Abstract
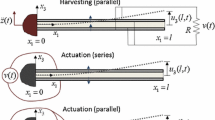
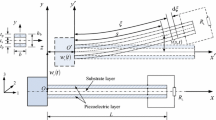
We explore the modeling and analysis of nonlinear nonconservative dynamics of macro-fiber composite (MFC) piezoelectric structures, guided by rigorous experiments, for resonant vibration-based energy harvesting, as well as other applications leveraging the direct piezoelectric effect, such as resonant sensing. The MFCs employ piezoelectric fibers of rectangular cross section embedded in Kapton with interdigitated electrodes to exploit the 33-mode of piezoelectricity. Existing modeling and analysis efforts for resonant nonlinearities have so far considered conventional piezoceramics that use the 31-mode of piezoelectricity. In the present work, we develop a framework to represent and predict nonlinear electroelastic dynamics of MFC bimorph cantilevers under resonant base excitation for primary resonance behavior. The interdigitated electrodes are shunted to a set of resistive electrical loads to quantify the electrical power output. Experiments are conducted on a set of MFC bimorphs over a broad range of mechanical excitation levels to identify the types of nonlinearities present and to compare the harmonic balance model predictions and experiments. The experimentally observed interaction of quadratic piezoelectric material softening and cubic geometric hardening effects is captured and demonstrated by the model. It is shown that the linearized version of the model yields highly inaccurate results for typical base acceleration levels and frequencies involved in vibration energy harvesting, while the nonlinear framework presented here can accurately predict the amplitude-dependent resonant frequency response.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hagood, N.W., Chung, W.H., von Flotow, A.: Modeling of piezoelectric actuator dynamics for active structural control. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1, 327–354 (1990)
Hagood, N.W., von Flotow, A.: Damping of structural vibrations with piezoelectric materials and passive electrical networks. J. Sound Vib. 146(2), 243–268 (1991)
Smits, J.G., Choi, W.S.: The constituent equations of piezoelectric heterogeneous bimorphs. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 38(3), 256–270 (1991)
Dosch, J.J., Inman, D.J., Garcia, E.: A self-sensing piezoelectric actuator for collocated control. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 3(1), 166–185 (1992)
Baz, A., Ro, J.: Vibration control of plates with active constrained layer damping. Smart Mater. Struct. 5(3), 272 (1996)
Leo, D.J.: Engineering Analysis of Smart Material Systems. Wiley, Hoboken (2007)
Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: An experimentally validated bimorph cantilever model for piezoelectric energy harvesting from base excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 18(2), 025009 (2009)
Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. Wiley, Chichester (2011)
Erturk, A.: Assumed-modes modeling of piezoelectric energy harvesters: Euler–Bernoulli, Rayleigh, and Timoshenko models with axial deformations. Comput. Struct. 106, 214–227 (2012)
Leadenham, S., Erturk, A.: Unified nonlinear electroelastic dynamics of a bimorph piezoelectric cantilever for energy harvesting, sensing, and actuation. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(3), 1727–1743 (2015)
Leadenham, S., Erturk, A.: Nonlinear M-shaped broadband piezoelectric energy harvester for very low base accelerations: primary and secondary resonances. Smart Mater. Struct. 24(5), 055021 (2015)
Yuan, T., Yang, J., Chen, L.: Experimental identification of hardening and softening nonlinearity in circular laminated plates. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 95, 296–306 (2017)
Yuan, T., Yang, J., Chen, L.: Nonlinear characteristic of a circular composite plate energy harvester: experiments and simulations. Nonlinear Dyn. 90(4), 2495–2506 (2017)
