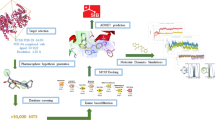
Abstract
PDE4 inhibitors have been largely studied because of their promising therapeutic effects concerning inflammation and neurodegenerative dysfunctions, such as depression, schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s diseases. In this context, the PDE4B isoform proved to be particularly involved in the activation of inflammatory responses, while the PDE4D subfamily is more associated with neuropathologies. The clinical use of PDE4 inhibitors was restricted by the presence of prominent side effects probably due to their non-specific action across the different isoforms. Therefore, this work deals with the development of 3D-QSAR models, supported by molecular docking studies, to identify the key requirements underlying selective PDE4B or PDE4D inhibition. The results highlighted the ligand-based approach as a promising tool to guide the rational design of novel PDE4 inhibitors endowed with high affinity and selectivity profiles.
Graphical Abstract
The alignment of compound 1–85 and the model A statistical results are depicted.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li L, Yee C, Beavo JA (1999) CD3- and CD28-dependent induction of PDE7 required for T cell activation. Science 283:848–851. doi:10.1126/science.283.5403.848
Dousa TP (1999) Cyclic-3\(^\prime \),5\(^\prime \)-nucleotide phosphodiesterases isoenzyme in cell biology and pathophysiology of the kidney. Kidney Int 55:29–62. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00233.x
Pfister C, Bennett N, Bruckert F, Catty P, Clerc A, Pages F, Deterre P (1993) Interactions of a G-protein with its effector: transducin and cGMP phosphodiesterase in retinal rods. Cell Signal 5:235–241. doi:10.1016/0898-6568(93)90015-E
Jin SL, Richard FJ, Kuo WP, D’Ercole AJ, Conti M (1999) Impaired growth and fertility of c-AMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE4D-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:11998–12003. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.21.11998
Bender AT, Beavo JA (2006) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: molecular regulation to clinical use. Pharmacol Rev 58:488–520. doi:10.1124/pr.58.3.5
Manganiello VC, Murata T, Taira M, Belfrage P, Degerman E (1995) Diversity in cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isoenzyme families. Arch Biochem Biophys 322:1–13. doi:10.1006/abbi.1995.1429
Lugnier C (2006) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) superfamily: a new target for the development of specific therapeutic agents. Pharmacol Ther 109:366–398. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2005.07.003
Omori K, Kotera J (2007) Overview of PDEs and their regulation. Circ Res 100:309–327. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000256354.95791.f1
Conti M, Beavo J (2007) Biochemistry and physiology of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases: essential components in cyclic nucleotide signaling. Annu Rev Biochem 76:481–511. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.060305.150444
Houslay MD, Baillie GS, Maurice DH (2007) cAMP-Specific phosphodiesterase-4 enzymes in the cardiovascular system: a molecular toolbox for generating compartmentalized cAMP signaling. Circ Res 100:950–966. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000261934.56938.38
Houslay MD, Adams RD (2003) PDE4 cAMP phosphodiesterases: modular enzymes that orchestrate signalling cross-talk, desensitization and compartmentalization. Biochem J 370:1–18. doi:10.1042/BJ20021698
Page GP, Spina D (2011) Phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Handb Exp Pharmacol 204:391–414. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-17969-3_17
Conti M, Iona S, Cuomo M, Swinnen JV, Odeh J, Svoboda ME (1995) Characterization of a hormone-inducible, high affinity adenosine 3\(^\prime \)-5\(^\prime \)-cyclic monophosphate phosphodiesterase from the rat Sertoli cell. Biochemistry 34:7979–7987. doi:10.1021/bi00025a003
Houslay MD (2001) PDE4 cAMP-specific phosphodiesterases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 69:249–315. doi:10.1016/S0079-6603(01)69049-4
Beard MB, Olsen AE, Jones RE, Erdogan S, Houslayan MD, Bolger GB (2000) UCR1 and UCR2 domains unique to the cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase family form a discrete module via electrostatic interactions. J Biol Chem 275:10349–10358. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.14.10349
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res 28:235–242. doi:10.1093/nar/28.1.235
Wang H, Liu Y, Hou J, Zheng M, Robinson H, Ke H (2007) Structural insight into substrate specificity of phosphodiestererase 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5782–5787. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700279104
Card GL, England BP, Suzuki Y, Fong D, Powell B, Lee B, Luu C, Tabrizizad M, Gillette S, Ibrahim PN, Artis DR, Bollag G, Milburn MV, Kim SH, Sclessinger J, Zhang KY (2004) Structural basis for the activity of drugs that inhibit phosphodiesterases. Structure 12:2233–2247. doi:10.1016/j.str.2004.10.004
