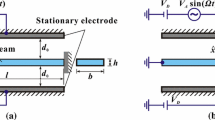
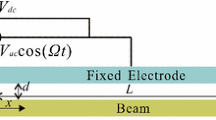
Abstract
This paper investigates analytically and numerically the effect of initial offset imperfection on the mechanical behaviors of microbeam-based resonators. Symmetry breaking of DC actuation, due to different initial offset distances of microbeam to lower and upper electrodes, is concerned. For qualitative analysis, time-varying capacitors are introduced and a lumped parameter model, considering nonlinear electrostatic force and midplane stretching of microbeam, is adopted to examine the system statics and dynamics. The Method of Multiple Scales (MMS) is applied to determine the primary resonance solution under small vibration assumption. Meanwhile, the Finite Difference Method (FDM) combined with Floquet theory is utilized to generate frequency response curves for medium- and large-amplitude vibration simulations. Static bifurcation, phase portrait and Hamiltonian function are firstly investigated to examine the system inherent behaviors. Besides, basins of attraction are briefly depicted to grasp the effects of initial offset and AC excitation on the system global dynamics. Then, variation of equivalent natural frequency versus DC voltage is analyzed. Results show that initial offset may induce complex frequency rebound phenomenon as well as a separate frequency branch under secondary pull-in condition. In what follows, emergences of softening, linear and hardening vibration are classified through discussing a key parameter obtained from the frequency response equation. New linear behavior induced by initial offset imperfection is found, which exhibits much higher sensitivity to DC voltage. Medium- and large-amplitude in-well motions are also investigated, indicating the existence of alternations of softening and hardening behaviors. Finally, lumped parameters are deduced via Galerkin procedure, and case studies are provided to illustrate the effectiveness of the whole analysis.





























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Younis, M.I.: MEMS Linear and Nonlinear Statics and Dynamics. Springer, NewYork (2011)
Lee, K.B.: Principles of Microelectromechanical Systems. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Liu, C.: Foundations of MEMS. China Machine Press, Beijing (2008)
Hu, Y.C., Chang, C.M., Huang, S.C.: Some design considerations on the electrostatically actuated microstructures. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 112, 155–161 (2004)
Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Nayfeh, A.H.: Secondary resonances of electrically actuated resonant microsensors. J. Micromech. Microeng. 13, 491–501 (2003)
Najar, F., Choura, S., Abdel-Rahman, E.M., El-Borgi, S., Nayfeh, A.H.: Dynamic analysis of variable-geometry electrostatic microactuators. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, 2449–2457 (2006)
Hammad, B.K., Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Nayfeh, A.H.: Modeling and analysis of electrostatic MEMS filters. Nonlinear Dyn. 60, 385–401 (2010)
Li, Y., Fan, S.C., Guo, Z.S., Li, J., Cao, L.: Study of dynamic characteristics of resonators for MEMS resonant vibratory gyroscopes. Microsyst. Technol. 18, 639–647 (2012)
Nayfeh, A.H., Younis, M.I., Abdel-Rahman, E.M.: Dynamic pull-in phenomenon in MEMS resonators. Nonlinear Dyn. 48, 153–163 (2007)
Zhang, W.M., Yan, H., Peng, Z.K., Meng, G.: Electrostatic pull-in instability in MEMS/NEMS: a review. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 214, 187–218 (2014)
Nayfeh, A.H., Younis, M.I., Abdel-Rahman, E.M.: Reduced-order models for MEMS applications. Nonlinear Dyn. 41, 211–236 (2005)
Nayfeh, A.H., Ouakad, H.M., Najar, F., Choura, S., Abdel-Rahman, E.M.: Nonlinear dynamics of a resonant gas sensor. Nonlinear Dyn. 59, 607–618 (2010)
Elshurafa, A.M., Khirallah, K., Tawfik, H.H., Emira, A.: Nonlinear dynamics of spring softening and hardening in folded-MEMS comb drive resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 20, 943–958 (2011)
Younesian, D., Sadri, M., Esmailzadeh, E.: Primary and secondary resonance analyses of clamped–clamped micro-beams. Nonlinear Dyn. 76, 1867–1884 (2014)
Xu, T.T., Younis, M.I.: Nonlinear dynamics of carbon nanotubes under large electrostatic force. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 11, 021009 (2016)
Younis, M.I., Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Nayfeh, A.H.: A reduced-order model for electrically actuated microbeam-based MEMS. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 15, 672–680 (2003)
Mestrom, R.M.C., Fey, R.H.B., Phan, K.L., Nijmeijer, H.: Simulations and experiments of hardening and softening resonances in a clamped–clamped beam MEMS resonator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 162, 225–234 (2010)
