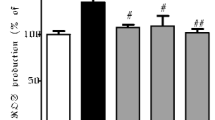
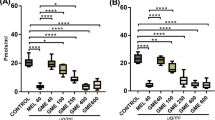
Abstract
Maneb (MB) and paraquat (PQ) are environmental toxins that have been experimentally used to induce selective damage of dopaminergic neurons leading to the development of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Although the mechanism of this selective neuronal toxicity in not fully understood, oxidative stress has been linked to the pathogenesis of PD. The present study investigates the mechanisms of neuroprotection elicited by Withania somnifera (Ws), a herb traditionally recognized by the Indian system of medicine, Ayurveda. An ethanolic root extract of Ws was co-treated with the MB–PQ induced mouse model of PD and was shown to significantly rescue canonical indicators of PD including compromised locomotor activity, reduced dopamine in the substantia nigra and various aspects of oxidative damage. In particular, Ws reduced the expression of iNOS, a measure of oxidative stress. Ws also significantly improved the MB + PQ mediated induction of a pro-apoptotic state by reducing Bax and inducing Bcl-2 protein expression, respectively. Finally, Ws reduced expression of the pro-inflammatory marker of astrocyte activation, GFAP. Altogether, the present study suggests that Ws treatment provides nigrostriatal dopaminergic neuroprotection against MB–PQ induced Parkinsonism by the modulation of oxidative stress and apoptotic machinery possibly accounting for the behavioural effects.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum D, Torch S, Lambeng N, Nissou M, Benabid L, Sadoul R, Verna JM (2001) Molecular pathways involved in the neurotoxicity of 6-OHDA, dopamine and MPTP: contribution to the apoptotic theory in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 65:135–172
Simunovic F, Yi M, Wang Y, Macey L, Brown LT, Krichevsky AM, Andersen SL, Stephens RM, Benes FM, Sonntag KC (2009) Gene expression profiling of substantia nigra dopamine neurons, further insights into Parkinson’s disease pathology. Brain 132:1795–1809
Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F (1973) Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci 20:415–455
Yadav S, Dixit A, Agrawal S, Singh A, Srivastava G, Singh AK, Srivastava PK, Prakash O, Singh MP (2012) Rodent models and contemporary molecular techniques: notable feats yet incomplete explanations of Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Mol Neurobiol 829:1–8
Prakash J, Yadav SK, Chouhan S, Singh SP (2013) Neuroprotective role of Withania somnifera root extract in Maneb–Paraquat induced mouse model of parkinsonism. Neurochem Res 38:972–980
Rajasankara S, Manivasagam T, Sankar V, Prakash S, Muthusamy R, Krishnamurti A, Surendran S (2009) Withania somnifera root extract improves catecholamines and physiological abnormalities seen in a Parkinson’s disease model mouse. J Ethnopharmacol 125:369–373
Somayajulu-Niţu M, Sandhu JK, Cohen J, Sikorska M, Sridhar TS, Matei A, Borowy-Borowski H, Pandey S (2009) Paraquat induces oxidative stress, neuronal loss in substantia nigra region and parkinsonism in adult rats: neuroprotection and amelioration of symptoms by water soluble formulation of coenzyme Q10. BMC Neurosci 10:1–12
Srivastava G, Dixit A, Yadav S, Patel DK, Prakash O, Singh MP (2012) Resveratrol potentiates cytochrome P4502d22-mediated neuroprotection in maneb- and paraquat-induced Parkinsonism in the mouse. Free Radic Biol Med 52:1294–1306
Pezzoli G, Cereda E (2013) Exposure to pesticides or solvents and risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 80:2035–2041
Singhal NK, Chauhan AK, Jain SK, Shanker R, Singh C, Singh MP (2013) Silymarin and melatonin-mediated changes in the expression of selected genes in pesticides-induced Parkinsonism. Mol Cell Biochem 384:47–58
