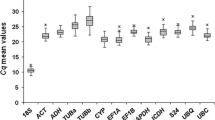
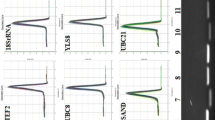
Abstract
Accuracy in quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) requires the use of stable endogenous controls. Normalization with multiple reference genes is the gold standard, but their identification is a laborious task, especially in species with limited sequence information. Coffee (Coffea ssp.) is an important agricultural commodity and, due to its economic relevance, is the subject of increasing research in genetics and biotechnology, in which gene expression analysis is one of the most important fields. Notwithstanding, relatively few works have focused on the analysis of gene expression in coffee. Moreover, most of these works have used less accurate techniques such as northern blot assays instead of more accurate techniques (e.g., qPCR) that have already been extensively used in other plant species. Aiming to boost the use of qPCR in studies of gene expression in coffee, we uncovered reference genes to be used in a number of different experimental conditions. Using two distinct algorithms implemented by geNorm and Norm Finder, we evaluated a total of eight candidate reference genes (psaB, PP2A, AP47, S24, GAPDH, rpl39, UBQ10, and UBI9) in four different experimental sets (control versus drought-stressed leaves, control versus drought-stressed roots, leaves of three different coffee cultivars, and four different coffee organs). The most suitable combination of reference genes was indicated in each experimental set for use as internal control for reliable qPCR data normalization. This study also provides useful guidelines for reference gene selection for researchers working with coffee plant samples under conditions other than those tested here.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
Brunner A, Yakovlev I, Strauss S (2004) Validating internal controls for quantitative plant gene expression studies. BMC Plant Biol 4:14. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-4-14
Czechowski T, Stitt M, Altmann T, Udvardi MK, Scheible WR (2005) Genome-wide identification and testing of superior reference genes for transcript normalization in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:5–17. doi:10.1104/pp.105.063743
Defilippi BG, Kader AA, Dandekar AM (2005) Apple aroma: alcohol acyltransferase, a rate limiting step for ester biosynthesis, is regulated by ethylene. Plant Sci 168:1199–1210. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2004.12.018
Etienne H, Anthony F, Dussert S, Fernandez D, Lashermes P, Bertrand B (2002) Biotechnological applications for the improvement of coffee (Coffea arabica L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 38:129–138. doi:10.1079/IVP2001273
FAOSTAT (2008) http://faostat.fao.org/site/406/default.aspx. Accessed date 7 Oct 2008
Fernandez D, Santos P, Agostini C, Bon MC, Petitot AS, Silva MC, Guerra-Guimaraes L, Ribeiro A, Argout X, Nicole M (2004) Coffee (Coffea arabica L.) genes early expressed during infection by the rust fungus (Hemileia vastatrix). Mol Plant Pathol 5:527–536. doi:10.1111/j.1364-3703.2004.00250.x
Frost P, Nilsen F (2003) Validation of reference genes for transcription profiling in the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, by quantitative real-time PCR. Vet Parasitol 118:169–174. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2003.09.020
Gachon C, Mingam A, Charrier B (2004) Real-time PCR: what relevance to plant studies? J Exp Bot 55:1445–1454. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh181
Ganesh D, Petitot AS, Silva MC, Alary R, Lecouls AC, Fernandez D (2006) Monitoring of the early molecular resistance responses of coffee (Coffea arabica L.) to the rust fungus (Hemileia vastatrix) using real-time quantitative RT-PCR. Plant Sci 170:1045–1051. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2005.12.009
Hellemans J, Mortier G, De Paepe A, Speleman F, Vandesompele J (2007) qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol 8:R19. doi:10.1186/gb-2007-8-2-r19
Huggett J, Dheda K, Bustin S, Zumla A (2005) Real-time RT-PCR normalisation; strategies and considerations. Genes Immun 6:279–284. doi:10.1038/sj.gene.6364190
Lepelley M, Cheminade G, Tremillon N, Simkin A, Caillet V, McCarthy J (2007) Chlorogenic acid synthesis in coffee: an analysis of CGA content and real-time RT-PCR expression of HCT, HQT, C3H1, and CCoAOMT1 genes during grain development in C. canephora. Plant Sci 172:978–996. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.02.004
Lin CW, Mueller LA, Mc Carthy J, Crouzillat D, Petiard V, Tanksley SD (2005) Coffee and tomato share common gene repertoires as revealed by deep sequencing of seed and cherry transcripts. Theor Appl Genet 112:114–130. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0112-2
Mueller LA, Solow TH, Taylor N, Skwarecki B, Buels R, Binns J, Lin C, Wright MH, Ahrens R, Wang Y, Herbst EV, Keyder ER, Menda N, Zamir D, Tanksley SD (2005) The SOL Genomics Network. A comparative resource for Solanaceae biology and beyond. plant physiol 138:1310–1317. doi:10.1104/pp.105.060707
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: bestkeeper—excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26:509–515. doi:10.1023/B:BILE.0000019559.84305.47
