Abstract
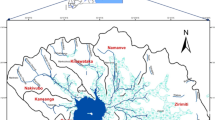
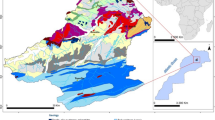
Erosion and the production of sediments effect the siltation of reservoirs and create large environmental problems. This work calculates the volume of sediments caused by erosion in a hydrological basin using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation 2 (USLE–RUSLE2), applying, or not, the sediment delivery ratio, and is compared with the volume of sediments transported using the Lawrence method. The USLE–RUSLE2 method is validated in the study area, the Jerte Valley, using the geographic information systems. The result obtained showed an erosion of 7 Tm/ha year and low risk of siltation, which suggest that the Plasencia reservoir has a long life expectancy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avendaño C, Calvo JP, Cobo R, Sanz ME (1994) La modelización matemática, ajuste y contraste del sediment delivery ratio a los embalses. Aplicación al cálculo de la erosión de cuencas fluviales. CEDEX, Madrid, p 40
Avendaño C, Calvo JP, Cobo R, Sanz ME (1995) Procedimiento para evaluar la degradación específica de cuencas de embalses a partir de los sedimentos acumulados en los mismos. Aplicación al estudio de embalses españoles. Ing Civ 99:51–58
Bodoque JM, Pedraza J, Martin-Duque JF, Sanz MA, Carrasco RM, Diez A, Mattera M (2001) Evaluación de la degradación específica en la cuenca vertiente al embalse Puente Alta (Segovia) mediante métodos de estimación directos e indirectos. Rev C&G 15:21–36
Brown CB (1943) Discussion of sedimentation in reservoir by Witzig. Am Soc Civ Eng 109:1080–1086
Carrasco González RM (1991) Geomorfología del Valle del Jerte. Las líneas maestras del paisaje. Universidad de Extremadura, Salamanca
Chen P, Lian Y (2016) Modeling of soil loss and impact factors in the Guijiang Karst River Basin in Southern China. Environ Earth Sci 75(352):1–14
Cobo R (2008) Los sedimentos de los embalses españoles. CEDEX. Ing Agua 15:231–250
Constantine M, Ogbu K (2015) Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE2 model and GIS in upper Ebonyi river watershed, Enugu. Int J Remote Sens Geosci 4:7–17
Cruchaga P (2013) Aplicación de sistemas de información geográfica (SIG) a la estimación de la erosión en la cuenca del embalse de Arguis. Lucas Mellada 15:67–84
Flores E (2004) Introducción a la hidrología aplicada. UTO-FNI-CIVIL, Oruro
Horton RE (1945) Erosional development of stream and their drainage basins: hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol Soc Am Bull 56:275–370
Lawrence P, Cascio A, Goldsmith P, Abbott C (2004) Sedimentation in small dams. Development of a catchment characterization and sediment yield prediction procedure. Report OD TN 120. Department for International Development HR Wallingford, pp 1–20
León J, Badía D, Echevarría MT (2015) Comparison of different methods to measure soil erosion in the central Ebro valley. Cuad Investig Geogr 41:165–180
Martinez-Graña AM, Goy JL, Cimarra C (2015) 2D to 3D geologic mapping transformation using virtual globes and flight simulators and their applications in the analysis of geodiversity in natural areas. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8023–8034
Martínez-Graña AM, Goy JL, Zazo C (2014) Water and wind erosion risk in natural parks. A case study in “Las Batuecas-Sierra de Francia” and “Quilamas” protected parks (Central System, Spain). Int J Environ Res 8(1):61–68
Martínez-Graña AM, Goy JL, Zazo C (2015) Dominant soil map in “Las Batuecas-Sierra de Francia” and “Quilamas” nature parks (Central System, Salamanca, Spain). J Maps 11:371–379. https://doi.org/10.1080/17445647.2014.960014
Martínez-Graña AM, Boski T, Goy JL, Zazo C, Dabrio CJ (2016a) Coastal-flood risk management in central Algarve: vulnerability and flood risk indices (South Portugal). Ecol Ind 71:302–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.07.021
Martínez-Graña AM, Goy JL, Zazo C, Silva PG (2016b) Soil map and 3D virtual tour using a database of soil-forming factors. Environ Earth Sci 75(21):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6225-x
Palau A (2002) La sedimentación en embalses. Medidas preventivas y correctoras. Actas de I congreso de Ingeniería civil, territorio y Medio Ambiente, Madrid, pp 847–856
Panagos P, Borrelli P, Ballabio C (2015) The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ Sci Policy 54:438–447
Roth V, Nigussie TK, Lemann T (2016) Model parameter transfer for streamflow and sediment loss prediction with SWAT in a tropical watershed. Environ Earth Sci 75(1321):1–13
Strahler AN (1965) Introduction to physical geography. Wiley, New York, p 455
Zhao N, Yu F, Li C, Wang H, Liu J, Mu W (2014) Investigation of rainfall-runoff processes and soil moisture dynamics in grassland plots under simulated rainfall conditions. Water 6(9):2671–2689. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6092671
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the USAL research Projects CGL2012-37281-C02.01, CGL2015-67169-P and CGL2015-69919-R (MINECO-FEDER).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez, Y., Martínez-Graña, A., Santos-Francés, F. et al. Influence of the sediment delivery ratio index on the analysis of silting and break risk in the Plasencia reservoir (Central System, Spain). Nat Hazards 91, 1407–1421 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3182-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3182-6