Feenstra, J., Granstrom, J., Sodano, H.: Energy harvesting through a backpack employing a mechanically amplified piezoelectric stack. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 22(3), 721–734 (2008)
Cunefare, K.A., Skow, E.A., Erturk, A., Savor, J., Verma, N., Cacan, M.R.: Energy harvesting from hydraulic pressure fluctuations. Smart Mater. Struct. 22(2), 025036 (2013)
Zhao, S., Erturk, A.: Deterministic and band-limited stochastic energy harvesting from uniaxial excitation of a multilayer piezoelectric stack. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 214, 58–65 (2014)
Skow, E.A., Cunefare, K.A., Erturk, A.: Power performance improvements for high pressure ripple energy harvesting. Smart Mater. Struct. 23(10), 104011 (2014)
Shahab, S., Erturk, A.: Contactless ultrasonic energy transfer for wireless systems: acoustic-piezoelectric structure interaction modeling and performance enhancement. Smart Mater. Struct. 23(12), 125032 (2014)
Shahab, S., Gray, M., Erturk, A.: Ultrasonic power transfer from a spherical acoustic wave source to a free-free piezoelectric receiver: modeling and experiment. J. Appl. Phys. 117(10), 104903 (2015)
Bent, A.A., Hagood, N.W.: Piezoelectric fiber composites with interdigitated electrodes. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 8(11), 903–919 (1997)
Bent, A.A.: Active fiber composites for structural actuation. Thesis (1997)
Bent, A.A., Hagood, N.W., Rodgers, J.P.: Anisotropic actuation with piezoelectric fiber composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 6(3), 338–349 (1995)
Wilkie, W.K., Bryant, R.G., High, J.W., Fox, R.L., Hellbaum, R.F., Jalink, A., Jr., Little, B.D., Mirick, P.H.: Low-cost piezocomposite actuator for structural control applications. In: SPIE’s 7th Annual International Symposium on Smart Structures and Materials, pp. 323–334. International Society for Optics and Photonics
Wilkie, W.K., High, J.W.: Method of fabricating NASA-standard macro-fiber composite piezoelectric actuators, NASA/TM-2003-212427, NASA (2003)
Browning, J.S.: F-16 ventral fin buffet alleviation using piezoelectric actuators. Thesis (2009)
Sodano, H.A., Park, G., Inman, D.J.: An investigation into the performance of macro-fiber composites for sensing and structural vibration applications. Mechan. Syst. Signal Process. 18(3), 683–697 (2004)
Erturk, A., Delporte, G.: Underwater thrust and power generation using flexible piezoelectric composites: an experimental investigation toward self-powered swimmer-sensor platforms. Smart Mater. Struct. 20(12), 125013 (2011)
Cen, L., Erturk, A.: Bio-inspired aquatic robotics by untethered piezohydroelastic actuation. Bioinspir. Biomim. 8(1), 016006 (2013)
Collet, M., Ruzzene, M., Cunefare, K.A.: Generation of lamb waves through surface mounted macro-fiber composite transducers. Smart Mater. Struct. 20(2), 025020 (2011)
Matt, H.M., di Scalea, F.L.: Macro-fiber composite piezoelectric rosettes for acoustic source location in complex structures. Smart Mater. Struct. 16(4), 1489 (2007)
Kim, D.K., Han, J.H.: Smart flapping wing using macrofiber composite actuators. In: Smart Structures and Materials, pp. 61730F. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham
Kim, D.K., Kim, H.I., Han, J.H., Kwon, K.J.: Experimental investigation on the aerodynamic characteristics of a biomimetic flapping wing with macro-fiber composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 19(3), 423–431 (2008)
Bilgen, O., Kochersberger, K.B., Inman, D.J., Ohanian, O.J.: Novel, bidirectional, variable-camber airfoil via macro-fiber composite actuators. J. Aircr. 47(1), 303–314 (2010)
Paradies, R., Ciresa, P.: Active wing design with integrated flight control using piezoelectric macro fiber composites. Smart Mater. Struct. 18(3), 035010 (2009)
Cha, Y., Kim, H., Porfiri, M.: Energy harvesting from underwater base excitation of a piezoelectric composite beam. Smart Mater. Struct. 22(11), 115026 (2013)
Shahab, S., Erturk, A.: Electrohydroelastic dynamics of macro-fiber composites for underwater energy harvesting from base excitation. In: SPIE Smart Structures and Materials+ Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, vol. 9057, pp. 90570C. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham
