. Z Tech Phys. 1931;12:593–601.
Tauc J, Grigorovici R, Vancu A. Optical properties and electronic structures of amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi. 1966;15:627–37.
Wood DL, Tauc J. Weak absorption tails in amorphous semiconductors. Phys Rev B. 1972;5:3144–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pawlikowska, M., Piątkowska, M. & Tomaszewicz, E. Synthesis and thermal stability of rare-earths molybdates and tungstates with fluorite- and scheelite-type structure. J Therm Anal Calorim 130, 69–76 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6127-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6127-5