Abstract
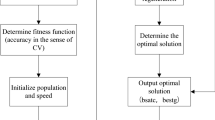
For water inrush from coal floor, due to different kinds of controlling factors and their internal correlations, the accuracy of prediction model is mostly below expectation. In this paper, it studies on which controlling factors should be selected for water inrush prediction model because all these factors have different influence on water inrush incidents based on the analysis of in situ data. Some factors are proved having limited impacts on water inrush, it is no necessary to collect in situ data of those factors from coal mining work face. Therefore, the workload and expense will decrease. In this paper, an index system of factors influencing water inrush from coal floor is established based on the current water inrush controlling theory and detailed analysis of in situ data obtained from mining regions. Following the Wrapper method in feature selection, 10 main controlling factors were selected from 14 existing indicators which were thought could affect water inrush. After training on dynamic GRU model which is made for water inrush prediction, a comparison among dynamic GRU model and stable SVM and BPMN models turns out the advantages of the previous with a higher accuracy in train, validation and test set against the latter. It is believed GRU model is able to predict water inrush water inrush from coal floor with high accuracy and hence enhances mining safety.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao Y, Zhai S, Chen J, Xu P, Sun X, Zhan J, Zhang W, Zhou X (2020) The evolution of the Samaoding paleolandslide river blocking event at the upstream reaches of the Jinsha River, Tibetan Plateau. Geomorphology 351:106970
Cho K, Merrienboer VB, Gulcehre C, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bahdanau D, Bengio Y (2014) Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. Comput Sci
Dong D, Chen Z, Lin G, Li X, Zhang RM, Ji Y (2019) Combining the fisher feature extraction and support vector machine methods to identify the water inrush source: a case study of the Wuhai mining area. Mine Water Environ 38:855–862
Hu Y, Sun LM, Yu SC, Huang JL (2013) Coal mine disaster warning internet of things intrusion detection system based on back propagation neural network improved by genetic algorithms. Appl Mech Materials 441:343–346
Huang Z, Zeng W, Zhao K (2019) Experimental investigation of the variations in hydraulic properties of a fault zone in Western Shandong, China. J Hydrol 574:822–835
Kern AN, Addison P, Oommen T, Salazar SE, Coffman RA (2017) Machine learning based predictive modeling of debris flow probability following wildfire in the intermountain Western United States. Math Geosci 49:717–735
Li BY (1999) Down three zones in the prediction of the water inrush from coal bed floor aquifer-theory, development and application. J Shandong Inst Min Technol (Nat Sci) 18:11–18
Li SC, Zhou ZQ, Li LP, Xu ZH, Zhang QQ, Shi SS (2013) Risk assessment of water inrush in karst tunnels based on attribute synthetic evaluation system. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 38:50–58
Li Y, Chiu YH, Lin TY (2019) Coal production efficiency and land destruction in China’s coal mining industry. Resour Policy 63:101–109
Li Y, Wei ML, Liu L, Xue Q, Yu BW (2020) Adsorption of toluene on various natural soils: influences of soil properties, mechanisms, and model. Sci Tot Environ 740:140104
Ma D, Duan H, Cai X, Li Z, Li Q, Zhang Q (2018) A global optimization-based method for the prediction of water inrush hazard from mining floor. Water 10:1618
Meng ZP, Li GQ, Xie XT (2012) A geological assessment method of floor water inrush risk and its application. Eng Geol 2012(143–144):51–60
Noiriel C, Renard F, Doan ML, Gratier JP (2010) Intense fracturing and fracture sealing induced by mineral growth in porous rocks. Chem Geol 269:197–209
Oda M, Takemura T, Aoki T (2002) Damage growth and permeability change in triaxial compression tests of Inada granite. Mech Mater 34:313–331
Pang YH, Wang G, Ding Z (2014) Mechanical model of water inrush from coal seam floor based on triaxial seepage experiments. Int J Coal Sci Technol 1:428–433
Peng SP, Meng ZP, Wang H, Ma CL, Pan JN (2003) Testing study on pore ratio and permeability of sandstone under different confining pressures. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 22:74–746
Pu S, Zhu Z, Song L (2020) Fractional-order visco-elastoplastic constitutive model for rock under cyclic loading. Araab Geosci 13:326
Qian MG, Miao XX, Xu JL (1996) Theoretical study of key stratum in ground control. J China Coal Soc 21(3):225–230
Qiu L, Song D, He X, Wang E, Li Z, Yin S, Wei M, Liu Y (2020) Multifractal of electromagnetic waveform and spectrum about coal rock samples subjected to uniaxial compression. Fractals. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218348X20500619
