Abstract
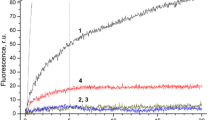
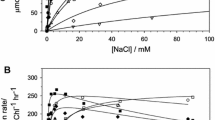
Extraction of Ca2+ from the oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II (PSII) in the absence of a chelator inhibits O2 evolution without significant inhibition of the light-dependent reduction of the exogenous electron acceptor, 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol (DCPIP) on the reducing side of PSII. The phenomenon is known as “the decoupling effect” (Semin et al. Photosynth Res 98:235–249, 2008). Extraction of Cl− from Ca2+-depleted membranes (PSII[–Ca]) suppresses the reduction of DCPIP. In the current study we investigated the nature of the oxidized substrate and the nature of the product(s) of the substrate oxidation. After elimination of all other possible donors, water was identified as the substrate. Generation of reactive oxygen species HO, H2O2, and O ·−2 , as possible products of water oxidation in PSII(–Ca) membranes was examined. During the investigation of O ·−2 production in PSII(–Ca) samples, we found that (i) O ·−2 is formed on the acceptor side of PSII due to the reduction of O2; (ii) depletion of Cl− does not inhibit water oxidation, but (iii) Cl− depletion does decrease the efficiency of the reduction of exogenous electron acceptors. In the absence of Cl− under aerobic conditions, electron transport is diverted from reducing exogenous acceptors to reducing O2, thereby increasing the rate of O ·−2 generation. From these observations we conclude that the product of water oxidation is H2O2 and that Cl− anions are not involved in the oxidation of water to H2O2 in decoupled PSII(–Ca) membranes. These results also indicate that Cl− anions are not directly involved in water oxidation by the Mn cluster in the native PSII membranes, but possibly provide access for H2O molecules to the Mn4CaO5 cluster and/or facilitate the release of H+ ions into the lumenal space.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Buffer A(–Cl):
-
Buffer A without Cl−
- Chl:
-
Chlorophyll
- DCPIP:
-
2,6-Dichlorophenol indophenol
- DCMU:
-
3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethylurea
- Decoupled PSII(–Ca):
-
Ca2+-depleted PSII that are inhibited in O2 evolution without significant inhibition of the light-dependent reduction of an exogenous electron acceptor
- DMAB:
-
3-(Dimethylamino) benzoic acid
- DMBQ:
-
2,6-Dimethyl-p-benzoquinone
- DPC:
-
1,5-Diphenycarbazide
- HA site:
-
High-affinity Mn-binding site
- LA site:
-
Low-affinity electron donation site
- MBTH:
-
3-Methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone hydrochloride hydrate
- OEC:
-
Oxygen-evolving complex
- POBN:
-
4-Pyridyl-1-oxide-N-tert-butylnitrone
- PSII:
-
Photosystem II
- PSII(–Ca):
-
Ca2+-depleted PSII
- PSII(–Ca, –Cl):
-
Ca2+- and Cl−-depleted PSII
- PSII(–Mn):
-
Mn-depleted PSII
- PSII(–PsbO):
-
PsbO-depleted PSII
- RC:
-
Reaction center
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- YZ :
-
Redox-active tyrosine (D1-Tyr161), the first electron donor to P680 + in PSII
References
Ananyev GM, Wydrzynski T, Renger G, Klimov V (1992) Transient peroxide formation by the manganese-containing, redox-active donor side of photosystem II upon inhibition of O2 evolution with lauroylchloline chloride. Biochim Biophys Acta 1100:303–311
Ananyev GM, Renger G, Wacker U, Klimov V (1994) The photoproduction of superoxide radicals and the superoxide dismutase activity of photosystem II. The possible involvement of cytochrome b-559. Photosynth Res 41:327–338
Andréasson LE, Vass I, Styring S (1995) Ca2+ depletion modifies the electron transfer on both donor and acceptor sides in photosystem II from spinach. Biochim Biophys Acta 1230:155–164
Arato A, Bondarava N, Krieger-Liszkay A (2004) Production of reactive oxygen species in chloride- and calcium-depleted photosystem II and their involvement in photoinhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1608:171–180
Armstrong JM (1964) The molar extinction coefficient of 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol. Biochim Biophys Acta 86:194–197
Asada K, Kiso K, Yoshikawa K (1974) Univalent reduction of molecular oxygen by spinach chloroplasts on illumination. J Biol Chem 249:2175–2181
Blubaugh DJ, Cheniae GM (1990) Kinetics of photoinhibition in hydroxylamine-extracted photosystem II membranes: relevance to photoactivation and sites of electron donation. Biochemistry 29:5109–5118
Bock A, Krieger-Liszkay A, de Zarate IBO, Schönknecht G (2001) Cl− channel inhibitors of the arylaminobenzoate type act as photosystem II herbicides: a functional and structural study. Biochemistry 40:3273–3281
Boussac A, Picaud M, Etienne A-L (1986) Effect of potassium iridic chloride on the electron donation by Mn2+ to photosystem II particles. Photochem Photobiophys 10:201–211
Boussac A, Zimmermann J-L, Rutherford AW (1990) Factors influencing the formation of modified S2 EPR signal and the S3 EPR signal in Ca(2+)-depleted photosystem II. FEBS Lett 277:69–74
