Abstract
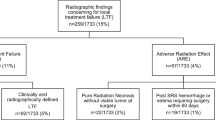
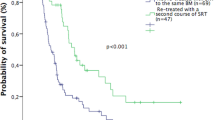
In the present study we have evaluated the efficacy and toxicity of repeated stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) in patients with recurrent/progressive brain metastases. Between March 2006 and October 2014, 43 patients (21 men and 22 women) with 47 lesions received a second course of SRS given in three daily fractions of 7–8 Gy. With a follow-up study of 19 months, the 1- and 2-year survival rates from repeated SRS were 37 and 20 %, respectively, and the 1- and 2-year local control rates were 70 and 60 %, respectively. Actuarial local control was significantly better for breast and lung metastases as compared with melanoma metastases; specifically, 1-year local control rates were 38 % for melanoma, 78 % for breast carcinoma and 73 % for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) metastases (p = 0.01). The cause of death was progressive systemic disease in 25 patients and progressive brain disease in 11 patients. Stable extracranial disease (p = 0.01) and Karnofsky performance status (KPS; p = 0.03) were predictive of longer survival. Radiologic changes suggestive of brain radionecrosis were observed in 9 (19 %) out of 47 lesions, with an actuarial risk of 34 % at 12 months. Neurological deficits (RTOG Grade 2 or 3) associated with brain necrosis occurred in 14 % of patients. In conclusion, a second course of SRS given in three daily fractions is a feasible treatment for selected patients with recurrent/progressive brain metastases. Further studies are needed to explore the efficacy and safety of different dose-fractionation schedules, especially in patients with melanoma or large metastases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanghavi SN, Miranpuri SS, Chappell R, Buatti JM, Sneed PK, Suh JH, Regine WF, Weltman E, King VJ, Goetsch SJ, Breneman JC, Sperduto PW, Scott C, Mabanta S, Mehta MP (2001) Radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis, stratified by the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis method. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:426–434
Sneed PK, Suh JH, Goetsch SJ, Sanghavi SN, Chappell R, Buatti JM, Regine WF, Weltman E, King VJ, Breneman JC, Sperduto PW, Mehta MP (2002) A multi-institutional review of radiosurgery alone vs. radiosurgery with whole brain radiotherapy as the initial management of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:519–526
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Tago M, Nakagawa K, Toyoda T, Hatano K, Kenjyo M, Oya N, Hirota S, Shioura H, Kunieda E, Inomata T, Hayakawa K, Katoh N, Kobashi G (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295:2483–2491
Frazier JL, Batra S, Kapor S, Vellimana A, Gandhi R, Carson KA, Shokek O, Lim M, Kleinberg L, Rigamonti D (2010) Stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of brain metastases: an institutional retrospective analysis of survival. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:1486–1492
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villà S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann RD, Carrie C, Hassel MB, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge D, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller RP (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 29:134–141
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 10:1037–1044
Vecil GG, Suki D, Maldaun MV, Lang FF, Sawaya R (2005) Resection of brain metastases previously treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 102:209–215
Truong MT, St Clair EG, Donahue BR, Rush SC, Miller DC, Formenti SC, Knopp EA, Han K, Golfinos JG (2006) Results of surgical resection for progression of brain metastases previously treated by gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 59:86–97
Yamanaka K, Iwai Y, Yasui T, Nakajima H, Komiyama M, Nishikawa M, Morikawa T, Kishi H (1999) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumor: the usefulness of repeated Gamma Knife radiosurgery for recurrent cases. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 72(Suppl):73–80
Chen JC, Petrovich Z, Giannotta SL, Yu C, Apuzzo ML (2000) Radiosurgical salvage therapy for patients presenting with recurrence of metastatic disease to the brain. Neurosurgery 46:860–866
Shaw E, Scott C, Souhami L, Dinapoli R, Kline R, Loeffler J, Farnan N (2000) Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47:291–298
Hoffman R, Sneed PK, McDermott MW, Chang S, Lamborn KR, Park E, Wara WM, Larson DA (2001) Radiosurgery for brain metastases from primary lung carcinoma. Cancer J 7:121–131
Noël G, Simon JM, Valery CA, Cornu P, Boisserie G, Hasboun D, Ledu D, Tep B, Delattre JY, Marsault C, Baillet F, Mazeron JJ (2003) Radiosurgery for brain metastasis: impact of CTV on local control. Radiother Oncol 68:15–21
Shuto T, Fujino H, Inomori S, Nagano H (2004) Repeated gamma knife radiosurgery for multiple metastatic brain tumours. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:989–993
Akyurek S, Chang EL, Mahajan A, Hassenbusch SJ, Allen PK, Mathews LA, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Woo SY (2007) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of cerebral metastases arising from breast cancer. Am J Clin Oncol 30:310–314
Kwon KY, Kong DS, Lee JI, Nam DH, Park K, Kim JH (2007) Outcome of repeated radiosurgery for recurrent metastatic brain tumors. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 109:132–137
Cicone F, Minniti G, Romano A, Papa A, Scaringi C, Tavanti F, Bozzao A, Maurizi Enrici R, Scopinaro F (2015) Accuracy of F-DOPA PET and perfusion-MRI for differentiating radionecrotic from progressive brain metastases after radiosurgery. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 42:103–111