Burgin AB, Magnusson OT, Singh J, Witte P, Staker BL, Bjornsson JM, Thorsteinsdottir M, Hrafnsdottir S, Hagen T, Kiselyov AS, Stewart LJ, Gurney ME (2010) Design of phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D) allosteric modulators for enhancing cognition with improved safety. Nat Biotechnol 28:63–70. doi:10.1038/nbt.1598
Fox D, Burgin AB, Gurney ME (2014) Structural basis for the design of selective phosphodiesterase 4B inhibitors. Cell Signal 26:657–663. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.12.003
Gurney ME, Burgin AB, Magnusson OT, Stewart LJ (2011) Small molecule allosteric modulators of phosphodiesterase 4. Handb Exp Pharmacol 204:167–192. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-17969-3_7
Lipworth BJ (2005) Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors for asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 365:167–175. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17708-3
Houslay MD, Schafer P, Zhang KYJ (2005) Phosphodiesterase-4 as a therapeutic target. Drug Discov Today 10:1503–1519. doi:10.1016/S1359-6446(05)03622-6
Lerner A, Epstein PM (2006) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases as targets for treatment of haematological malignancies. Biochem J 393:21–41. doi:10.1042/BJ20051368
Huang Z, Mancini JA (2006) Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors for the treatment of asthma and COPD. Curr Med Chem 13:3253–3263. doi:10.2174/092986706778773040
Ariga M, Neitzert B, Nakae S, Mottin G, Bertrand C, Pruniaux MP, Jin SL, Conti M (2004) Nonredudant function of phosphodiesterases 4D and 4B in neutrophil recruitment to the site of inflammation. J Immunol 173:7531–7538. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.173.12.7531
Jin SL, Lan L, Zoudilova M, Conti M (2005) Specific role of phosphodiesterase 4B in lipopolysaccharide-induced signaling in mouse macrophages. J Immunol 175:1523–1531. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.175.3.1523
Gurney ME, D’Amato EC, Burgin AB (2015) Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) molecular pharmacology and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 12:49–56. doi:10.1007/s13311-014-0309-7
Brooks M (21 March 2014) FDA clears apremilast (Otezla) for psoriatic arthritis. Medscape Medical News (WebMD). http://www.medscape.com. Retrieved 28 March 2014
Peter D, Jin SL, Conti M, Hatzelmann A, Zitt C (2007) Differential expression and function of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) subtypes in human primary CD4+ T cells: predominant role of PDE4D. J Immunol 178:4820–4831. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.178.8.4820
O’Donnell JM, Zhang HT (2004) Antidepressant effects of inhibitors of cAMP phosphodiesterase (PDE4). Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:158–163. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2004.01.003
Kanes SJ, Tokarczyk SJ, Bilker W, Abel T, Kelly MP (2007) Rolipram: a specific phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor with potential antipsychotic activity. Neuroscience 144:239–246. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.09.026
Robichaud A, Stamatiou PB, Jin SL, Lachance N, MacDonald D, Laliberte F, Liu S, Huang Z (2002) Adrenoceptor-mediated anesthesia, a behavioral correlate of emesis. J Clin Invest 110:1045–1052. doi:10.1172/JCI15506
Li YF, Cheng YF, Huang Y, Conti M, Wilson SP, O’Donnell JM, Zhang HT (2011) Phosphodiesterase-4D knock-out and RNA interference-mediated knock-down enhance memory and increase hippocampal neurogenesis via increased cAMP signaling. J Neurosci 31:172–183. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5236-10.2011
Bruno O, Fedele E, Prickaerts J, Parker LA, Canepa E, Brullo C, Cavallero A, Gardella E, Balbi A, Domenicotti C, Bollen E, Gijselaers HJ, Vanmierlo T, Erb K, Limebeer CL, Argellati F, Marinari UM, Pronzato MA, Ricciarelli R (2011) GEBR-7b, a novel PDE4D selective inhibitor that improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses. Br J Pharmacol 164:2054–2063. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01524.x
Sierksma AS, Van den Hove DL, Pfau F, Philippens M, Bruno O, Fedele E, Ricciarelli R, Steinbusch HW, Van Mierlo T, Prickaerts J (2014) Improvement of spatial memory function in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice after chronic inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 4D. Neuropharmacology 77:120–130. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.09.015
Srivani P, Usharani D, Jemmis ED, Sastry GN (2008) Subtype selectivity in phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4): a bottleneck in rational drug design. Curr Pharm Des 14:3854–3872. doi:10.2174/138161208786898653
Cichero E, Cesarini S, Fossa P, Spallarossa A, Mosti L (2009) Thiocarbamates as non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors: docking-based CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses. Eur J Med Chem 44:2059–2070. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2008.10.014
