Abstract
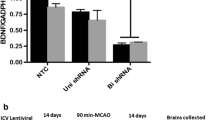
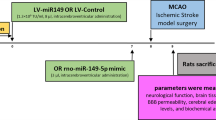
The pro-survival effect of VEGF-B has been documented in different in vivo and in vitro models. We have previously shown an enhanced VEGF-B expression in response to candesartan treatment after focal cerebral ischemia. In this study, we aimed to silence VEGF-B expression to assess its contribution to candesartan’s benefit on stroke outcome. Silencing VEGF-B expression was achieved by bilateral intracerebroventricular injections of lentiviral particles containing short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against VEGF-B. Two weeks after lentiviral injections, rats were subjected to either 90 min or 3 h of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and randomized to intravenous candesartan (1 mg/kg) or saline at reperfusion. Animals were sacrificed at 24 or 72 h and brains were collected and analyzed for hemoglobin (Hb) excess and infarct size, respectively. Functional outcome at 24, 48 and 72 h was assessed blindly. Candesartan treatment improved neurobehavioral and motor function, and decreased infarct size and Hb. While silencing VEGF-B expression diminished candesartan’s neuroprotective effect, candesartan-mediated vascular protection was maintained even in the absence of VEGF-B suggesting that this growth factor is not the mediator of candesartan’s vascular protective effects. However, VEGF-B is a mediator of neuroprotection achieved by candesartan and represents a potential drug target to improve stroke outcome. Further studies are needed to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms of VEGF-B in neuroprotection and recovery after ischemic stroke.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARBs:
-
Angiotensin II type-1 receptor blockers
- KD:
-
VEGF-B knockdown
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- NTC:
-
Non-targeting control
- shRNA:
-
Short hairpin RNA
- VEGF-B:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-B
References
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER 3rd, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Pandey DK, Paynter NP, Reeves MJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB (2014) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2014 update: a report from the american heart association. Circulation 129:e28–e292
Engelhorn T, Goerike S, Doerfler A, Okorn C, Forsting M, Heusch G, Schulz R (2004) The angiotensin II type 1-receptor blocker candesartan increases cerebral blood flow, reduces infarct size, and improves neurologic outcome after transient cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:467–474
Brdon J, Kaiser S, Hagemann F, Zhao Y, Culman J, Gohlke P (2007) Comparison between early and delayed systemic treatment with candesartan of rats after ischaemic stroke. J Hypertens 25:187–196
Kozak A, Ergul A, El-Remessy AB, Johnson MH, Machado LS, Elewa HF, Abdelsaid M, Wiley DC, Fagan SC (2009) Candesartan augments ischemia-induced proangiogenic state and results in sustained improvement after stroke. Stroke 40:1870–1876
Elewa HF, Kozak A, Johnson MH, Ergul A, Fagan SC (2007) Blood pressure lowering after experimental cerebral ischemia provides neurovascular protection. J Hypertens 25:855–859
Fagan SC, Kozak A, Hill WD, Pollock DM, Xu L, Johnson MH, Ergul A, Hess DC (2006) Hypertension after experimental cerebral ischemia: candesartan provides neurovascular protection. J Hypertens 24:535–539
Guan W, Kozak A, El-Remessy AB, Johnson MH, Pillai BA, Fagan SC (2011) Acute treatment with candesartan reduces early injury after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion. Transl Stroke Res 2:179–185
Yamakawa H, Jezova M, Ando H, Saavedra JM (2003) Normalization of endothelial and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in brain microvessels of spontaneously hypertensive rats by angiotensin II AT1 receptor inhibition. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:371–380
Guan W, Somanath PR, Kozak A, Goc A, El-Remessy AB, Ergul A, Johnson MH, Alhusban A, Soliman S, Fagan SC (2011) Vascular protection by angiotensin receptor antagonism involves differential VEGF expression in both hemispheres after experimental stroke. PLoS ONE 6:e24551
Soliman S, El-Remessy A, Ishrat T, Pillai A, Somanath P, Ergul A, Fagan S (2014) Candesartan induces a prolonged proangiogenic effect and augments endothelium-mediated neuroprotection after oxygen and glucose deprivation: role of VEGF-A and B. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 349:444–457
