Abstract
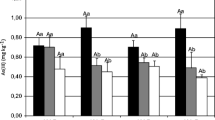
A split root device was designed to assess the possible role of AMF in translocation and detoxification of As by maize plants. Half of each maize root system grew in As-amended or unamended soil and the remainder was inoculated with either Glomus mosseae or Acaulospora morrowiae. External mycelium was collected from a third compartment. Neither shoot nor root As concentrations were affected by inoculation with either fungus. Soil As amendment produced higher As concentrations in roots in the second compartment and in the external mycelium. The As concentrations in the matrix solution of the second root compartment were lower in mycorrhizal treatments with no differences in soluble As in the hyphal compartments. Mycorrhiza exerted little effect on As translocation within plants but may have influenced root As efflux. Deposition of As in external mycelium indicates a possible role of mycorrhizal fungi in the detoxification of As in the host plants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin MJ, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2002) Uptake kinetics of arsenic species in rice plants. Plant Physiol 128:1120–1128
Ahmed FRS, Killham K, Alexander I (2006) Influences of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae on growth and nutrition of lentil irrigated with arsenic contaminated water. Plant Soil 258:33–41
Al Agely A, Sylvia DM, Ma LQ (2005) Mycorrhizae increase arsenic uptake by the hyperaccumulator Chinese brake fern (Pteris vittata L.). J Environ Qual 34:2181–2186
Campos V, Aparecida M, Pires F (2004) Phytoremoval of arsenic from soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 35:2137–2146
Chen BD, Christie P, Li XL (2001) A modified glass bead compartment cultivation system for studies on nutrient and trace metal uptake by arbuscular mycorrhiza. Chemosphere 42:185–192
Chen BD, Christie P, Zhu YG, Smith FA, Xie ZM, Smith SE (2007) The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae gives contradictory effects on phosphorus and arsenic acquisition by Medicago sativa Linn. Sci Total Environ 379:226–236
Duan GL, Zhu YG, Tong YP, Cai C, Kneer R (2005) Characterization of arsenate reductase in the extract of root and fronds of Chinese brake fern, an arsenic hyperaccumulator. Plant Physiol 138:461–469
Ghosh M, Shen J, Rosen BP (1999) Pathways of As (III) detoxification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:5001–5006
Giovannetti M, Mosse B (1980) An evaluation of techniques for measuring vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in roots. New Phytol 84:489–500
Göhre V, Paszkowski U (2006) Contribution of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis to heavy metal phytoremediation. Planta 223:1115–1122
Gonzalez-Chavez C, Harris PJ, Dodd J, Meharg AA (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi confer enhanced arsenate resistance on Holcus lanatus. New Phytol 155:163–171
Harrison MJ, van Buuren ML (1995) A phosphate transporter from the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus versiforme. Nature 378:626–632
Harrison MJ, Dewbre GR, Liu J (2002) A phosphate transporter from Medicago trunculata involved in the acquisition of phosphate released by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Plant Cell 14:1–17
Joner EJ, Briones R, Leyval C (2000) Metal binding capacity of arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelium. Plant Soil 226:227–234
Khan AG, Kuek C, Chaudhry TM, Khoo CS, Hayes WJ (2000) Role of plants, mycorrhizae and phytochelators in heavy metal contaminated land remediation. Chemosphere 41:197–207
Leung HM, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2006) Interactions of mycorrhizal fungi with Pteris vittata (As hyperaccumulator) in As-contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 139:1–8
Maldonado-Mendoza IE, Dewbre GR, Harrison MJ (2001) A phosphate transporter gene from the extraradical mycelilum of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices is regulated in response to phosphate in the environment. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:1140–1148
Mallarino AP, Atia AM (2005) Correlation of a resin membrane soil phosphorus test with corn yield and routine soil tests. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:266–272
Meharg AA (2004) Arsenic in rice: understanding a new disaster for South-East Asia. Trends Plant Sci 9:415–417
Meharg AA, Macnair MR (1991) The mechanisms of arsenate tolerance in Deschampsia cespitosa (L.) Beauv and Agrostis capillaris L. New Phytol 119:291–297
Meharg AA, Hartley-Whitaker J (2002) Arsenic uptake and metabolism in arsenic resistant and nonresistant plant species. New Phytol 154:29–43