Poncet V, Rondeau M, Tranchant C, Cayrel A, Hamon S, de Kochko A, Hamon P (2006) SSR mining in coffee tree EST databases: potential use of EST-SSRs as markers for the Coffea genus. Mol Genet Genomics 276:436–449. doi:10.1007/s00438-006-0153-5
Pre M, Caillet V, Sobilo J, McCarthy J (2008) Characterization and expression analysis of genes directing galactomannan synthesis in coffee. Ann Bot (London) 102:207–220. doi:10.1093/aob/mcn076
Privat I, Foucrier S, Prins A, Epalle T, Eychenne M, Kandalaft L, Caillet V, Lin C, Tanksley S, Foyer C, McCarthy J (2008) Differential regulation of grain sucrose accumulation and metabolism in Coffea arabica (Arabica) and Coffea canephora (Robusta) revealed through gene expression and enzyme activity analysis. New Phytol 178:781–797. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02425.x
Reid KE, Olsson N, Schlosser J, Peng F, Lund ST (2006) An optimized grapevine RNA isolation procedure and statistical determination of reference genes for real-time RT-PCR during berry development. BMC Plant Biol 6:27. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-6-27
Remans T, Smeets K, Opdenakker K, Mathijsen D, Vangronsveld J, Cuypers A (2008) Normalisation of real-time RT-PCR gene expression measurements in Arabidopsis thaliana exposed to increased metal concentrations. Planta 227:1343–1349. doi:10.1007/s00425-008-0706-4
Robinson TL, Sutherland IA, Sutherland J (2007) Validation of candidate bovine reference genes for use with real-time PCR. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 115:160–165. doi:10.1016/j.vetimm.2006.09.012
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386
Salmona J, Dussert S, Descroix F, de Kochko A, Bertrand B, Joet T (2008) Deciphering transcriptional networks that govern Coffea arabica seed development using combined cDNA array and real-time RT-PCR approaches. Plant Mol Biol 66:105–124. doi:10.1007/s11103-007-9256-6
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA (2000) Effect of experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: validation by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. J Biochem Biophys Methods 46:69–81. doi:10.1016/S0165-022X(00)00129-9
Simkin AJ, Qian TZ, Caillet V, Michoux F, Ben Amor M, Lin CW, Tanksley S, McCarthy J (2006) Oleosin gene family of Coffea canephora: quantitative expression analysis of five oleosin genes in developing and germinating coffee grain. J Plant Physiol 163:691–708. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2005.11.008
Simkin AJ, Moreau H, Kuntz M, Pagny G, Lin C, Tanksley S, McCarthy J (2008) An investigation of carotenoid biosynthesis in Coffea canephora and Coffea arabica. J Plant Physiol 165:1087–1106. doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2007.06.016
Udvardi MK, Czechowski T, Scheible W-R (2008) Eleven golden rules of quantitative RT-PCR. Plant Cell 20:1736–1737. doi:10.1105/tpc.108.061143
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:7. doi:10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Vieira LGE, Andrade AC, Colombo CA, AHdA Moraes, Metha Â, ACd Oliveira, Labate CA, Marino CL, CdB Monteiro-Vitorello, DdC Monte, Giglioti É, Kimura ET, Romano E, Kuramae EE, Lemos EGM, ERPd Almeida, Jorge ÉC, Albuquerque ÉVS, FRd Silva, Vinecky F, Sawazaki HE, Dorry HFA, Carrer H, Abreu IN, Batista JAN, Teixeira JB, Kitajima JP, Xavier KG, LMd Lima, LEAd Camargo, Pereira LFP, Coutinho LL, Lemos MVF, Romano MR, Machado MA, MMdC Costa, MFGd Sá, Goldman MHS, Ferro MIT, Tinoco MLP, Oliveira MC, Van Sluys M-A, Shimizu MM, Maluf MP, MTSd Eira, Guerreiro Filho O, Arruda P, Mazzafera P, Mariani PDSC, RLBCd Oliveira, Harakava R, Balbao SF, Tsai SM, SMZd Mauro, Santos SN, Siqueira WJ, Costa GGL, Formighieri EF, Carazzolle MF, Pereira GAG (2006) Brazilian coffee genome project: an EST-based genomic resource. Braz J Plant Physiol 18:95–108
Zhao S, Fernald RD (2005) Comprehensive algorithm for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. J Comput Biol 12:1047–1064. doi:10.1089/cmb.2005.12.1047
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Fatima Barbosa, Luiz Frade, and Sarah Muniz Nardeli for technical assistance; to Bruna Matta M.Sc. for help with data management and analysis; to Adriana Martinelli Ph.D., Erica D.,Silveira M.Sc., and Ute Achenbach Ph.D. for comments on the manuscript; and to Eduardo Arcoverde Ph.D. for help with the Scholander-type pressure chamber. This work is part of Fernanda Cruz’s Ph.D. thesis in Department of Genetics, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—CNPQ (grants no. 310254/2007-8 to M.A.-F.), the Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro—FAPERJ (grant no. E-26/102.861/2008 to M.A.-F.), the International Foundation of Science (grant no.C/3962-1 to M.A.-F.), and the International Basic Science Program (grant no. IBSP/UNESCO-3-BR-28 to M.A.-F.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11032_2009_9259_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences and efficiencies estimated by the Miner software. Independent efficiencies ± standard deviation (SD) were calculated for every different experimental situation evaluated (DOC 42 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cruz, F., Kalaoun, S., Nobile, P. et al. Evaluation of coffee reference genes for relative expression studies by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Mol Breeding 23, 607–616 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9259-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-009-9259-x