Hamai M, Iwai M, Ide A, Tomochika H, Tomono Y, Mogi M, Horiuchi M (2006) Comparison of inhibitory action of candesartan and enalapril on brain ischemia through inhibition of oxidative stress. Neuropharmacology 51:822–828
Ishrat T, Pillai B, Soliman S, Fouda AY, Kozak A, Johnson MH, Ergul A, Fagan SC (2015) Low-dose candesartan enhances molecular mediators of neuroplasticity and subsequent functional recovery after ischemic stroke in rats. Mol Neurobiol 51:1542–1553
Fouda AY, Alhusban A, Ishrat T, Pillai B, Eldahshan W, Waller JL, Ergul A, Fagan SC (2017) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor knockdown blocks the angiogenic and protective effects of angiotensin modulation after experimental stroke. Mol Neurobiol 54:661–670
Greenberg ME, Xu B, Lu B, Hempstead BL (2009) New insights in the biology of BDNF synthesis and release: implications in CNS function. J Neurosci 29:12764–12767
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO, Logvinova A, Greenberg DA (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest 111:1843–1851
He J, Zhang Y, Xu T, Zhao Q, Wang D, Chen CS, Tong W, Liu C, Ju Z, Peng Y, Peng H, Li Q, Geng D, Zhang J, Li D, Zhang F, Guo L, Sun Y, Wang X, Cui Y, Li Y, Ma D, Yang G, Gao Y, Yuan X, Bazzano LA, Chen J (2014) Effects of immediate blood pressure reduction on death and major disability in patients with acute ischemic stroke: the CATIS randomized clinical trial. JAMA 311:479–489
Sandset EC, Bath PM, Boysen G, Jatuzis D, Korv J, Luders S, Murray GD, Richter PS, Roine RO, Terent A, Thijs V, Berge E, Group SS (2011) The angiotensin-receptor blocker candesartan for treatment of acute stroke (SCAST): a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Lancet 377:741–750
Li Y, Zhang F, Nagai N, Tang Z, Zhang S, Scotney P, Lennartsson J, Zhu C, Qu Y, Fang C, Hua J, Matsuo O, Fong GH, Ding H, Cao Y, Becker KG, Nash A, Heldin CH, Li X (2008) VEGF-B inhibits apoptosis via VEGFR-1-mediated suppression of the expression of BH3-only protein genes in mice and rats. J Clin Invest 118:913–923
Poesen K, Lambrechts D, Van Damme P, Dhondt J, Bender F, Frank N, Bogaert E, Claes B, Heylen L, Verheyen A, Raes K, Tjwa M, Eriksson U, Shibuya M, Nuydens R, Van Den Bosch L, Meert T, D’Hooge R, Sendtner M, Robberecht W, Carmeliet P (2008) Novel role for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor-1 and its ligand VEGF-B in motor neuron degeneration. J Neurosci 28:10451–10459
Yamazaki Y, Morita T (2006) Molecular and functional diversity of vascular endothelial growth factors. Mol Divers 10:515–527
Barleon B, Sozzani S, Zhou D, Weich HA, Mantovani A, Marme D (1996) Migration of human monocytes in response to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is mediated via the VEGF receptor flt-1. Blood 87:3336–3343
Clauss M, Weich H, Breier G, Knies U, Rockl W, Waltenberger J, Risau W (1996) The vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flt-1 mediates biological activities. Implications for a functional role of placenta growth factor in monocyte activation and chemotaxis. J Biol Chem 271:17629–17634
Luttun A, Tjwa M, Moons L, Wu Y, Angelillo-Scherrer A, Liao F, Nagy JA, Hooper A, Priller J, De Klerck B, Compernolle V, Daci E, Bohlen P, Dewerchin M, Herbert JM, Fava R, Matthys P, Carmeliet G, Collen D, Dvorak HF, Hicklin DJ, Carmeliet P (2002) Revascularization of ischemic tissues by PlGF treatment, and inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, arthritis and atherosclerosis by anti-Flt1. Nat Med 8:831–840
Autiero M, Waltenberger J, Communi D, Kranz A, Moons L, Lambrechts D, Kroll J, Plaisance S, De Mol M, Bono F, Kliche S, Fellbrich G, Ballmer-Hofer K, Maglione D, Mayr-Beyrle U, Dewerchin M, Dombrowski S, Stanimirovic D, Van Hummelen P, Dehio C, Hicklin DJ, Persico G, Herbert JM, Communi D, Shibuya M, Collen D, Conway EM, Carmeliet P (2003) Role of PlGF in the intra- and intermolecular cross talk between the VEGF receptors Flt1 and Flk1. Nat Med 9:936–943
Pipp F, Heil M, Issbrucker K, Ziegelhoeffer T, Martin S, van den Heuvel J, Weich H, Fernandez B, Golomb G, Carmeliet P, Schaper W, Clauss M (2003) VEGFR-1-selective VEGF homologue PlGF is arteriogenic: evidence for a monocyte-mediated mechanism. Circ Res 92:378–385
Autiero M, Luttun A, Tjwa M, Carmeliet P (2003) Placental growth factor and its receptor, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1: novel targets for stimulation of ischemic tissue revascularization and inhibition of angiogenic and inflammatory disorders. J Thromb Haemost 1:1356–1370