Rhoads, J.F., Shaw, S.W., Turner, K.L.: The nonlinear response of resonant microbeam systems with purely-parametric electrostatic actuation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, 890–899 (2006)
Alkharabsheh, S.A., Younis, M.I.: Statics and dynamics of MEMS arches under axial forces. J. Vib. Acoust. 135, 021007 (2013)
Krylov, S., Harari, I., Cohen, Y.: Stabilization of electrostatically actuated microstructures using parametric excitation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 1188–1204 (2005)
Mobki, H., Rezazadeh, G., Sadeghi, M., Vakili-Tahami, F., Seyyed-Fakhrabadi, M.M.: A comprehensive study of stability in an electro-statically actuated micro-beam. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 48, 78–85 (2013)
Stanciulescu, I., Mitchell, T., Chandra, Y., Eason, T., Spottswood, M.: A lower bound on snap-through instability of curved beams under thermomechanical loads. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 47, 561–575 (2012)
Younis, M.I., Ouakad, H.M., Alsaleem, F.M., Miles, R., Cui, W.L.: Nonlinear dynamics of MEMS arches under harmonic electrostatic actuation. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 19, 647–656 (2010)
Mora, K., Gottlieb, O.: Parametric excitation of a microbeam-string with asymmetric electrodes: multimode dynamics and the effect of nonlinear damping. J. Vib. Acoust. 139, 040903 (2017)
Krylov, S., Ilic, B.R., Schreiber, D., Seretensky, S., Craighead, H.: The pull-in behavior of electrostatically actuated bistable microstructures. J. Micromech. Microeng. 18, 055026 (2008)
Tajaddodianfar, F., Pishkenari, H.N., Yazdi, M.R.H.: Prediction of chaos in electrostatically actuated arch micro-nano resonators: analytical approach. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 30, 182–195 (2016)
Medina, L., Gilat, R., Llic, B.R., Krylov, S.: Experimental dynamic trapping of electrostatically actuated bistable micro-beams. Appl. Phys. Lett. 108, 073503 (2016)
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y.S., Li, Z.H., Huang, Y.B., Li, D.H.: Snap-through and pull-in instabilities of an arch-shaped beam under an electrostatic loading. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 16, 684–693 (2007)
Chen, X., Meguid, S.A.: On the parameters which govern the symmetric snap-through buckling behavior of an initially curved microbeam. Int. J. Solids Struct. 66, 77–87 (2015)
Ouakad, H.M.: Electrostatic fringing-fields effects on the structural behavior of MEMS shallow arches. Microsyst. Technol. 1–9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-016-2985-1
Jia, X.L., Yang, J., Kitipornchai, S., Lim, C.W.: Pull-in instability and free vibration of electrically actuated poly-SiGe graded micro-beams with a curved ground electrode. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 1875–1884 (2012)
Ouakad, H.M., Younis, M.I.: The dynamic behavior of MEMS arch resonators actuated electrically. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 45, 704–713 (2010)
Das, K., Batra, R.C.: Symmetry breaking, snap-through and pull-in instabilities under dynamic loading of microelectromechanical shallow arches. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 115008 (2009)
Krylov, S., Dick, N.: Dynamic stability of electrostatically actuated initially curved shallow micro beams. Contin. Mech. Therm. 22, 445–468 (2010)
Farokhi, H., Ghayesh, M.H., Hussain, S.: Pull-in characteristics of electrically actuated MEMS arches. Mech. Mach. Theory 98, 133–150 (2016)
Ouakad, H.M.: An electrostatically actuated MEMS arch band-pass filter. Shock Vib. 20, 809–819 (2013)
Ramini, A.H., Hennawi, Q.M., Younis, M.I.: Theoretical and experimental investigation of the nonlinear behavior of an electrostatically actuated in-plane MEMS arch. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 25, 570–578 (2016)
Ghayesh, M.H., Farokhi, H., Alici, G.: Size-dependent electro-elasto-mechanics of MEMS with initially curved deformable electrodes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 103, 247–264 (2015)
Ruzziconi, L., Lenci, S., Younis, M.I.: An imperfect microbeam under an axial load and electric excitation: nonlinear phenomena and dynamical integrity. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23, 1350026 (2013)
Ruzziconi, L., Younis, M.I., Lenci, S.: An efficient reduced-order model to investigate the behavior of an imperfect microbeam under axial load and electric excitation. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 8, 011014 (2013)
Ramini, A., Bellaredj, M.L.F., Al Hafiz, M.A., Younis, M.I.: Experimental investigation of snap-through motion of in-plane MEMS shallow arches under electrostatic excitation. J. Micromech. Microeng. 26, 015012 (2015)
Rahim, F.A., Younis, M.I.: Control of bouncing in MEMS switches using double electrodes. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 3479752 (2016)