Xu D, Duan H, Zhang Z, Cui W, Wang L, Sun Y, Lang M, Hoi PM, Han Y, Wang Y, Lee SM (2013) The novel TetramethylpyrazineBis-nitrone (TN-2) protects against MPTP/MPP+-induced neurotoxicity via inhibition of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 9:245–258
Alam N, Hossain M, Khalil MI, Moniruzzaman M, Sulaiman SA, Gan SH (2012) Recent advances in elucidating the biological properties of Withania somnifera and its potential role in health benefit. Phytochemistry 11:97–112
Orru A, Marchese G, Casu G, Casu MA, Kasture S, Cottiglia F, Acquas E, Mascia MP, Anzani N, Ruiu S (2013) Withania somnifera root extract prolongs analgesia and suppresses hyperalgesia in mice treated with morphine. Phytomedicine 21:745–752
Kuboyama T, Tohda C, Zhao J, Nakamura N, Hattori M, Komatsu K (2002) Axon or dendrite predominant outgrowth induced by constituents from Ashwagandha. Neuroreport 13:1715–1720
Tohda C, Joyashiki E (2009) Sominone enhances neurite outgrowth and spatial memory mediated by the neurotrophic factor receptor RET. Br J Pharmacol 157:1427–1440
Dhuley JN (1997) Effect of some Indian herbs on macrophage functions in ochratoxin A treated mice. J Ethnopharmacol 58:15–20
Chaurasia SS, Panda S, Kar A (2000) Withania somnifera root extract in the regulation of lead-induced oxidative damage in male mouse. Pharmacol Res 44:663–666
Singh S, Singh K, Patel DK, Singh C, Nath C, Singh VK, Singh RK, Singh MP (2009) The expression of CYP2D22 an ortholog of human CYP2D6 in mouse striatum and its modulation in 1-methyl 4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine induced Parkinson’s disease phenotype and nicotine mediated neuroprotection. Rejuvenation Res 12:185–197
Chaurasiya ND, Uniyal GC, Lal P, Misra L, Sangwan NL, Tuli R, Sangwan RS (2008) Analysis of withanolides in root and leaf of Withania somnifera by HPLC with photodiode array and evaporative light scattering detection. Phytochem Anal 19:148–154
Tiwari MN, Singh AK, Ahmad I, Upadhyay G, Singh D, Patel DK, Singh C, Prakash O, Singh MP (2010) Effects of cypermethrin on monoamine transporters, xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes and lipid peroxidation in the rat nigrostriatal system. Free Radic Res 44:1416–1424
Martin PY, Bianchi M, Roger F, Niksic L, Féraille E (2002) Arginine vasopressin modulates expression of neuronal NOS in rat renal medulla. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:559–568
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Gupta SP, Patel S, Yadav S, Singh AK, Singh S, Singh MP (2010) Involvement of nitric oxide in maneb and paraquat-induced Parkinson’s disease phenotype in mouse: is there any link with lipid peroxidation. Neurochem Res 35:1206–1213
Kasture S, Pontis S, Pinna A, Schintu N, Spina L, Longoni R, Simola N, Ballero M, Morelli M (2009) Assessment of symptomatic and neuroprotective efficacy of Mucuna pruriens seed extract in rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 15:111–122
Yadav SK, Prakash J, Chouhan S, Westfall S, Verma M, Singh TD, Singh SP (2014) Comparison of the neuroprotective potential of Mucuna pruriens seed extract with estrogen in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced PD mice model. Neurochem Int 65:1–13
Mochizuki H, Hayakawa H, Migit M, Shibata M, Tanaka R, Suzuki A, Shimo NY, Urabe T, Yamada M, Tamayos K, Shimada T, Miura M, Mizuno Y (2001) An AAV-derived Apaf-1 dominant negative inhibitor prevents MPTP toxicity as antiapoptotic gene therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10918–10923
Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Saxena G, Nath C (2009) Cholinergic influence on memory stages A study on scopolamine amnesic mice. Indian J Pharmacol 41:192–196
Widodo N, Kaur K, Shrestha BG, Takagi Y, Ishii T, Wadhwa R, Kaul SC (2007) Selective killing of cancer cells by leaf extract of Ashwagandha Identification of a tumor inhibitory factor and the first molecular insights to its effect. Clin Cancer Res 13:2298–2306