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Luttun A, Vincenti V, Compernolle V, De Mol M, Wu Y, Bono F, Devy L, Beck H, Scholz D, Acker T, DiPalma T, Dewerchin M, Noel A, Stalmans I, Barra A, Blacher S, VandenDriessche T, Ponten A, Eriksson U, Plate KH, Foidart JM, Schaper W, Charnock-Jones DS, Hicklin DJ, Herbert JM, Collen D, Persico MG (2001) Synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and placental growth factor contributes to angiogenesis and plasma extravasation in pathological conditions. Nat Med 7:575–583
Li X, Lee C, Tang Z, Zhang F, Arjunan P, Li Y, Hou X, Kumar A, Dong L (2009) VEGF-B: a survival, or an angiogenic factor? Cell Adhes Migr 3:322–327
Zhang F, Tang Z, Hou X, Lennartsson J, Li Y, Koch AW, Scotney P, Lee C, Arjunan P, Dong L, Kumar A, Rissanen TT, Wang B, Nagai N, Fons P, Fariss R, Zhang Y, Wawrousek E, Tansey G, Raber J, Fong GH, Ding H, Greenberg DA, Becker KG, Herbert JM, Nash A, Yla-Herttuala S, Cao Y, Watts RJ, Li X (2009) VEGF-B is dispensable for blood vessel growth but critical for their survival, and VEGF-B targeting inhibits pathological angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:6152–6157
Sun Y, Jin K, Childs JT, Xie L, Mao XO, Greenberg DA (2004) Increased severity of cerebral ischemic injury in vascular endothelial growth factor-B-deficient mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:1146–1152
Xie L, Mao X, Jin K, Greenberg DA (2013) Vascular endothelial growth factor-B expression in postischemic rat brain. Vasc Cell 5:8
Jean LeBlanc N, Guruswamy R, ElAli A (2017) Vascular endothelial growth factor isoform-B stimulates neurovascular repair after ischemic stroke by promoting the function of pericytes via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1. Mol Neurobiol 55:3611–3626
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H (1986) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17:472–476
Watanabe T, Okuda Y, Nonoguchi N, Zhao MZ, Kajimoto Y, Furutama D, Yukawa H, Shibata MA, Otsuki Y, Kuroiwa T, Miyatake S (2004) Postischemic intraventricular administration of FGF-2 expressing adenoviral vectors improves neurologic outcome and reduces infarct volume after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:1205–1213
Machado LS, Sazonova IY, Kozak A, Wiley DC, El-Remessy AB, Ergul A, Hess DC, Waller JL, Fagan SC (2009) Minocycline and tissue-type plasminogen activator for stroke: assessment of interaction potential. Stroke 40:3028–3033
Ishrat T, Pillai B, Ergul A, Hafez S, Fagan SC (2013) Candesartan reduces the hemorrhage associated with delayed tissue plasminogen activator treatment in rat embolic stroke. Neurochem Res 38:2668–2677
Fagan SC, Lapchak PA, Liebeskind DS, Ishrat T, Ergul A (2013) Recommendations for preclinical research in hemorrhagic transformation. Transl Stroke Res 4:322–327
Fouda AY, Alhusban A, Ishrat T, Pillai B, Eldahshan W, Waller JL, Ergul A, Fagan SC (2016) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor knockdown blocks the angiogenic and protective effects of angiotensin modulation after experimental stroke. Mol Neurobiol 54:661–670
Alhusban A, Kozak A, Ergul A, Fagan SC (2013) AT1 receptor antagonism is proangiogenic in the brain: BDNF a novel mediator. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 344:348–359
Xiong Y, Mahmood A, Chopp M (2010) Angiogenesis, neurogenesis and brain recovery of function following injury. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 11:298–308
Ishrat T, Kozak A, Alhusban A, Pillai B, Johnson MH, El-Remessy AB, Ergul A, Fagan SC (2014) Role of matrix metalloproteinase activity in the neurovascular protective effects of angiotensin antagonism. Stroke Res Treat 2014:560491
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institute of Health [RO1-NS063965 (SCF), RO1-NS083559 (AE), R01NS097800-01 (TI)], Veterans Affairs Merit Review [BX-000891 (SCF), BX-BX000347 (AE)], and the American Heart Association (12PRE12030197 (SS)). Adviye Ergul is a Research Career Scientist at the Charlie Norwood Veterans Affairs Medical Center in Augusta, Georgia. The authors gratefully acknowledge Abdelrahman Fouda for the technical assistance with animal tissue collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclosures
The contents do not represent the views of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States government.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishrat, T., Soliman, S., Eldahshan, W. et al. Silencing VEGF-B Diminishes the Neuroprotective Effect of Candesartan Treatment After Experimental Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Neurochem Res 43, 1869–1878 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2604-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2604-x