Krylov, S.: Parametric excitation and stabilization of electrostatically actuated microstructures. Int. J. Multiscale Comput. 6, 563–584 (2009)
Han, J.X., Zhang, Q.C., Wang, W.: Static bifurcation and primary resonance analysis of a MEMS resonator actuated by two symmetrical electrodes. Nonlinear Dyn. 80, 1585–1599 (2015)
Han, J.X., Zhang, Q.C., Wang, W.: Design considerations on large amplitude vibration of a doubly clamped microresonator with two symmetrically located electrodes. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 22, 492–510 (2015)
Mestrom, R.M.C., Fey, R.H.B., van Beek, J.T.M., Phan, K.L., Nijmeijer, H.: Modelling the dynamics of a MEMS resonator: simulations and experiments. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 142, 306–315 (2008)
Luo, A.C.J., Wang, F.Y.: Chaotic motion in a microelectro-mechanical system with non-linearity from capacitors. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 7, 31–49 (2002)
Lenci, S., Rega, G.: Control of pull-in dynamics in a nonlinear thermoelastic electrically actuated microbeam. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, 390–401 (2006)
Lakrad, F., Belhaq, M.: Suppression of pull-in instability in MEMS using a high-frequency actuation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15, 3640–3646 (2010)
Haghighi, H.S., Markazi, A.H.D.: Chaos prediction and control in MEMS resonators. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15, 3091–3099 (2010)
Ibrahim, M.I., Younis, M.I.: The dynamic response of electrostatically driven resonators under mechanical shock. J. Micromech. Microeng. 20, 025006 (2010)
Tusset, A.M., Balthazar, J.M., Bassinello, D.G., Pontes, B.R., Felix, J.L.P.: Statements on chaos control designs, including a fractional order dynamical system, applied to a “MEMS” comb-drive actuator. Nonlinear Dyn. 69, 1837–1857 (2012)
Chen, C.P., Hu, H.T., Dai, L.M.: Nonlinear behavior and characterization of a piezoelectric laminated microbeam system. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18, 1304–1315 (2013)
Tajaddodianfar, F., Pishkenari, H.N., Yazdi, M.R.H., Miandoab, E.M.: On the dynamics of bistable micro/nano resonators: analytical solution and nonlinear behavior. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 20, 1078–1089 (2015)
Miandoab, E.M., Yousefi-Koma, A., Pishkenari, H.N., Tajaddodianfar, F.: Study of nonlinear dynamics and chaos in MEMS/NEMS resonators. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 22, 611–622 (2015)
Shao, S., Masri, K.M., Younis, M.I.: The effect of time-delayed feedback controller on an electrically actuated resonator. Nonlinear Dyn. 74, 257–270 (2013)
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.T.: Nonlinear Oscillations. Wiley, New York (2008)
Alkharabsheh, S.A., Younis, M.I.: Dynamics of MEMS arches of flexible supports. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 22, 216–224 (2013)
Alsaleem, F.M., Younis, M.I., Ruzziconi, L.: An experimental and theoretical investigation of dynamic pull-in in MEMS resonators actuated electrostatically. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 19, 794–806 (2010)
Nayfeh, A.H., Balachandran, B.: Applied Nonlinear Dynamics. Wiley, New York (1995)
Masri, K.M., Shao, S., Younis, M.I.: Delayed feedback controller for microelectromechanical systems resonators undergoing large motion. J. Vib. Control. 21, 2604–2615 (2015)
Najar, F.: Static and Dynamic Behaviors of MEMS Microactuators. University of Waterloo, Waterloo (2008)
Kacem, N., Hentz, S., Pinto, D., Reig, B., Nguyen, V.: Nonlinear dynamics of nanomechanical beam resonators: improving the performance of NEMS-based sensors. Nanotechnology 20, 275501 (2009)
Azizi, S., Ghazavi, M.R., Khadem, S.E., Rezazadeh, G., Cetinkaya, C.: Application of piezoelectric actuation to regularize the chaotic response of an electrostatically actuated micro-beam. Nonlinear Dyn. 73, 853–867 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 11702192, 11372210, 11772218, 51405343, 11602169), Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (Grant no. 15JCQNJC05000, 16JCQNJC04700), Innovation Team Training Plan of Tianjin Universities and colleges (Grant no. TD12-5043), Tianjin Science and Technology Planning Project (Grant no. 15ZXZNGX00220) and the Scientific Research Foundation of Tianjin University of Technology and Education (Grant no. KYQD1701, KYQD16009) and Scientific Research Program of Tianjin Education Committee (Grant no. JWK1602).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Qi, H., Jin, G. et al. Mechanical behaviors of electrostatic microresonators with initial offset imperfection: qualitative analysis via time-varying capacitors. Nonlinear Dyn 91, 269–295 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3868-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3868-4