Bricker TM, Roose JL, Fagerlund RD, Frankel LK, Eaton-Rye JJ (2012) The extrinsic proteins of photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1817:121–142
Cleland RE, Grace SC (1999) Voltammetric detection of superoxide production by photosystem II. FEBS Lett 457:348–352
Fine PL, Frash WD (1992) The oxygen-evolving complex requires chloride to prevent hydrogen peroxide formation. Biochemistry 31:12204–12210
Ghanotakis DF, Babcock GT (1983) Hydroxylamine as an inhibitor between Z and P680 in photosystem II. FEBS Lett 153:231–234
Ghanotakis DF, Babcock GT, Yocum CF (1984) Calcium reconstitutes high rates of oxygen evolution in polypeptide depleted photosystem II preparations. FEBS Lett 167:127–130
Hillier W, Wydrzynski T (1993) Increases in peroxide formation by the photosystem II oxygen evolving reactions upon removal of the extrinsic 16, 22 and 33 kDa proteins are reversed by CaCl2 addition. Photosynth Res 38:417–423
Hoganson CW, Ghanotakis DF, Babcock GT, Yocum CF (1989) Mn2+ reduces Y +Z in manganese-depleted photosystem II preparations. Photosynth Res 22:285–293
Inoue H, Wada T (1987) Requirement of manganese for electron donation of hydrogen peroxide in photosystem II reaction center complex. Plant Cell Physiol 28:767–773
Kawakami K, Umena Y, Kamiya N, Shen J-R (2009) Location of chloride and its possible functions in oxygen-evolving photosystem II revealed by X-ray crystallography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:8567–8572
Khorobrych SA, Ivanov BN (2002) Oxygen reduction in a plastoquinone pool of isolated pea thylakoids. Photosynth Res 71:209–219
Kolbeck RC, She ZW, Callahan LA, Nosek TM (1997) Increased superoxide production during fatigue in the perfused rat diaphragm. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:140–145
Krieger A, Rutherford AW, Johnson GN (1995) On the determination of redox midpoint potential of the primary quinone electron acceptor, QA, in photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1229:193–201
Krishtalik LI (1986) Energetics of multielectron reactions. Photosynthetic oxygen evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta 849:162–171
Kruck J, Jemiola-Rzemi’nska M, Strzalka K (2003) Cytochrome c is reduced mainly by plastoquinol and not by superoxide in thylakoid membranes at low and medium light intensities: its specific interaction with thylakoid membrane lipids. Biochem J 375:215–220
Kurashov VN, Lovyagina ER, Shkolnikov DY, Solntsev MK, Mamedov MD, Semin BK (2009) Investigation of the low-affinity oxidation site for exogenous electron donors in the Mn-depleted photosystem II complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1787:1492–1498
Mano J, Takahashi M, Asada K (1987) Oxygen evolution from hydrogen peroxide in photosystem II: flash-induced catalytic activity of water-oxidizing photosystem II membranes. Biochemistry 26:2495–2501
Moser CC, Anderson JLR, Dutton PL (2010) Guidelines for tunneling in enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1797:1573–1586
Ngo TT, Lenhoff HM (1980) A sensitive and versatile chromogenic assay for peroxidase and peroxidase-coupled reactions. Anal Biochem 105:389–397
Ono T, Inoue Y (1990) Abnormal redox reactions in photosynthetic O2-evolving centers in NaCl/EDTA-washed PS II. A dark-stable EPR multiline signal and an unknown positive charge accumulator. Biochim Biophys Acta 1020:269–277
Ono T, Mino H (1999) Unique binding site for Mn2+ ion responsible for reducing an oxidized YZ tyrosine in manganese-depleted photosystem II membranes. Biochemistry 38:8778–8785
Popelková H, Yocum CF (2007) Current status of the role of Cl− ion in the oxygen-evolving complex. Photosynth Res 93:111–121
Porra RJ, Tompson WA, Kriedemann PE (1989) Determination of accurate extinction coefficients and simultaneous-equations for assaying chlorophyll-A and chlorophyll-B extracted with 4 different solvents—verification of the concentration of chlorophyll standards by atomic-absorption spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 975:384–394
Pospišil P (2012) Molecular mechanisms of production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species by photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta 1817:218–231
Pospišil P, Haumann H, Dittmer J, Sole VA, Dau H (2003) Stepwise transition of the tetra-manganese complex of photosystem II to a binuclear Mn2(μ-O)2 complex in response to a temperature jump: a time-resolved structural investigation employing X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Biophys J 84:1370–1386
Pospišil P, Arato A, Krieger-Liszkay A, Rutherford AW (2004) Hydroxyl radical generation by photosystem II. Biochemistry 43:6783–6792
Rabinovich RA, Khavin ZYa (1963) Brief chemical reference book. Moscow, “Chemistry”
