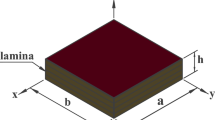
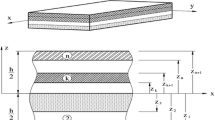
Two hyperbolic displacement models, HPSDT1 and HPSDT2, are developed for a bending analysis of orthotropic laminated composite plates. These models take into account the parabolic distribution of transverse shear stresses and satisfy the condition of zero shear stresses on the top and bottom surfaces of the plates. The accuracy of the analysis presented is demonstrated by comparing the results with solutions derived from other higher-order models and with data found in the literature. It is established that the HPSDT1 model is more accurate than some theories of laminates developed previously, and therefore the analysis can be expanded to laminated composite shells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Reissner, “The effect of transverse shear deformation on the bending of elastic plates,” J. Appl. Mech., 12, 69-77 (1945).
R. D. Mindlin, “Influence of rotatory inertia and shear on flexural motions of isotropic elastic plates,” J. Appl. Mech., 18, 31-38 (1951).
E. Reissner, “On the theory of bending of elastic plates,” J. Math. Phys., 23, 184-191 (1944).
Y. Nath and K. K. Shukla, “Non-linear transient analysis of moderately thick laminated composite plates,” J. Sound Vibrat., 247, No. 3, 509-526 (2001).
S. Hui-Shen, “Nonlinear bending of simply supported rectangular Reissner–Mindlin plates under transverse and in-plane loads and resting on elastic foundations,” Eng. Struct., 22, 847-856 (2000).
T. Kant and K. Swaminathan, “Analytical solutions for the static analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates based on a higher order refined theory,” Compos. Struct., 56, 329-344 (2002).
L. H. Donnel, “A theory for thick plates,” in: Proc. Second U.S. Nat. Congr. Appl. Mech., ASME Publ. Univ. Michigan, Michigan (1955), pp. 369-373.
E. Reissner, “On the derivation of boundary conditions for plate theory,” in: Proc. Roy. Soc. London, 276, Ser. A, No. 1364, 178-186 (1963).
K. H. Lo, R. M. Christensen, and E. M. Wu, “A higher-order theory of plate deformation. Pt. 1: Homogeneous plates,” ASME J. Appl. Mech., 44, 663-668 (1977).
K. H. Lo, R. M. Christensen, and E. M. Wu, “A higher-order theory of plate deformation. Pt. 2: Laminated plates,” ASME J. Appl. Mech., 44, 669-676 (1977).
M. Levinson, “An accurate simple theory of the statics and dynamics of elastic plates,” Mech. Res. Commun., No. 7, 343-350 (1980).
M. V. V. Murthy, An Improved Transverse Shear Deformation Theory for Laminated Anisotropic Plates, NASA Techn. Paper (1981), pp. 1-37.
J. N. Reddy, “A simple higher order theory for laminated composite plates,” J. Appl. Mech., 51, 745-752 (1984).
J. N. Reddy, “A refined nonlinear theory of plates with transverse shear deformation,” Int. J. Solids Struct., 20, No. 9, 881-896 (1984).
M. Touratier, “An efficient standard plate theory,” Int. J. Eng. Sci., 29, No. 8, 901-916 (1991).
K. P. Soldatos, “A transverse shear deformation theory for homogenous monoclinic plates,” Acta Mech., 94, Nos. 3-4, 1995-2200 (1992).
M. Karama, K. S. Afaq, and S. Mistou, “Mechanical behaviour of laminated composite beam by new multi-layered laminated composite structures model with transverse shear stress continuity,” Int. J. Solids Struct., 40, No. 6, 1525-1546 (2003).
A. J. M. Ferreira, C. M. C. Roque, and R. M. N. Jorge, “Analysis of composite plates by trigonometric shear deformation theory and multiquadrics,” Comput. Struct., 83, 225-2237 (2005).
A. Idlbi, M. Karama, and M. Touratier, “Comparison of various laminated plate theories,” Compos. Struct., 37, No. 2, 173-184 (1997).
H. Altenbach, “Theories for laminated and sandwich plates,” Mech. Compos. Mater., 34, No. 3, 243-252 (1998).
J. N. Reddy and C. M. Wang, “An overview of the relationships between solutions of the classical and shear deformation plate theories,” Compos. Sci. Technol., 60, 2327-2335 (2000).
N. J. Pagano and S. J. Hatfield, “Elastic behaviour of multilayered bidirectional composites,” AIAA J. Techn. Notes, 10, No. 7, 931-933 (1972).
N. J. Pagano, “Exact solutions for rectangular bidirectional composites and sandwich plates,” J. Compos. Mater., 4, 20-34 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Russian translation published in Mekhanika Kompozitnykh Materialov, Vol. 46, No. 2, pp. 311-326, March-April, 2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akavci, S.S. Two new hyperbolic shear displacement models for orthotropic laminated composite plates. Mech Compos Mater 46, 215–226 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-010-9140-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11029-010-9140-3