Abstract
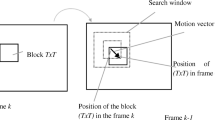
The present paper focuses on high-accuracy block-based sub-pixel motion estimation utilizing a straightforward error minimization approach. In particular, the mathematics of bilinear interpolation are utilized for the selection of the candidate motion vectors that minimize the error criterion, by estimating local minima in the error surface with arbitrary accuracy. The implemented approach favors optimum accuracy over computational load demands, making it ideal as a benchmark for faster methods to compare against; however, it is not best suited to real-time critical applications (i.e. video compression). Other video processing needs relying on motion vectors and requiring high-resolution/accuracy can also take advantage of the proposed solution (and its simplified nature in terms of underlying theoretical complexity), such as motion-compensation filtering for super resolution image enhancement, motion analysis in sensitive areas (e.g. high-speed video monitoring, medical imaging, motion analysis in sport science, big-data visual surveillance, etc.). The proposed method is thoroughly evaluated using both real video and synthetic motion sequences from still images, adopting well-tested block-based motion estimation evaluation procedures. Assessment includes comparisons to a number of existing block-based methods with respect to PSNR and SSIM metrics over ground-truth samples. The conducted evaluation takes into consideration both the original (arbitrary-accuracy) and the truncated motion vectors (after rounding them to the nearest half, quarter, or eighth of a pixel), where superior performance with more accurate motion vector estimation is revealed. In this context, the degree to which sub-pixel motion estimation methods actually produce sub-pixel motion vectors is investigated, and the implications thereof are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdou IE (1998) Practical approach to the registration of multiple frames of video images. In: Electronic Imaging'99. International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 371–382. doi:10.1117/12.334685
Argyriou V, Vlachos T (2003) Sub-pixel motion estimation using gradient cross-correlation. In: Signal Processing and Its Applications. Proceedings. Seventh International Symposium on, Jul. 2003. IEEE, pp 215–218. doi:10.1109/ISSPA.2003.1224852
Argyriou V, Vlachos T (2004) Using gradient correlation for sub-pixel motion estimation of video sequences. In: Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing. Proceedings.(ICASSP'04). IEEE International Conference on, May 2004. IEEE, pp iii-329-332 vol 323. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2004.1326548
Argyriou V, Vlachos T (2005) Performance study of gradient correlation for sub-pixel motion estimation in the frequency domain. IEE Proceedings-Vision, Image and Signal Processing 152(1):107–114. doi:10.1049/ip-vis:20051073
Argyriou V, Vlachos T A (2006) Study of sub-pixel motion estimation using phase correlation. In: BMVC. Citeseer, pp 387–396
Barron JL, Fleet DJ, Beauchemin SS (1994) Performance of optical flow techniques. Int J Comput Vis 12(1):43–77. doi:10.1007/BF01420984
Bovik AC (2010) Handbook of image and video processing. Academic press
Brehm M, Paysan P, Oelhafen M, Kachelrieß M (2013) Artifact-resistant motion estimation with a patient-specific artifact model for motion-compensated cone-beam CT. Med Phys 40(10):101913. doi:10.1118/1.4820537
Brox T, Bruhn A, Papenberg N, Weickert J (2004) High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In: European conference on computer vision. Springer, pp 25–36. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-24673-2_3
Chen Z (2009) Efficient block matching algorithm for motion estimation. International Journal of Signal Processing 5(2):133–137
Cheng F-H, Sun S-N (1999) New fast and efficient two-step search algorithm for block motion estimation. Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, IEEE Transactions on 9(7):977–983. doi:10.1109/76.795049
Chi YM, Tran TD Etienne-Cummings R (2007) Optical flow approximation of sub-pixel accurate block matching for video coding. In: Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. ICASSP 2007. IEEE International Conference on, Apr. 2007. IEEE, pp I-1017-I-1020. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2007.366083
Chi YM, Tran TD, Etienne-Cummings R (2007) Optical flow approximation of sub-pixel accurate block matching for video coding. In: 2007 I.E. International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing-ICASSP'07. IEEE, pp I-1017-I-1020. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2007.366083