Cichero E, Cesarini S, Fossa P, Spallarossa A, Mosti L (2009) Acylthiocarbamates as non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors: docking studies and ligand-based CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses. J Mol Model 15:871–884. doi:10.1007/s00894-008-0441-6
Cichero E, Fossa P (2012) Docking-based 3D-QSAR analyses of pyrazole derivatives as HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Mol Model 18:1153–1582. doi:10.1007/s00894-011-1190-5
Cichero E, Bruno O, Fossa P (2011) Docking-based CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses of tetrahydro-\(\beta \)-carboline derivatives as type-5 phosphodiesterase inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 27:730–743. doi:10.3109/14756366.2011.611136
Bhansali SG, Kulkarni VM (2014) Combined 2D and 3D-QSAR, molecular modelling and docking studies of pyrazolodiazepinones as novel phosphodiesterase 2 inhibitors. SAR QSAR Environ Res 25:905–937. doi:10.1080/1062936X.2014.969309
Patel SR, Gangwal R, Sangamwar AT, Jain R (2015) Synthesis, biological evaluation and 3D QSAR study of 2,4-disubstituted quinolines as anti-tuberculosis agents. Eur J Med Chem 93:511–522. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.02.034
Mella-Raipán J, Hernández-Pino S, Morales-Verdejo C, Pessoa-Mahana D (2014) 3D-QSAR/CoMFA-based structure-affinity/selectivity relationships of aminoalkylindoles in the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Molecules 19:2842–2861. doi:10.3390/molecules19032842
Naganuma K, Omura A, Maekawara N, Saitoh M, Ohkawa N, Kubota T, Nagumo H, Kodama T, Takemura M, Ohtsuka Y, Nakamura J, Tsujita R, Kawasaki K, Yokoi H, Kawanishi (2009) Discovery of selective PDE4B inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:3174–3176. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.04.121
Hagen TJ, Mo X, Burgin AB, Fox D 3rd, Zhang Z, Gurney ME (2014) Discovery of triazines as selective PDE4B versus PDE4D inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24:4031–4034. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.06.002
Goto T, Shiina A, Murata T, Tomii M, Yamazaki T, Yoshida K, Yoshino T, Suzuki O, Sogawa Y, Mizukami K, Takagi N, Yoshitomi T, Etori M, Tsuchida H, Mikkaichi T, Nakao N, Takahashi M, Takahashi H, Sasaki S (2014) Identification of the 5,5-dioxo-7,8-dihydro-6H-thiopyrano[3,2-d] pyrimidine derivatives as highly selective PDE4B inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 24:893–899. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.12.076
MOE: Chemical Computing Group Inc., Montreal. http://www.chemcomp.com
Cramer RD III, Patterson DE, Bunce JD (1988) Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J Am Chem Soc 110:5959–5967. doi:10.1021/ja00226a005
Sybyl-X 1.0. Tripos Inc., St. Louis
Cichero E, Ligresti A, Allarà M, Di Marzo V, Lazzati Z, D’Ursi P, Marabotti A, Milanesi L, Spallarossa A, Ranise A, Fossa P (2011) Homology modeling in tandem with 3D-QSAR analyses: a computational approach to depict the agonist binding site of the human CB2 receptor. Eur J Med Chem 46:4489–4505. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2011.07.023
Cichero E, Buffa L, Fossa P (2011) 3,4,5-Trisubstituted-1,2,4–4H-triazoles as WT and Y188L mutant HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: docking-based CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses. J Mol Model 7:1537–1550. doi:10.1007/s00894-010-0857-7
Cichero E, Cesarini S, Mosti L, Fossa P (2010) CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses on 1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrrolo[3,4-b]indole and benzimidazole derivatives as selective CB2 receptor agonists. J Mol Model 16:1481–1498. doi:10.1007/s00894-010-0664-1
Cichero E, Cesarini S, Mosti L, Fossa P (2010) CoMFA and CoMSIA analyses on 4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline and 4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-1,5-, -1,6- and -1,8-naphthyridine derivatives as selective CB2 receptor agonists. J Mol Model 16:677–691. doi:10.1007/s00894-009-0580-4
Jain AN (1996) Scoring noncovalent protein-ligand interactions: a continuous differentiable function tuned to compute binding affinities. J Comput Aided Mol Des 10:427–440. doi:10.1007/BF00124474
Aspiotis R, Deschenes D, Dubè D, Girard Y, Huang Z, Lalibertè F, Liu S, Pappa R, Nicholson DW, Young RN (2010) The discovery and synthesis of highly potent subtype selective phosphodiesterase 4D inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:5502–5505. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.07.076
Acknowledgments
The University of Genoa financially supported this work. Authors would like to thank Mr. V. Ruocco for the informatics support to calculations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guariento, S., Bruno, O., Fossa, P. et al. New insights into PDE4B inhibitor selectivity: CoMFA analyses and molecular docking studies. Mol Divers 20, 77–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-015-9631-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-015-9631-1