Abstract
Background and aims
Endophytic actinobacteria are known to benefit their hosts by improving plant growth and by reducing the severity of soil borne diseases. In this study, their role in enhancing the growth of lucerne and their interaction with its rhizobial symbiosis is examined. Comparison is made between endophytic actinobacteria isolated from wheat plants and isolates from the roots and nodules of four different legume species: lucerne (Medicago sativa L.), field pea (Pisum sativum L.), subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum L.) and burr medic (Medicago polymorpha L.).
Methods
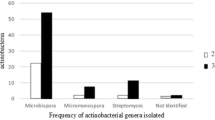
Two hundred and twenty five isolates of actinobacteria were recovered from the legumes. Five selected legume isolates were compared to five wheat isolates for their effects on rhizobial growth on agar and on the early nodulation and growth of lucerne plants inoculated with Sinorhizobium meliloti strain RRI 128.
Results
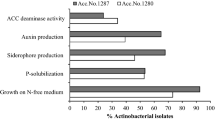
Co-inoculation with lucerne isolates Streptomyces spp. LuP30 and LuP47B, increased lucerne shoot dry weight at 7 weeks after inoculation by 25 to 35 %, and shoot nitrogen content by 22 to 28 % respectively, compared to plants treated with Sinorhizobium meliloti RRI 128 alone.
Conclusions
This study shows that some endophytic actinobacteria have the potential to enhance the lucerne – rhizobia symbiosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander DB, Zuberer DA (1991) Use of chrome azurol S reagents to evaluate siderophore production by rhizosphere bacteria. Biol Fertil Soils 12:39–45
Ali B, Hayat S, Hasan SA, Ahmad A (2008) A comparative effect of IAA and 4-Cl-IAA on growth, nodulation and nitrogen fixation in Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 30:35–41
Antoun H, Bordeleau LM, Gagnon C, Lachance RA (1978) Actinomycetes antagonistic to fungi and not affecting Rhizobium meliloti. Can J Microbiol 24:558–562
Beneduzi A, Peres D, Vargas LK, Bodanese-Zanettini MH, Passaglia LMP (2008) Evaluation of genetic diversity and plant growth promoting activities of nitrogen-fixing bacilli isolated from rice fields in South Brazil. Appl Soil Ecol 39:311–320
Coombs JT, Franco CMM (2003) Isolation and identification of actinobacteria from surface-sterilized wheat roots. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5603–5608
Coombs JT, Franco CMM, Loria R (2003) Complete sequencing and analysis of pEN2701, a novel 13-kb plasmid from an endophytic Streptomyces sp. Plasmid 49:86–92
Damirgi SM, Johnson HW (1966) Effect of soil actinomycetes on strains of Rhizobium japonicum. Agron J 58:223–224
Doumbou CL, Salove MKH, Crawford DL, Beaulieu C (2001) Actinomycetes, promising tools to control plant diseases and to promote plant growth. Phytoprotection 82:85–102
El-Tarabily KA, Nassar HA, Sivasithamparam K (2008) Promotion of growth of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in a calcareous soil by a phosphate-solubilizing, rhizosphere-competent isolate of Micromonospora endolithica. Appl Soil Ecol 39:161–171
Ferguson BJ, Indra Sumunar A, Hayashi S, Lin M, Lin Y, Reid DE, Gresshoff PM (2010) Molecular analysis of legume nodule development and autoregulation. J Integ Plant Biol 52:61–76
Fitscher H (1994) Genetic regulation of Nitrogen fixation in rhizobia. Microbiological Reviews 58:352–386
Franco CMM, Michelsen P, Percy N, Conn V, Listiana E, Moll S, Loria R, Coombs TJ (2007) Actinobacterial endophytes for improved crop performance Australasian. Plant Pathol 36:524–531
Giller KE (2001) Nitrogen fixation in tropical cropping systems. doi: 10.1079/9780851994178.0000
Gregor AK, Klubek B, Varsa EC (2003) Identification and use of actinomycetes for enhanced nodulation of soybean co-inoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Can J Microbiol 49:483–491
Khanmna S, Yokota A, Lumyong S (2009) Actinomycetes isolated from medicinal plant rhizosphere soils: diversity and screening of antifungal compounds, indole-3-acetic acid and siderophore production. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:649–655
Kiss SA, Stefanovits-Ba’nyai E, Taka’cs-Ha’jos M (2004) Magnesium-content of Rhizobium nodules in different plants: the importance of magnesium in nitrogen-fixation of nodules. J Am Coll Nutr 23:751S–753S
Le HX (2010) Interaction of endophytic actinobacteria with rhizobia in leguminous plants. Flinders University
Le HX, Franco CMM, Ballard RA (2014) Isolation and characterisation of endophytic actinobacteria and their effect on the early growth and nodulation of lucerne (Medicago sativa L.). In: Gupta VVSR, Unkovich M, Kaiser BN (eds) The 17th Australian Nitrogen Fixation Conference, Adelaide, Australia. pp 134–135
Martínez-Hidalgo P, Galindo-Villardón P, Igual JM, Martínez-Molina E (2014) Micromonospora from nitrogen fixing nodules of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). A new promising plant probiotic bacteria. Sci Rep 4:1–9
