Abstract
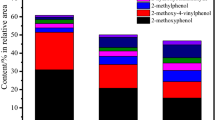
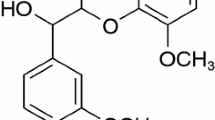
In order to understand the catalytic effects of inherent inorganic elements in biomass on the pyrolysis mechanism of lignin, density functional theory with a Gaussian method of M06-2X and basic set of 6-31 + G(d,p) was employed to simulate the pyrolysis pathways of a β-O-4 type lignin dimer model compound (1-methoxy-2-(4-methoxyphenethoxy)benzene) catalyzed by NaCl and KCl which are major inorganic constituents of biomass at microscale level. The calculation results indicate that cations (Na+ and K+) in alkali metal chlorides are facile to combine with the oxygen-containing functional groups in the lignin dimer model compound. Both cations increase the Cβ−O bond length and shorten the Cα–Cβ bond length, which will further affect their bond dissociation energies. In the initial pyrolysis process of the lignin dimer model compound, NaCl and KCl can promote the Cβ–O homolytic reaction and concerted decomposition reaction, while restrain the Cα–Cβ homolytic reaction. Therefore, the lignin dimer model compound decomposes mainly through the concerted decomposition and Cβ–O homolytic mechanisms under NaCl and KCl catalytic pyrolysis conditions, producing 1-methoxy-4-vinylbenzene, 1-ethyl-4-methoxybenzene, 2-methoxyphenol, catechol and 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, among which NaCl and KCl have inhibitory effect on 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde, but have promoting effect on the other pyrolytic products.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zakzeski J, Bruijnincx PCA, Jongerius AL, Weckhuysen BM. The catalytic valorization of lignin for the production of renewable chemicals. Chem Rev. 2010;110:3552–99.
Pandey MP, Kim CS. Lignin depolymerization and conversion: a review of thermochemical methods. Chem Eng Technol. 2011;34:29–41.
Dong CQ, Zhang ZF, Lu Q, Yang YP. Characteristics and mechanism study of analytical fast pyrolysis of poplar wood. Energy Convers Manag. 2012;57:49–59.
Azadi P, Inderwildi OR, Farnood R, King DA. Liquid fuels, hydrogen and chemicals from lignin: a critical review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2013;21:506–23.
Zhang ZB, Lu Q, Ye XN, Xiao LP, Dong CQ, Liu YQ. Selective production of phenolic-rich bio-oil from catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass: comparison of K3PO4, K2HPO4, and KH2PO4. BioResources. 2014;9:4050–62.
Zhang ZB, Lu Q, Ye XN, Li WT, Hu B, Dong CQ. Production of phenolic-rich bio-oil from catalytic fast pyrolysis of biomass using magnetic solid base catalyst. Energy Convers Manag. 2015;106:1309–17.
Shen D, Jin W, Hu J, Xiao R, Luo K. An overview on fast pyrolysis of the main constituents in lignocellulosic biomass to valued-added chemicals: structures, pathways and interactions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2015;51:761–74.
Elder T. A computational study of pyrolysis reactions of lignin model compounds. Holzforschung. 2010;64:435–40.
Elder T, Beste A. Density functional theory study of the concerted pyrolysis mechanism for lignin models. Energy Fuels. 2014;28:5229–35.
Beste A, Buchanan AC. Kinetic simulation of the thermal degradation of phenethyl phenyl ether, a model compound for the beta-O-4 linkage in lignin. Chem Phys Lett. 2012;550:19–24.
Huang J, He C. Pyrolysis mechanism of α-O-4 linkage lignin dimer: a theoretical study. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2015;113:655–64.
Huang J, Liu C, Wu D, Tong H, Ren L. Density functional theory studies on pyrolysis mechanism of β-O-4 type lignin dimer model compound. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 2014;109:98–108.
Huang J, He C, Pan G, Tong H. A theoretical research on pyrolysis reactions mechanism of coumarone-contained lignin model compound. Comput Theor Chem. 2016;1091:92–8.
Jiang XY, Lu Q, Ye XN, Hu B, Dong CQ. Experimental and theoretical studies on the pyrolysis mechanism of β-1-type lignin dimer model compound. BioResources. 2016;11:6232–43.
Zhang JJ, Jiang XY, Ye XN, Chen L, Lu Q, Wang XH, Dong CQ. Pyrolysis mechanism of a β-O-4 type lignin dimer model compound. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;123:501–10.
Lane DJ, van Eyk PJ, Ashman PJ, Kwong CW, de Nys R, Roberts DA, Cole AJ, Lewis DM. Release of Cl, S, P, K, and Na during thermal conversion of algal biomass. Energy Fuels. 2015;29:2542–54.