Davis CQ, Karul Z, Freeman DM (1995) Equivalence of subpixel motion estimators based on optical flow and block matching. In: Computer Vision, Proceedings., International Symposium on, Nov 1995. IEEE, pp 7–12. doi:10.1109/ISCV.1995.476969
Dimoulas C, Avdelidis K, Kalliris G, Papanikolaou G (2008) Joint wavelet video denoising and motion activity detection in multimodal human activity analysis: application to video-assisted bioacoustic/psychophysiological monitoring. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing 2008:34. doi:10.1155/2008/792028
Dimoulas CA, Kalliris GM, Chatzara EG, Tsipas NK, Papanikolaou GV (2014) Audiovisual production, restoration-archiving and content management methods to preserve local tradition and folkloric heritage. J Cult Herit 15(3):234–241. doi:10.1016/j.culher.2013.05.003
Dufaux F, Moscheni F (1995) Motion estimation techniques for digital TV: a review and a new contribution. Proc IEEE 83(6):858–876. doi:10.1109/5.387089
Faires JD, Burden R (2002) Numerical methods. 3rd edn. Brooks Cole
Foroosh H, Zerubia JB, Berthod M (2002) Extension of phase correlation to subpixel registration. Image Processing, IEEE Transactions on 11(3):188–200. doi:10.1109/83.988953
Hoge WS (2003) A subspace identification extension to the phase correlation method [MRI application]. Medical Imaging, IEEE Transactions on 22(2):277–280. doi:10.1109/TMI.2002.808359
Hu J, Luo Y (2015) Noise-robust video super-resolution using an adaptive spatial-temporal filter. Multimedia Tools and Applications 74(21):9259–9278. doi:10.1007/s11042-014-2079-y
Jeong J (2003) Fast sub-pixel motion estimation having lower complexity. In: Consumer Electronics. ICCE. 2003 I.E. International Conference on, Jun. 2003. IEEE, pp 174–175. doi:10.1109/ICCE.2003.1218867
Keren D, Peleg S, Brada R (1988) Image sequence enhancement using sub-pixel displacements. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Proceedings CVPR'88., Computer Society Conference on, Jun. 1988. IEEE, pp 742–746. doi:10.1109/CVPR.1988.196317
Kwon DN, Agathoklis P, Driessen P (2005) Sub-pixel accuracy motion estimation using linear approximate model of the error criterion function. In: Communications, Computers and signal Processing. PACRIM. 2005 I.E. Pacific Rim Conference on, Aug. 2005. IEEE, pp 261–264. doi:10.1109/PACRIM.2005.1517275
Larson R, Edwards BH (2010) Calculus. Brooks/Cole
Lee VR (2015) Combining high-speed cameras and stop-motion animation software to support students’ modeling of human body movement. J Sci Educ Technol 24(2–3):178–191. doi:10.1007/s10956-014-9521-9
Li X, Gonzales C (1996) A locally quadratic model of the motion estimation error criterion function and its application to subpixel interpolations. Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, IEEE Transactions on 6(1):118–122. doi:10.1109/76.486427
Lucas BD, Kanade T (1981) An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In: IJCAI, pp 674–679
Magarey JF, Kingsbury NG (1996) Motion estimation using complex wavelets. In: SPIE's 1996 International Symposium on Optical Science, Engineering, and Instrumentation. International Society for Optics and Photonics, pp 674–685. doi:10.1117/12.255276
Marti-Puig P, Rodríguez S, De Paz JF, Reig-Bolaño R, Rubio MP, Bajo J (2012) Stereo video surveillance multi-agent system: new solutions for human motion analysis. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision 42(2–3):176–195. doi:10.1007/s10851-011-0290-2
Ng AC, Zeng B (1998) A new fast motion estimation algorithm based on search window sub-sampling and object boundary pixel block matching. In: Image Processing. ICIP 98. Proceedings. 1998 International Conference on, Oct. 1998. IEEE, pp 605–608. doi:10.1109/ICIP.1998.727336
Ouji K, Ardabilian M, Chen L, Ghorbel F (2013) 3D deformable super-resolution for multi-camera 3D face scanning. Journal of mathematical imaging and vision 47(1–2):124–137. doi:10.1007/s10851-012-0399-y
Park SC, Park MK, Kang MG (2003) Super-resolution image reconstruction: a technical overview. Signal Processing Magazine, IEEE 20(3):21–36. doi:10.1109/MSP.2003.1203207
Porto M, Cristani C, Dall’Oglio P, Grellert M, Mattos J, Bampi S, Agostini L (2013) Iterative random search: a new local minima resistant algorithm for motion estimation in high-definition videos. Multimedia tools and applications 63(1):107–127. doi:10.1007/s11042-012-1033-0
Ren J, Jiang J, Vlachos T (2010) High-accuracy sub-pixel motion estimation from noisy images in Fourier domain. Image Processing, IEEE Transactions on 19(5):1379–1384. doi:10.1109/TIP.2009.2039056