Meharg AA, Bailey J, Breadmore K, Nacnair MR (1994) Biomass allocation, phosphorus nutrition and vesicular–arbuscular mycorrhizal infection in clones of Yorkshire fog, Holcus lanatus L (Poaceae) that differ in their phosphate uptake kinetics and tolerance to arsenate. Plant Soil 160:11–20
Mukhopadhyay R, Rosen BP (2002) Arsenate reductase in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Environ Health Perspect 110:745–748
Mukhopadhyay R, Shi J, Rosen BP (2000) Purification and characterization of Acr2p, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae arsenate reductase. J Biol Chem 275:21149–21157
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp 403–430
Quaghebeur M, Rengel Z (2003) The distribution of arsenate and arsenite in shoots and roots of Holcus lanatus is influenced by arsenic tolerance and arsenate and phosphate supply. Plant Physiol 132:1600–1609
Rausch C, Darram P, Brunner S, Jansa J, Laloi M, Leggewie G et al (2001) A phosphate transporter expressed in arbuscule-containing cells in potato. Nature 414:462–470
Rosen BP (2002) Biochemistry of arsenic detoxification. FEBS Lett 529:86–92
Salt DE, Prince RC, Pickering IJ (2002) Chemical speciation of accumulated metals in plants: evidence from X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Microchem J 71:255–259
Sharples JM, Meharg AA, Chambers SM, Cairney JWG (2000) Mechanism of arsenate resistance in the ericoid mycorrhizal fungus Hymenoscyphus ericae. Plant Physiol 124:1327–1334
Shi J, Vlamis-Gardikas A, Aslund F, Holmgren A, Rosen BP (1999) Reactivity of glutaredoxins 1, 2, and 3 from Escherichia coli shows that glutaredoxin 2 is the primary hydrogen donor to arsC-catalyzed arsenate reduction. J Biol Chem 274:36039–36042
Smith SE, Read DJ (1997) Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Academic, London
Smith SE, Smith AF, Jakobsen I (2003) Mycorrhizal fungi can dominate phosphate supply to plants irrespective of growth responses. Plant Physiol 133:16–20
Trota A, Falaschi P, Cornara L, Minganti V, Fusconi A, Drava G et al (2006) Arbuscular mycorrhizae increase the arsenic translocation factor in the As hyperaccumulating fern Pteris vittata L. Chemosphere 65:74–81
Ullrich-Eberius CI, Sanz A, Novacky AJ (1989) Evaluation of arsenate and vandate-associated changes of electrical membrane potential and phosphate transport in Lemna gibba GI. J Exp Bot 40:119–128
Ultra V, Tanaka S, Sakurai K, Iwasaki K (2007a) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhiza and phosphorus application on arsenic toxicity in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and on the transformation of arsenic in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 290:29–41
Ultra V, Tanaka S, Sakurai K, Iwasaki K (2007b) Arbuscular mycorrhiza fungus (Glomus aggregatum) influences biotransformation of arsenic in the rhizosphere of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53:499–508
USEPA (1983) Method 3050. Acid digestion of sludges. Test methods for evaluating solid waste-Physical/chemical methods. SW846. USEPA, Washington, DC
Wachaupe RD (1983) Uptake, translocation and phytotoxicity of arsenic in plants. In: Fensterheim L (ed) Arsenic: industrial, biomédica, environmental perspectives. Arsenic Symposium, Gaithersburg, MD. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, pp 348–374
Webb SM, Gaillard JF, Ma LQ, Tu C (2003) (XAS) speciation of arsenic in a hyper-accumulating fern. Environ Sci Technol 37:754–760
Xu XY, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2007) Rapid reduction of arsenate in the medium mediated by plant roots. New Phytol 176:590–599
Xu PL, Christie P, Liu Y, Zhang JL, Li XL (2008) The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae can enhance arsenic tolerance in Medicago truncatula by increasing plant phosphorus status and restricting arsenate uptake. Environ Pollut doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2008.01.003
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Projects 30571105 and 30370818), the British Council (Project DelPHE 1.64) and the Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry. We also thank two anonymous reviewers whose helpful suggestions have greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: F. Andrew Smith.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, ZH., Zhang, JL., Christie, P. et al. Influence of inoculation with Glomus mosseae or Acaulospora morrowiae on arsenic uptake and translocation by maize. Plant Soil 311, 235–244 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9677-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9677-2