Rashid A, Carpentier R (1990) The 16 and 23 kDa extrinsic polypeptides and the associated Ca2+ and Cl− modify atrazine interaction with the photosystem II core complex. Photosynth Res 24:221–227
Rivalta I, Amin M, Luber S, Vassiliev S, Pokhrel R, Umena Y, Kawakami K, Shen J-R, Kamiya N, Bruce D, Brudwig GW, Gunner MR, Batista VS (2011) Structural–functional role of chloride in photosystem II. Biochemistry 50:6312–6315
Roose JL, Frankel LK, Bricker TM (2010) Documentation of significant electron transport defects on the reducing side of photosystem II upon removal of the PsbP and PsbQ extrinsic proteins. Biochemistry 49:36–41
Seibert M, DeWit M, Staehelin LA (1987) Structural localization of the O2-evolving apparatus to multimeric (tetrameric) particles on the lumenal surface of freeze-etched photosynthetic membranes. J Cell Biology 105:2257–2265
Semin BK, Seibert M (2009) A simple colorimetric determination of the manganese content in photosynthetic membranes. Photosynth Res 100:45–48
Semin BK, Ghirardi ML, Seibert M (2002) Blocking of electron donation by Mn(II) to YZ following incubation of Mn-depleted photosystem II membranes with Fe(II) in the light. Biochemistry 41:5854–5864
Semin BK, Davletshina LN, Aleksandrov AYu, Lanchinskaya VY, Novakova AA, Ivanov II (2004) pH dependence of the efficiency of binding of iron cations to the donor side of photosystem II. Biochemistry (Moscow) 69:331–339
Semin BK, Davletshina LN, Ivanov II, Rubin AB, Seibert M (2008) Uncoupling of processes of molecular synthesis and electron transport in the Ca2+-depleted PSII membranes. Photosynth Res 98:235–249
Semin BK, Davletshina LN, Ivanov II, Seibert M, Rubin AB (2012) Rapid degradation of the tetrameric Mn cluster in illuminated, PsbO-depleted photosystem II preparations. Biochemistry (Moscow) 77:152–156
Serrat FB (1994) Colorimetric method for determination of chlorine with 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Talanta 41:2091–2094
Sheptovitsky YG, Brudvig GW (1996) Isolation and characterization of spinach photosystem II membranes-associated catalase and polyphenoloxidase. Biochemistry 35:16255–16263
Sivaraja M, Tso J, Dismukes GC (1989) A calcium-specific site influence the structure and activity of the manganese cluster responsible for photosynthetic water oxidation. Biochemistry 28:9459–9464
Stemler A, Govindjee (1974) Bicarbonate stimulation of oxygen evolution, ferricyanide reduction and photoinactivation using isolated chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 15:533–544
Thompson LK, Miller AF, Buser CA, de Paula JC, Brudvig GW (1989) Characterization of the multiple forms of cytochrome b559 in photosystem II. Biochemistry 28:8048–8056
Umena Y, Kawakami K, Shen J-R, Kamiya N (2011) Crystal structure of oxygen evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Å. Nature 473:55–60
Wydrzynski TJ, Huggins BJ, Jursinic PA (1985) Uncoupling of detectable O2 evolution from the apparent S-state transitions in photosystem II by lauroylcholine chloride: possible implications in the photosynthetic water-splitting mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta 809:125–136
Yadav DK, Pospíšil P (2012) Role of chloride ion in hydroxyl radical production in photosystem II under heat stress: electron paramagnetic resonance spin-trapping study. J Bioenergy Biomembr 44:365–372
Yamashita A, Nijo N, Pospíšil P, Morita N, Takenaka D, Aminaka R, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto Y (2008) Quality control of photosystem II. Reactive oxygen species are responsible for the damage to photosystem II under moderate heat stress. J Biol Chem 283:28380–28391
Zhang S, Weng J, Pan J, Tu T, Yao S, Xu C (2003) Study on the photo-generation of superoxide radicals in Photosystem II with EPR spin trapping techniques. Photosynth Res 75:41–48
Zuo L, Christofi FL, Wright VP, Bao S, Clanton TL (2004) Lipoxygenase-dependent superoxide release in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 97:661–668
Acknowledgments
The work at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory was carried out under US Department of Energy contract number DE-AC36-08-GO28308. This study was also supported in part by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, Project Numbers 08-04-00354 (AR), by the Chemical Sciences, Geosciences and Biosciences Division, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Office of Science, U.S. Department of Energy (MS), and by the NREL pension program (MS). The authors would like to thank Drs. Gary Brudvig and Ken Sauer for their valuable comments and recommendations during the inception of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semin, B.K., Davletshina, L.N., Timofeev, K.N. et al. Production of reactive oxygen species in decoupled, Ca2+-depleted PSII and their use in assigning a function to chloride on both sides of PSII. Photosynth Res 117, 385–399 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9870-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9870-x