Shahab, S., Erturk, A.: Underwater dynamic actuation of macro-fiber composite flaps with different aspect ratios: electrohydroelastic modeling, testing, and characterization. In: ASME 2014 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, pp. V002T06A007. American Society of Mechanical Engineers
Shahab, S., Erturk, A.: Unified electrohydroelastic investigation of underwater energy harvesting and dynamic actuation by incorporating Morison’s equation. In: SPIE Smart Structures and Materials+ Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, pp. 94310C. International Society for Optics and Photonics
Shahab, S., Erturk, A.: Experimentally validated nonlinear electrohydroelastic Euler-Bernoulli-Morison model for macro-fiber composites with different aspect ratios. In: ASME 2015 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, pp. V008T13A030. American Society of Mechanical Engineers
Shahab, S., Tan, D., Erturk, A.: Hydrodynamic thrust generation and power consumption investigations for piezoelectric fins with different aspect ratios. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 224(17–18), 3419–3434 (2015)
Cha, Y., Chae, W., Kim, H., Walcott, H., Peterson, S.D., Porfiri, M.: Energy harvesting from a piezoelectric biomimetic fish tail. Renew. Energy 86, 449–458 (2016)
Williams, R.B., Inman, D.J., Wilkie, W.K.: Temperature-dependent thermoelastic properties for macro fiber composite actuators. J. Therm. Stresses 27(10), 903–915 (2004)
Williams, R.B., Grimsley, B.W., Inman, D.J., Wilkie, W.K.: Manufacturing and mechanics-based characterization of macro fiber composite actuators. In: ASME 2002 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, pp. 79–89. American Society of Mechanical Engineers
Williams, R.B., Inman, D.J., Schultz, M.R., Hyer, M.W., Wilkie, W.K.: Nonlinear tensile and shear behavior of macro fiber composite actuators. J. Compos. Mater. 38(10), 855–869 (2004)
Deraemaeker, A., Nasser, H., Benjeddou, A., Preumont, A.: Mixing rules for the piezoelectric properties of macro fiber composites. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 20(12), 1475–1482 (2009)
Shahab, S., Erturk, A.: Coupling of experimentally validated electroelastic dynamics and mixing rules formulation for macro-fiber composite piezoelectric structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 28(12), 1575–1588 (2017)
Shahab, S., Erturk, A.: Electrohydroelastic Euler–Bernoulli–Morison model for underwater resonant actuation of macro-fiber composite piezoelectric cantilevers. Smart Mater. Struct. 25(10), 105007 (2016)
Goldschmidtboeing, F., Eichhorn, C., Wischke, M., Kroener, M., Woias, P.: The influence of ferroelastic hysteresis on mechanically excited PZT cantilever beams. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Workshop on Micro and Nanotechnology for Power Generation and Energy Conversion Applications, pp. 114–117
Agarwal, B .D., Broutman, L .J., Chandrashekhara, K.: Analysis and Performance of Fiber Composites. Wiley, Hoboken (2006)
Crespo da Silva, M .R .M., Glynn, C .C.: Nonlinear flexural-flexural-torsional dynamics of inextensional beams. i. equations of motion. J. Struct. Mech. 6(4), 437–448 (1978)
Malatkar, P.: Nonlinear vibrations of cantilever beams and plates. Thesis (2003)
Tan, D., Erturk, A.: In vacuo elastodynamics of a flexible cantilever for wideband energy harvesting. In: SPIE Smart Structures and Materials+ Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.T.: Nonlinear Oscillations. Wiley, Hoboken (2008)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the NSF Grant CMMI-1254262, which is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, D., Yavarow, P. & Erturk, A. Resonant nonlinearities of piezoelectric macro-fiber composite cantilevers with interdigitated electrodes in energy harvesting. Nonlinear Dyn 92, 1935–1945 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4172-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4172-7