Abstract
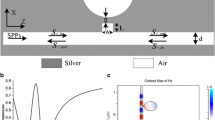
We present a nano-scale electro-plasmonic scheme operating at 1550 nm based on plasmonic Metal-Insulator-Metal waveguide and stub filter configuration. The linear dependency of the transmission spectra of the stub filter to the length of the stubs allows designing a switch that works as normally ON or OFF switch by selecting the length of the stubs 300 or 410 nm, respectively. In our proposed waveguide-based structure, the core is an electro-optic material known as 4-dimethyl-amino-Nmethyl-4-stilbazolium tosylate with the refractive index 2.2 while the metal cladding is silver. Three-dimensional Finite Element Method simulations demonstrated that by applying a 10 V voltage to the silver cladding, a red-shift in the transmission spectra of the filter leads to turn the switch OFF or ON with calculated extinction ratio \(-13.83\) and 11.81 dB, respectively. The calculation of the capacitance implies that the switching rise-time of the switch is less than 20 fs and the bandwidth is far beyond the 18 GHz. At the maximum dimension \(460\,\hbox {nm}\times 450\,\hbox {nm}\), the subwavelength size of the switch promises the potential for future compact integrated plasmonic circuitry. For the verification of three dimensional simulation results, we have tried it, using two-dimensional transmission line method for modeling the stub filter, which demonstrates a reasonable accuracy in comparison with three-dimensional finite element method.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes, W.L., Dereux, A., Ebbesen, T.W.: Surface Plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424, 824–830 (2003)
Çetin, A., Yanik, A., Mertiri, A., Erramilli, A., Müstecaplıoğlu, Ö., Altug, H.: Field-effect active plasmonics for ultracompact electro-optic switching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 121113 (2012)
Collin, S., Pardo, F., Pelouard, J.: Waveguiding in nanoscale metallic apertures. Opt. Express 15(7), 4310–4320 (2007)
Gramotnev, D.K., Bozhevolnyi, S.I.: Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit. Nat. Photon. 4, 83–91 (2010)
Jin, Z.Y., Guange, H.X., Xian, M.: A surface plasmon polariton electro-optic switch based on a metal-insulator-metal structure with a strip waveguide and two side-coupled cavities. Chin. Phys. Lett. 29(6), 064214 (2012)
Kaatuzian, H.: Quantum Photonics, A Theory for Attosecond Optics. AKU Press, Tehran (2012)
Liu, J., Fang, G., Zhao, G., Zhang, Y., Liu, S.: Surface plasmon reflector based on serial stub structure. Opt. Express 17, 20134–20139 (2009)
Liu, Y., Zhou, F., Cao, J., Mao, Q.: High-extinction-ratio and low-insertion-loss plasmonic filter with coherent coupled nano-cavity array in a MIM waveguide. Plasmonics 8, 1035–1041 (2013)
Manolatou, C., Lipson, M.: All-optical silicon modulators based on carrier injection by two-photon absorption. J. Lightwave Technol. 24(3), 1433–1439 (2006)
Mei, X., Huang, X., Jin, T.: A sub-wavelength electro-optic switch based on plasmonic T-shaped waveguide. Plasmonics 6, 613–618 (2011)
Min, C., Veronis, G.: Absorption switches in metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguides. Opt. Express 17(13), 10757–10766 (2009)
Naseri Taheri, A., Kaatuzian, H.: Simulation and design of a submicron ultrafast plasmonic switch based on nonlinear doped silicon MIM waveguide. J. Comput. Commun., 1, 23–16 (2013). Scientific Research Publishers
Nielsen, M., Elezzabi, A.: Frequency-selective 3-D integration of nanoplasmonic circuits on a Si platform. Opt. Express 20(8), 8592–8597 (2012)
Pan, F., McCallion, K., Chiappetta, N.: Waveguide fabrication and high-speed in-line intensity modulation in 4-N, N-48-dimethylamino-48-N8-methyl-stilbazolium tosylate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 74(4), 492–494 (1999)
Pannipitiya, A., Rukhlenko, I.D., Premaratne, M., Hattori, H.T., Agrawal, G.P.: Improved transmission model for metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguides with stub structure. Opt. Express 18(6), 6191 (2010)
Park, J., Kim, H., Lee, B.: High order plasmonic Bragg reflection in the metal-insulator-metal waveguide Bragg grating. Opt. Express 16(1), 413–425 (2008)
Perron, D., Wu, M., Horvath, C., Bachman, D., Van, V.: All-plasmonic switching based on thermal nonlinearity in a polymer plasmonic microring resonator. Opt. Lett. 36(14), 2731–2733 (2011)
Sederberg, S., Driedger, D., Nielsen, M., Elezzabi, A.Y.: Ultrafast all-optical switching in a silicon-based plasmonic nanoring resonator. Opt. Express 19(2), 23494–23503 (2011)
Sweatlock, L., Diest, K.: Vanadium dioxide based plasmonic modulators. Opt. Express 20(18), 8700–8709 (2012)
Tao, J., Wang, Q., Haung, X.: All-optical plasmonic switches based on coupled nano-disk cavity structures containing nonlinear material. Plasmonics 6, 753–759 (2011)
Thomas, R., Ikonic, Z., Kelsall, R.: Electro-optic metal-insulator-semiconductor-insulator-metal Mach-Zehnder plasmonic modulator. Photon. Nanostruct. Fundam. Appl. 10, 183–189 (2012)
Yu, Z., Veronis, G., Fanb, S.: Gain-induced switching in metal-dielectric-metal plasmonic waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 041117 (2008)
Zho, J., Huang, X., Mei, X.: Plasmonic electro-optical switches operating at telecom wavelengths. Plasmonics 6, 605–612 (2011)
Zhu, J., Huang, X., Xu, W.: Plasmonic optical switches based on Mach-Zender interferometer. Phys. Plasmas 18, 072112 (2011)
Zia, R., Schuller, J.A., Chandran, A., Brongersma, M.L.: Plasmonics: The next chip-scale technology. Mater. Today 9, 20–27 (2006)
Zografopoulos, D.C., Beccherelli, R.: Long-range plasmonic directional coupler switches controlled by nematic liquid crystals. Opt. Express 21(7), 8240–8250 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taheri, A.N., Kaatuzian, H. Numerical investigation of a nano-scale electro-plasmonic switch based on metal-insulator-metal stub filter. Opt Quant Electron 47, 159–168 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-014-9895-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11082-014-9895-1