Le Brech Y, Ghislain T, Leclerc S, Bouroukba M, Delmotte L, Brosse N, Snape C, Chaimbault P, Dufour A. Effect of potassium on the mechanisms of biomass pyrolysis studied using complementary analytical techniques. Chemsuschem. 2016;9:863–72.
Jensen PA, Frandsen FJ, Dam-Johansen K, Sander B. Experimental investigation of the transformation and release to gas phase of potassium and chlorine during straw pyrolysis. Energy Fuels. 2000;14:1280–5.
Zhao HB, Song Q, Wu XY, Yao Q. Study on the transformation of inherent potassium during the fast-pyrolysis process of rice straw. Energy Fuels. 2015;29:6404–11.
Wang Y, Wu H, Sárossy Z, Dong C, Glarborg P. Release and transformation of chlorine and potassium during pyrolysis of KCl doped biomass. Fuel. 2017;197:422–32.
Fahmi R, Bridgwater AV, Darvell LI, Jones JM, Yates N, Thain S, Donnison IS. The effect of alkali metals on combustion and pyrolysis of Lolium and Festuca grasses, switchgrass and willow. Fuel. 2007;86:1560–9.
Fahmi R, Bridgwater AV, Donnison I, Yates N, Jones JM. The effect of lignin and inorganic species in biomass on pyrolysis oil yields, quality and stability. Fuel. 2008;87:1230–40.
Di Blasi C, Galgano A, Branca C. Influences of the chemical state of alkaline compounds and the nature of alkali metal on wood pyrolysis. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2009;48:3359–69.
Di Blasi C, Galgano A, Branca C. Analysis of the physical and chemical mechanisms of potassium catalysis in the decomposition reactions of wood. Ind Eng Chem Res. 2011;50:3864–73.
Jakab E, Faix O, Till F, Székely T. The effect of cations on the thermal decomposition of lignins. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 1993;25:185–94.
Eom IY, Kim JY, Kim TS, Lee SM, Choi D, Choi IG, Choi JW. Effect of essential inorganic metals on primary thermal degradation of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol. 2012;104:687–94.
Hwang H, Oh S, Cho TS, Choi IG, Choi JW. Fast pyrolysis of potassium impregnated poplar wood and characterization of its influence on the formation as well as properties of pyrolytic products. Bioresour Technol. 2013;150:359–66.
Frisch MJ, Trucks GW, Schlegel HB, Scuseria GE, Robb MA, Cheeseman JR, Scalmani G, Barone V, Mennucci B, Petersson GA, Nakatsuji H, Caricato M, Li X, Hratchian HP, Izmaylov AF, Bloino J, Zheng G, Sonnenberg JL, Hada M, Ehara M, Toyota K, Fukuda R, Hasegawa J, Ishida M, Nakajima T, Honda Y, Kitao O, Nakai H, Vreven T, Montgomery JA Jr, Peralta JE, Ogliaro F, Bearpark M, Heyd JJ, Brothers E, Kudin KN, Staroverov VN, Keith T, Kobayashi R, Normand J, Raghavachari K, Rendell A, Burant JC, Iyengar SS, Tomasi J, Cossi M, Rega N, Millam JM, Klene M, Knox JE, Cross JB, Bakken V, Adamo C, Jaramillo J, Gomperts R, Stratmann RE, Yazyev O, Austin AJ, Cammi R, Pomelli C, Ochterski JW, Martin RL, Morokuma K, Zakrzewski VG, Voth GA, Salvador P, Dannenberg JJ, Dapprich S, Daniels AD, Farkas O, Foresman JB, Ortiz JV, Cioslowski J, Fox DJ. Gaussian 09, revision B.01. Wallingford: Gaussian, Inc.; 2010.
Jarvis MW, Daily JW, Carstensen HH, Dean AM, Sharma S, Dayton DC, Robichaud DJ, Nimlos MR. Direct detection of products from the pyrolysis of 2-phenethyl phenyl ether. J Phys Chem A. 2011;115:428–38.
Mahadevan R, Adhikari S, Shakya R, Wang K, Dayton D, Lehrich M, Taylor SE. Effect of alkali and alkaline earth metals on in situ catalytic fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass: a microreactor study. Energy Fuels. 2016;30:3045–56.
Kleen M, Gellerstedt G. Influence of inorganic species on the formation of polysaccharide and lignin degradation products in the analytical pyrolysis of pulps. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis. 1995;35:15–41.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51576064, 51821004), Beijing Nova Program (Z171100001117064), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (3172030), Grants from Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation (161051), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2016YQ05 and 2018ZD08) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Xy., Lu, Q., Hu, B. et al. Influence of inherent alkali metal chlorides on pyrolysis mechanism of a lignin model dimer based on DFT study. J Therm Anal Calorim 137, 151–160 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7920-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7920-5