Abstract
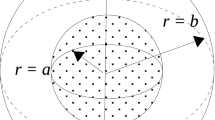
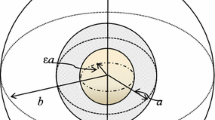
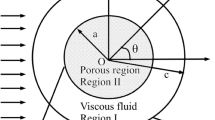
This paper concerns the Slow Motion of a Porous Cylindrical Shell in a concentric cylindrical cavity using particle-in-cell method. The Brinkman’s equation in the porous region and the Stokes equation for clear fluid in their stream function formulations are used. The hydrodynamic drag force acting on each porous cylindrical particle in a cell and permeability of membrane built up by cylindrical particles with a porous shell are evaluated. Four known boundary conditions on the hypothetical surface are considered and compared: Happel’s, Kuwabara’s, Kvashnin’s and Cunningham’s (Mehta-Morse’s condition). Some previous results for hydrodynamic drag force and dimensionless hydrodynamic permeability have been verified. Variation of the drag coefficient and dimensionless hydrodynamic permeability with permeability parameter σ, particle volume fraction γ has been studied and some new results are reported. The flow patterns through the regions have been analyzed by stream lines. Effect of particle volume fraction γ and permeability parameter σ on flow pattern is also discussed. In our opinion, these results will have significant contributions in studying, Stokes flow through cylindrical swarms.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ehlers W, Bluhm J (eds) (2002) Porous media, theory, experiments and numerical applications. Springer, Berlin. ISBN:3-540-43763-0
Happel J, Brenner H (1965) Low Reynolds number hydrodynamics with special applications to particulate media. Prentice-Hall, New York. Reprinted by Wolters-Nordhoff (1973); paperback edition, Martinus Nijhoff; Kluwer Academic Publishers (1983)
Uchida S (1954) Viscous flow in multiparticle systems: slow viscous flow through a mass of particles. Int Sci Technol Univ Tokyo 3:97 (in Japanese); (transl. by T. Motai) Abstract. Ind Eng Chem 46:1194–1195
Brenner H (1957) Eng. Sc. D. thesis, New York University
Deo S (2004) Stokes flow past a swarm of porous circular cylinder with Happel and Kuwabara boundary conditions. Sâdhana 29(4):381–387
Happel J (1959) Viscous flow relative to arrays of cylinders. AIChE 5(2):174–177
Kuwabara S (1959) The forces experienced by randomly distributed parallel circular cylinders or spheres in a viscous flow at small Reynolds number. J Phys Soc Jpn 14:527–532
Kvashnin AG (1979) Cell model of suspension of spherical particles. Fluid Dyn 14:598–602
Mehta GD, Morse TF (1975) Flow through charged membranes. J Chem Phys 63(5):1878–1889
Filippov AN, Vasin SI, Starov VM (2006) Mathematical modeling of the hydrodynamic permeability of a membrane built up from porous particles with a permeable shell. Colloids Surf A 282–283:272–278
Vasin SI, Filippov AN, Starov VM (2008) Hydrodynamic permeability of membranes built up by particles covered by porous shells: cell models. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 139:83–96
Stechkina IB (1979) Drag of porous cylinders in a viscous fluid at low Reynolds numbers. Fluid Dyn 14(6):912–915
Pop I, Cheng P (1992) Flow past a circular cylinder embedded in a porous medium based on the Brinkman model. Int J Eng Sci 30(2):257–262
Singh MP, Gupta JL (1971) The flow of a viscous fluid past an inhomogeneous porous cylinder. Z Angew Math Mech 54:17–25
Gupta JL (1980) Fluid motion past a porous circular cylinder with initial pressure gradient. J Appl Mech 47:489–492
Kaplun S (1957) Low Reynolds number flow past a circular cylinder. J Math Mech 6(5):585–603
Deo S (2004) Stokes flow past a swarm of porous circular cylinder with Happel and Kuwabara boundary conditions. Sâdhana 29(4):381–387
Ellero M, Kroger M, Hess S (2002) Viscoelastic flows studied by smoothed particle dynamics. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 105:35–51
Kim AS, Yuan R (2005) A new model for calculating specific resistance of aggregated colloidal cake layers in membrane filtration processes. J Membr Sci 249:89–101
Matthews MT, Hill JM (2006) Flow around nano spheres and nano cylinders. Q J Mech Appl Math 59(2):191–210
Palaniappan D, Archana K, Khan SK (1997) Two-dimensional creeping flows with permeable cylinders. Z Angew Math Mech 77(10):791–796
Datta S, Shukla M (2003) Drag on flow past a cylinder with slip. Bull Calcutta Math Soc 95(1):63–72
Qin Y, Kaloni PN (1988) A Cartesian-tensor solution of Brinkman equation. J Eng Math 22:177–188
Qin Y, Kaloni PN (1993) Creeping flow past a porous spherical shell. Z Angew Math Mech 77(2):77–84
Roux CL (2009) Flow of fluids with pressure dependent viscosities in an orthogonal rheometer subject to slip boundary conditions. Meccanica 44:71–83
Lok YY, Pop I, Ingham DB (2010) Oblique stagnation slip flow of a micropolar fluid. Meccanica 45:187–198
Deo S, Yadav PK (2008) Stokes flow past a swarm of porous nanocylindrical particles enclosing a solid core. Int J Math Math Sci. doi:10.1155/2008/651910. Article ID 651910 (published online)
Yadav PK, Deo S (2012) Stokes flow past a porous spheroid embedded in another porous medium. Meccanica 47:1499–1516
Prakash J, Raja Sekhar GP (2012) Arbitrary oscillatory Stokes flow past a porous sphere using Brinkman model. Meccanica 47(5):1079–1095
Vasin SI, Filippov AN (2009) Cell models for flows in concentrated media composed of rigid impermeable cylinders covered. Colloid J 71(2):141–155, 149–163
Deo S, Yadav PK, Tiwari A (2010) Slow viscous flow through a membrane built up from porous cylindrical particles with an impermeable core. Appl Math Model 34:1329–1343
Deo S, Filippov AN, Tiwari A, Vasin SI, Starov VM (2011) Hydrodynamic permeability of aggregates of porous particles with an impermeable core. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 164:21–27
Brinkman HC (1947) A calculation of viscous force exerted by a flowing fluid on a dense swarm of particles. J Appl Sci Res A 1:27–34
Abramowitz M, Stegun IA (1970) Handbook of mathematical functions. Dover, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Happel’s cell model


Kuwabara’s cell model


Kvashnin’s cell model


Cunningham/Mehta-Morse’s cell


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, P.K. Slow Motion of a Porous Cylindrical Shell in a concentric cylindrical cavity. Meccanica 48, 1607–1622 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-012-9689-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-012-9689-0