Sayed M, Badawy W, Jullien G (2009) Low-complexity algorithm for fractional-pixel motion estimation. In: Image Processing (ICIP) 16th IEEE International Conference on, Nov. 2009. IEEE, pp 1565–1568. doi:10.1109/ICIP.2009.5414600
Scharcanski J, Schardosim L, Santos D, Stuchi A (2013) Motion detection and compensation in infrared retinal image sequences. Comput Med Imaging Graph 37(5):377–385. doi:10.1016/j.compmedimag.2013.06.004
Schultz RR, Meng L, Stevenson RL (1998) Subpixel motion estimation for super-resolution image sequence enhancement. J Vis Commun Image Represent 9(1):38–50. doi:10.1006/jvci.1997.0370
Shekarforoush H, Berthod M, Zerubia J (1996) Subpixel image registration by estimating the polyphase decomposition of cross power spectrum. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Proceedings CVPR'96, 1996 I.E. Computer Society Conference on, 1996. IEEE, pp 532–537. doi:10.1109/CVPR.1996.517123
Steel K, Ellem E, Baxter D (2015) The application of biological motion research: biometrics, sport, and the military. Psychon Bull Rev 22(1):78–87. doi:10.3758/s13423-014-0659-5
Stone HS, Orchard MT, Chang E-C, Martucci SA (2001) A fast direct Fourier-based algorithm for subpixel registration of images. Geoscience and Remote Sensing, IEEE Transactions on 39(10):2235–2243. doi:10.1109/36.957286
Strang G (2006) Linear algebra and its applications. Thomson Brooks/Cole
Suh JW, Jeong J (2004) Fast sub-pixel motion estimation techniques having lower computational complexity. Consumer Electronics, IEEE Transactions on 50(3):968–973. doi:10.1109/TCE.2004.1341708
Suh J, Cho J, Jeong J (2009) Model-based quarter-pixel motion estimation with low computational complexity. Electron Lett 45(12):618–620. doi:10.1049/el.2009.3632
Tian Q, Huhns MN (1986) Algorithms for subpixel registration. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing 35(2):220–233. doi:10.1016/0734-189X(86)90028-9
Trocan M, Mikovicova B, Zhanguzin D (2012) An adaptive motion-compensated approach for video deinterlacing. Multimedia Tools and Applications 61(3):819–837. doi:10.1007/s11042-011-0845-7
Tsai R, Huang TS (1984) Multiframe image restoration and registration. Advances in computer vision and Image Processing 1(2):317–339
Vegiris CE, Avdelidis K, Dimoulas C, Papanikolaou G (2009) Live broadcasting of high definition audiovisual content using HDTV over broadband IP networks. International Journal of Digital Multimedia Broadcasting 2008. doi:10.1155/2008/250654
Wang Y, Ostermann J, Zhang Y-Q (2002) Video processing and communications, vol 5. Prentice Hall Upper Saddle River
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):1. doi:10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
Wong H-M, Au OC, Chang A (2005) Fast sub-pixel inter-prediction-based on texture direction analysis (FSIP-BTDA)[video coding applications]. In: Circuits and Systems. ISCAS 2005. IEEE International Symposium on, May 2005. IEEE, pp 5477–5480. doi:10.1109/ISCAS.2005.1465876
Yu Y, Wang J (2012) Highly accurate estimation of sub-pixel motion using phase correlation. In: Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition. Springer, pp 186–193. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-33506-8_24
Zhai B, Zheng J, Li B (2016) Digital image stabilization based on adaptive motion filtering with feedback correction. Multimedia Tools and Applications:1–28. doi:10.1007/s11042-015-3183-3
Zhang P, Zhuo T, Xie L, Zhang Y (2016) Deformable object tracking with spatiotemporal segmentation in big vision surveillance. Neurocomputing 204:87–96. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2015.07.149
Zhenyu W, Baochen J, Xudong Z, Yu C (2004) A new full-pixel and sub-pixel motion vector search algorithm for fast block-matching motion estimation in H. 264. In: Multi-Agent Security and Survivability. IEEE First Symposium on, Dec. 2004. IEEE, pp 345–348. doi:10.1109/ICIG.2004.13
Zhou B, Chen J (2003) A fast two-step search algorithm for half-pixel motion estimation. In: Electronics, Circuits and Systems. ICECS 2003. Proceedings of the 2003 10th IEEE International Conference on, Dec. 2003. IEEE, pp 611–614. doi:10.1109/ICECS.2003.1301859
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Konstantoudakis, K., Vrysis, L., Papanikolaou, G. et al. High accuracy block-matching sub-pixel motion estimation through detection of error surface minima. Multimed Tools Appl 77, 5837–5856 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4497-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-017-4497-0