Sperduto PW, Kased N, Roberge D, Xu Z, Shanley R, Luo X, Sneed PK, Chao ST, Weil RJ, Suh J, Bhatt A, Jensen AW, Brown PD, Shih HA, Kirkpatrick J, Gaspar LE, Fiveash JB, Chiang V, Knisely JP, Sperduto CM, Lin N, Mehta M (2012) Summary report on the graded prognostic assessment: an accurate and facile diagnosis-specific tool to estimate survival for patients with brain metastases. J Clin Oncol 30:419–425
Selek U, Chang EL, Hassenbusch SJ 3rd, Shiu AS, Lang FF, Allen P, Weinberg J, Sawaya R, Maor MH (2004) Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment in 103 patients for 153 cerebral melanoma metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:1097–1106
Manon R, O’Neill A, Knisely J, Werner-Wasik M, Lazarus HM, Wagner H, Gilbert M, Mehta M, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (2005) Phase II trial of radiosurgery for one to three newly diagnosed brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma, melanoma, and sarcoma: an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study (E 6397). J Clin Oncol 23:8870–8876
Dummer R, Goldinger SM, Turtschi CP, Eggmann NB, Michielin O, Mitchell L, Veronese L, Hilfiker PR, Felderer L, Rinderknecht JD (2014) Vemurafenib in patients with BRAF(V600) mutation-positive melanoma with symptomatic brain metastases: final results of an open-label pilot study. Eur J Cancer 50:611–621
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R, Grob JJ, Cowey CL, Lao CD, Schadendorf D, Dummer R, Smylie M, Rutkowski P, Ferrucci PF, Hill A, Wagstaff J, Carlino MS, Haanen JB, Maio M, Marquez-Rodas I, McArthur GA, Ascierto PA, Long GV, Callahan MK, Postow MA, Grossmann K, Sznol M, Dreno B, Bastholt L, Yang A, Rollin LM, Horak C, Hodi FS, Wolchok JD (2015) Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab or Monotherapy in Untreated Melanoma. N Engl J Med 373:23–34
Ribas A, Puzanov I, Dummer R, Schadendorf D, Hamid O, Robert C, Hodi FS, Schachter J, Pavlick AC, Lewis KD, Cranmer LD, Blank CU, O’Day SJ, Ascierto PA, Salama AK, Margolin KA, Loquai C, Eigentler TK, Gangadhar TC, Carlino MS, Agarwala SS, Moschos SJ, Sosman JA, Goldinger SM, Shapira-Frommer R, Gonzalez R, Kirkwood JM, Wolchok JD, Eggermont A, Li XN, Zhou W, Zernhelt AM, Lis J, Ebbinghaus S, Kang SP, Daud A (2015) Pembrolizumab versus investigator-choice chemotherapy for ipilimumab-refractory melanoma (KEYNOTE-002): a randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol 16:908–918
Nedzi LA, Kooy H, Alexander E 3rd, Gelman RS, Loeffler JS (1991) Variables associated with the development of complications from radiosurgery of intracranial tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 21:591–599
Voges J, Treuer H, Sturm V, Büchner C, Lehrke R, Kocher M, Staar S, Kuchta J, Müller RP (1996) Risk analysis of linear accelerator radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36:1055–1063
Aoyama H, Shirato H, Onimaru R, Kagei K, Ikeda J, Ishii N, Sawamura Y, Miyasaka K (2003) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy alone without whole brain irradiation for patients with solitary and oligo brain metastasis using noninvasive fixation of the skull. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:793–800
Ernst-Stecken A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Sauer R, Grabenbauer G (2006) Phase II trial of hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases: results and toxicity. Radiother Oncol 8:18–24
Vogelbaum MA, Angelov L, Lee SY, Li L, Barnett GH, Suh JH (2006) Local control of brain metastases by stereotactic radiosurgery in relation to dose to the tumor margin. J Neurosurg 104:907–912
Fahrig A, Ganslandt O, Lambrecht U, Grabenbauer G, Kleinert G, Sauer R, Hamm K (2007) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases–results from three different dose concepts. Strahlenther Onkol 183:625–630
Williams BJ, Suki D, Fox BD, Pelloski CE, Maldaun MV, Sawaya RE, Lang FF, Rao G (2009) Stereotactic radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors: a comprehensive review of complications. J Neurosurg 111:439–448
Blonigen BJ, Steinmetz RD, Levin L, Lamba MA, Warnick RE, Breneman JC (2010) Irradiated volume as a predictor of brain radionecrosis after linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 77:996–1001
Minniti G, Clarke E, Lanzetta G, Osti MF, Trasimeni G, Bozzao A, Romano A, Enrici RM (2011) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat Oncol 6:48
Yang HC, Kano H, Lunsford LD, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D (2011) What factors predict the response of larger brain metastases to radiosurgery? Neurosurgery 68:682–690
Minniti G, D’Angelillo RM, Scaringi C, Trodella LE, Clarke E, Matteucci P, Osti MF, Ramella S, Enrici RM, Trodella L (2014) Fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases. J Neurooncol 117:295–301
Torres-Reveron J, Tomasiewicz HC, Shetty A, Amankulor NM, Chiang VL (2013) Stereotactic laser induced thermotherapy (LITT): a novel treatment for brain lesions regrowing after radiosurgery. J Neurooncol 113:495–503
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Alessandro Bozzao, dr Andrea Romano and dr Guido Trasimeni, neuroradiologists, at Sant’Andrea Hospital, Neuroradiology Unit, for reviewing all MRI scans.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minniti, G., Scaringi, C., Paolini, S. et al. Repeated stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with progressive brain metastases. J Neurooncol 126, 91–97 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1937-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1937-4