Liou HH, Tsai MC, Chen CJ, Jeng JS, Chang YC, Chen SY, Chen RC (1997) Environmental risk factors and Parkinson’s disease, a case-control study in Taiwan. Neurology 48:1583–1591
Willis AW (2013) Parkinson disease in the elderly adult. Mo Med 110:406–410
Anglade P, Vyas S, Javoy-Agid F, Herrero MT, Michel PP, Marquez J, Mouatt-Prigent A, Ruberg M, Hirsch EC, Agid Y (1997) Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol Histopathol 12:25–31
Kingsbury AE, Mardsen CD, Foster OJ (1998) DNA fragmentation in human substantia nigra: apoptosis or perimortem effect? Mov Disord 13:877–884
Levy OA, Malagelada C, Greene LA (2009) Cell death pathways in Parkinson’s disease: proximal triggers, distal effectors, and final steps. Apoptosis 14:478–500
Schwarting RK, Bonatz AE, Carey RJ, Huston JP (1991) Relationships between indices of behavioral asymmetries and neurochemical changes following mesencephalic 6-hydroxydopamine injections. Brain Res 554:46–55
Konar A, Shah N, Singh R, Saxena N, Kaul SC, Wadhwa R, Thakur MK (2011) Protective role of Ashwagandha leaf extract and its component withanone on scopolamine-induced changes in the brain and brain-derived cells. PLoS One 6:1–11
Jinsmaa Y, Florang VR, Rees JN, Anderson DG, Strac S, Doorn JA (2009) Products of oxidative stress inhibit aldehyde oxidation and reduction pathways in dopamine catabolism yielding elevated levels of a reactive intermediate. Chem Res Toxicol 22:835–841
Marchitti SA, Deitrich RA, Vasiliou V (2007) Neurotoxicity and metabolism of the catecholamine-derived 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde: the role of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Pharmacol Rev 59:125–150
Hinterberger H (1971) The biochemistry of catecholamines in relation to Parkinson’s disease. Aust N Z J Med Suppl 1:8–14
Piggott MA, Marshall EF, Thomas N, Lloyd S, Court JA, Jaros E, Costa D, Perry RH, Perry EK (1999) Dopaminergic activities in the human striatum rostrocaudal gradients of uptake sites and of D1 and D2 but not of D3 receptor binding or dopamine. Neuroscience 90:433–445
Yang L, Matthews RT, Schulz JB, Klockgether T, Liao AW, Martinou JC, Penney JB Jr, Hyman BT, Beal MF (1998) 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyride neurotoxicity is attenuated in mice over expressing Bcl-2. J Neurosci 18:8145–8152
Bus JS, Gibson JE (1984) Paraquat: model for oxidant-initiated toxicity. Environ Health Perspect 55:37–46
Cohen GM, d’Arcy Doherty M (1987) Free radical mediated cell toxicity by redox cycling chemicals. Br J Cancer Suppl 8:46–52
Rappold PM, Tieu K (2010) Astrocytes and therapeutics for Parkinson’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 7:413–423
Mena MA, García de Yébenes J (2008) Glial cells as players in parkinsonism: the “good” the “bad” and the “mysterious” glia. Neuroscientist 14:544–560
Heneka MT, Rodríguez JJ, Verkhratsky A (2010) Neuroglia in neurodegeneration. Brain Res Rev 63:189–211
Jukkola P, Guerrero T, Gray V, Gu C (2013) Astrocytes differentially respond to inflammatory autoimmune insults and imbalances of neural activity. Acta Neuropathol Commun 23:1–10
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the Head, Department of Biochemistry and Zoology, BHU for providing the basic departmental and cryostat facility, respectively. We sincerely thank Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi for providing fellowship to Jay Prakash and Sachchida Nand Rai, Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi for providing fellowship to Satyndra Kumar Yadav, Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, for providing fellowship to Shikha Chouhan.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, J., Chouhan, S., Yadav, S.K. et al. Withania somnifera Alleviates Parkinsonian Phenotypes by Inhibiting Apoptotic Pathways in Dopaminergic Neurons. Neurochem Res 39, 2527–2536 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1443-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1443-7