Abstract
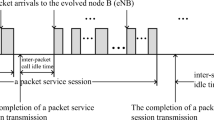
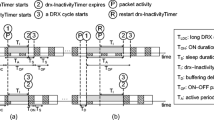
This paper investigates the power saving mechanism of Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS). UMTS discontinuous reception (DRX) is exercised between the network and a mobile station (MS) to save the power of the MS. The DRX mechanism is controlled by two parameters: the inactivity timer threshold t I and the DRX cycle t D . Analytic analysis and simulation model are proposed to study the optimal t I and t D selections that maximize the MS power saving under the given mean packet waiting time constraint. We also devise an adaptive algorithm called dynamic DRX (DDRX). This algorithm dynamically adjusts the t I and t D values to enhance the performance of UMTS DRX. Our study quantitatively shows how to select the best inactivity timer and DRX cycle values for various traffic patterns. We also show that DDRX nicely captures the user traffic patterns, and always adjusts the t I and t D close to the optimal values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
3GPP (2000) 3rd generation partnership project, Technical specification group radio access network, RRC protocol specification for release 1999. Technical specification 3G TS 25.331 version 3.5.0 (2000-12)
3GPP (2000) 3rd generation partnership project, Technical specification group services and systems aspects, General packet radio service (GPRS), service description, stage 2. Technical specification 3G TS 23.060 version 3.6.0 (2001-01)
3GPP (2001) 3rd generation partnership project, Technical specification group radio access network, UTRA high speed downlink packet access. Technical specification 3G TR 25.950 version 4.0.0 (2001-03)
3GPP (2002) 3rd generation partnership project, Technical specification group radio access network, UE procedures in idle mode and procedures for cell reselection in connected mode. Technical specification 3G TS 25.304 version 5.1.0 (2002-06)
CDPD Forum (January 1995) Cellular digital packet data system specification: release 1.1. Technical report. CDPD Forum, Chicago, IL
Chlamtac I, Fang Y, Zeng, H (1999) Call blocking analysis for PCS networks under general cell residence time. In: IEEE Wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC), New Orleans, September 1999
Fang Y, Chlamtac I (July 1999) Teletraffic analysis and mobility modeling for PCS networks. IEEE Trans Commun 47(7):1062–1072
Fang Y, Chlamtac I, Fei H-B (June 2000) Analytical results for optimal choice of location update interval for mobility database failure restoration in PCS networks. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst 11(6):615–624
Holma H, Toskala A (2000) WCDMA for UMTS. New York, Wiley
IEEE (April 1996) Wireless medium access control (MAC) and Physical layer (PHY) specifications. Draft standard 802.11 D3.1
Kelly FP (1979) Reversibility and stochastic networks. New York, Wiley
Kwon SJ, Chung YW, Sung DK (July 2003) Queueing model of sleep-mode operation in cellular digital packet data. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 52(4):1158–1162
Lin Y-B (1996) Estimating the likelihood of success of lazy cancellation in time warp simulations. Inter J Comput Simul 6(2):163–174
Lin Y-B, Chlamtac I (2001) Wireless and mobile network architectures. New York, Wiley
Lin Y-B, Chuang Y-M (March 1999) Modeling the sleep mode for cellular digital packet data. IEEE Commun Lett 3(3):63–65
Maron MJ, Lopez RJ (1991) Numerical analysis a practical approach, 3rd edn. Wadsworth, Belmont, CA
RAM Mobile Data (1994) Mobitex interface specification. Technical report. RAM Mobile Data
Salkintzis AK, Chamzas C (September 1998) An in-band power-saving protocol for mobile data networks. IEEE Trans Commun 46(9):1194–1205
Salkintzis AK, Chamzas C (May 2000) Performance analysis of a downlink MAC protocol with power-saving support. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 49(3):1029–1040
Salkintzis AK, Chamzas C (September 2002) An outband paging protocol for energy-efficient mobile communications. IEEE Trans Broadcast 48(3):246–256
Takagi H (1991) Queueing analysis—volume 1: vacation and priority systems, part 1. The Netherlands, Amsterdam
Yang S-R, Lin Y-B (November 2003) Performance evaluation of location management in UMTS. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 52(6):1603–1615
Yang S-R, Lin Y-B (January 2005) Modeling UMTS discontinuous reception mechanism. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 4(1):312–319
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, SR. Dynamic Power Saving Mechanism for 3G UMTS System. Mobile Netw Appl 12, 5–14 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-006-0002-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-006-0002-0