Miles AA, Misra SS (1938) The estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood. J Hyg 38:732–749
Nimmnoi P, Pongsilp N, Lumyong S (2014) Co-inoculation of soybean (Glycine max) with actinomycetes and Bradyrhizobium japonicum enhances plant growth, nitrogenase activity and plant growth. J Plant Nutr 37:432–446
Oka-Kira E, Kawaguchi M (2006) Long-distance signalling to control root nodule number. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:496–502
Patel JJ (1974) Antagonism of actinomycetes against Rhizobia. Plant Soil 41:395–402
Peoples MB, Baldock JA (2001) Nitrogen dynamics of pastures: nitrogen fixation inputs, the impact of legumes on soil nitrogen fertility, and the contributions of fixed nitrogen to Australian farming systems. Aust J Exp Agric 41:327–346
Radovic’ J, Solokovic’ D, Markovic’ J (2009) Alfalfa-most important legume in animal husbandry. Biotechnol Anim Husb 25:465–475
Reeve W, Ballard R, Drew E, Tian R, Brau L, Goodwin L, Huntemann M, Han J, Tatiparthi R, Chen A, Mavrommatis K, Markowitz V, Palaniappan K, Ivanova N, Pati A, Woyke T, Kyrpides N (2014) Genome sequence of the Medicago-nodulating Ensifer meliloti commercial inoculant strain RRI128. Standards in Genomic Sciences 9:602–613
Robertson MJ (2006) Lucerne prospects: drivers for the widespread adoption of Lucerne for profit and salinity management. Cooperative Research Centre for Plant -based Management of Dryland Salinity, Perth
Robson AD, O’Hara GW, Abbott LK (1981) Involvement of phosphorous in nitrogen fixation by subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum L.). Aust J Plant Physiol 8:427–436
Sharma S, Aneja MK, Mayer J, Munch JC, Schloter M (2005) Characterization of bacterial community structure in rhizosphere soil of grain legumes. Microb Ecol 49:407–415
Soe KM, Bhromsiri A, Karladee D, Yamakawa T (2012) Effects of endophytic actinomycetes and Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains on growth, nodulation, nitrogen fixation and seed weight of different soybean varieties. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 58:319–325. doi:10.1080/00380768.2012.682044
Solans M, Vobis G, Wall LG (2009) Saprophytic actinomycetes promote nodulation in Medicago sativa-Sinorhizobium meliloti symbiosis in the presence of high nitrogen. J Plant Growth Regul 28:106–114
Sturz AV, Christie BR, Matheson BG, Nowak J (1997) Biodiversity of endophytic bacteria which colonize red clover nodules, roots, stems and foliage and their influence on host growth. Biol Fertil Soils 25:13–19
Tokala RK, Strap JL, Jung CM, Crawford DL, Salove MH, Deobald LA, Bailey JF, Morra MJ (2002) Novel plant-microbe rhizosphere interaction involving Streptomyces lydicus WYEC108 and the pea plant (Pisum sativum). Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2161–2171
Trujillo ME, Alonso-Vega P, Rodri’guez R, Carro L, Cerda E, Alonso P, Marti’nez-Molina E (2010) The genus micromonospora is widespread in legume root nodules: the example of lupinus angustifolius. ISME J 4:1265–1281
Trujillo ME, Kroppenstedt RM, Fernandez-Molonero C, Schumann P, Marti’nez-Molina E (2007) Micromonospora lupini sp. nov. and Micromonospora saelicesensis sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Lupinus angustifolius. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2799–2804
Trujillo ME, Kroppenstedt RM, Schumann P, Martinez-Molina E (2006) Kribbella lupini sp. nov., isolated from the roots of Lupinus angustifolius. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:407–411
Verma VC, Singh SK, Prakash S (2011) Bio-control and plnt growth promotion potential of siderophore producing endophytic Streptomyces from Azadirachta indica A. Juss J Basic Microbiol 51:550–556
Whitman W, Goodfellow M, Kämpfer P, Busse H-J, Trujillo ME, Ludwig W, Suzuki K-I, Parte A (2012) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. In: Whitman WB et al (eds) The actinobacteria, part A, vol 5, 2nd edn. Springer, New York. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-68233-4
Yamagishi M, Yamamoto Y (1994) Effects of boron on nodule development and symbiotic nitrogen fixation in soybean plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 40:265–274
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to South Australian Research Institute for the supply of lucerne seeds and rhizobial cultures and Flinders University for an International Research Scholarship to Xuyen Hoang Le.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kari Saikkonen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Le, X.H., Franco, C.M.M., Ballard, R.A. et al. Isolation and characterisation of endophytic actinobacteria and their effect on the early growth and nodulation of lucerne (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Soil 405, 13–24 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2652-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2652-9