Rong XL, Zheng SS, Zhang YX (2020) Seismic behavior of frost-damaged squat RC shear walls under artificial climate environment: a further experimental research. Archiv Civ Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43452-020-00081-7
Shi SS, Bu L, Li SC, Xiong ZM, Xie XK, Li LP, Zhou ZQ, Xu ZH, Ma D (2017) Application of comprehensive prediction method of water inrush hazards induced by unfavourable geological body in high risk karst tunnel: a case study. Geomat Nat Haz Risk 8:1407–1423
Wang ZY, Liu HQ, Wang PY, Yu SC (1994) Theory and practice of coal mining discipline on confined water. J China Coal Soc 19:40–48
Wang Y, Yang WF, Ming Li, Liu X (2012) Risk assessment of floor water inrush in coal mines based on secondary fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Int J Rock Mech Min 2012(52):50–55
Wang J, Li SC, Li LP, Lin P, Xu ZZ (2019) Attribute recognition model for risk assessment of water inrush. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:1057–1071
Watanabe N, Ishibashi T, Ohsaki Y, Tsuchiya Y, Tamagawa T, Hirano N, Okabe H, Tsuchiya N (2011) X-ray CT based numerical analysis of fracture flow for core samples under various confining pressures. Eng Geol 123:338–346
Wu Y, Huang Z, Zhao K, Zeng W, Gu QX, Zhang R (2020) Unsteady seepage solutions for hydraulic fracturing around vertical wellbores in hydrocarbon reservoirs. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45:9496–9503
Yang BB, Yin KL, Lacasse S, Liu ZQ (2019) Time series analysis and long short-term memory neural network to predict landslide displacement. Landslides 16:677–694
Ye YX, Liu GY (2005) Research on coupling characteristics of fluid flow and stress within rock. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 24:2518–2523
Yu S, Zhang J, Ren X (2019) Numerical analysis of the seepage characteristics of slopes with weak interlayers under different rainfall levels. Appl Ecology Environ Res 17:12465–12478
Yu J, Yao W, Duan K (2020) Experimental study and discrete element method modeling of compression and permeability behaviors of weakly anisotropic sandstones. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 134:104437
Zhang JC, Wang JX (2006) Coupled behavior of stress and permeability and its engineering application. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 25:1981–1989
Zhang YH, Ge TT, Tian W, Liou YA (2019a) Debris flow susceptibility mapping using machine-learning techniques in Shigatse area, China. Remote Sens 11:2801
Zhang YG, Zhu SY, Zhang WQ, Liu H (2019b) Analysis of deformation characteristics and stability mechanisms of typical landslide mass based on the field monitoring in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J Earth Syst Sci 128:1
Zhang YG, Zhang Z, Xue S, Wang RJ, Xiao M (2020a) Stability analysis of a typical landslide mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir under varying reservoir water levels. Environ Earth Sci 79:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8779-x
Zhang LG, Chen XQ, Zhang YG, Wu FW, Chen F, Wang WT, Guo F (2020b) Application of GWO-ELM model to prediction of Caojiatuo landslide displacement in the Three Gorge Reservoir Area. Water 12:1860
Zhang YG, Zhu SY, Tan JK, Li LD, Yin XJ (2020c) The influence of water level fluctuation on the stability of landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Arab J Geosci 13:845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05828-3
Zhang YG, Tang J, He ZY, Tan JK, Li C (2020d) A novel displacement prediction method using gated recurrent unit model with time series analysis in the Erdaohe landslide. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04337-6
Zhang YG, Tang J, Liao RP, Zhang MF, Zhang Y, Wang XM, Su ZY (2020e) Application of an enhanced BP neural network model with water cycle algorithm on landslide prediction. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01920-y
Zhang YX, Bicici E, Sezen H (2020f) Reinforcement slip model considering corrosion effects. Constr Build Mater 235:117348
Zhou C, Yin KL, Cao Y, Ahmed B (2016) Application of time series analysis and PSO-SVM model in predicting the Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Eng Geol 204:108–120
Zhou W, Shi X, Lu X, Qi C, Luan B, Liu F (2020) The mechanical and microstructural properties of refuse mudstone-GGBS-red mud based geopolymer composites made with sand. Constr Build Mater 253:119193
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support provided by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2015XKMS035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Yang, L. A novel dynamic predictive method of water inrush from coal floor based on gated recurrent unit model. Nat Hazards 105, 2027–2043 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04388-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04388-9