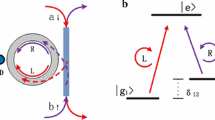
Abstract
We present two hybrid entanglement concentration protocols based on quantum dots (QDs) and optical microcavity coupled systems. The system is theoretically analyzed and used for photon and electron hybrid entanglement generation. Also, the proposed system can be further used for parity check that allows a quantum nondemolition measurement on the spin parity. By performing parity check process on electron spins, the entangled state can be concentrated into maximally entangled state efficiently.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C.H., Bernstein, H.J., Popescu, S., Schumacher, B.: Concentrating partial entanglement by local operations. Phys. Rev. A 53, 2046 (1996)
Shi, B.S., Jiang, Y.K., Guo, G.C.: Optimal entanglement purification via entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. A 62, 054301 (2000)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Imoto, N.: Concentration and purification scheme for two partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 64, 012304 (2001)
Zhao, Z., Pan, J.W., Zhan, M.S.: Practical scheme for entanglement concentration. Phys. Rev. A 64, 014301 (2001)
Zhao, Z., Yang, T., Chen, Y.A., Zhang, A.N., Pan, J.W.: Experimental realization of entanglement concentration and a quantum repeater. Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 207901 (2003)
Yamamoto, T., Koashi, M., Ozdemir, S.K., Imoto, N.: Experimental extraction of an entangled photon pair from two identically decohered pairs. Nature 421, 343 (2003)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Nonlocal entanglement concentration scheme for partially entangled multipartite systems with nonlinear optics. Phys. Rev. A 77, 062325 (2008)
Sheng, Y.B., Deng, F.G., Zhou, H.Y.: Single-photon entanglement concentration for long-distance quantum communication. Quantum Inf. Comput. 10, 272 (2010)
Wang, H.-F., Zhang, S., Yeon, K.-H.: Linear-optics-based entanglement concentration of unknown partially entangled three-photon W states. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27, 2159–2164 (2010)
Wang, H.-F., Zhang, S., Yeon, K.-H.: Linear optical scheme for entanglement concentration of two partially entangled three-photon states. Euro. Phys. J. D 56, 271–275 (2010)
Gu, B.: Single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration of partially entangled multiphoton W states with linear optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 29, 1685–1689 (2012)
Xiong, W., Ye, L.: Schemes for entanglement concentration of two unknown partially entangled states with cross-Kerr nonlinearity. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 28, 2030–2037 (2011)
Wang, T.J., Long, G.L.: Entanglement concentration for arbitrary unknown less-entangled three-photon W states with linear optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 30, 1069–1076 (2013)
Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Jin, G.S.: Entanglement purification and concentration of electron-spin entangled states using quantum-dot spins in optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 84, 032307 (2011)
Sheng, Y.B., Zhou, L., Zhao, S.M., Zheng, B.Y.: Efficient single-photon-assisted entanglement concentration for partially entangled photon pairs. Phys. Rev. A 85, 012307 (2012)
Deng, F.G.: Optimal nonlocal multipartite entanglement concentration based on projection measurements. Phys. Rev. A 85, 022311 (2012)
Ren, B.C., Du, F.F., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement concentration for two-photon four-qubit systems with linear optics. Phys. Rev. A 88, 012302 (2013)
Ren, B.C., Deng, F.G.: Hyperentanglement purification and concentration assisted by diamond NV centers inside photonic crystal cavities. Laser Phys. Lett. 10, 115201 (2013)
Waks, E., Vuckovic, J.: Dipole induced transparency in drop-filter cavity-waveguide systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 153601 (2006)
Hu, C.Y., Young, A., O’Brien, J.L., Munro, W.J., Rarity, J.G.: Giant optical Faraday rotation induced by a single-electron spin in a quantum dot: applications to entangling remote spins via a single photon. Phys. Rev. B 78, 085307 (2008)
Hu, C.Y., Munro, W.J., Rarity, J.G.: Deterministic photon entangler using a charged quantum dot inside a microcavity. Phys. Rev. B 78, 125318 (2008)
An, J.H., Feng, M., Oh, C.H.: Quantum-information processing with a single photon by an input-output process with respect to low- Q cavities. Phys. Rev. A 79, 032303 (2009)
Hu, C.Y., Rarity, J.G.: Loss-resistant state teleportation and entanglement swapping using a quantum-dot spin in an optical microcavity. Phys. Rev. B 83, 115303 (2011)
Bonato, C., Haupt, F., Oemrawsingh, S.S.R., Gudat, J., Ding, D., van Exter, M.P., Bouwmeester, D.: CNOT and Bell-state analysis in the weak-coupling cavity QED regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 160503 (2010)
Walls, D.F., Milburn, G.J.: Quantum Optics. Springer, Berlin (1994)
Hu, C.Y., Munro, W.J., O’Brien, J.L., Rarity, J.G.: Proposed entanglement beam splitter using a quantum-dot spin in a double-sided optical microcavity. Phys. Rev. B 80, 205326 (2009)
Ren, B.C., Wei, H.R., Deng, F.G.: Deterministic photonic spatial-polarization hyper-controlled-not gate assisted by a quantum dot inside a one-side optical microcavity. Laser Phys. Lett. 10, 095202 (2013)
Wei, H.R., Deng, F.G.: Universal quantum gates for hybrid systems assisted by quantum dots inside double-sided optical microcavities. Phys. Rev. A 87, 022305 (2013)
Young, A.B., Oulton, R., Hu, C.Y., Thijssen, A.C.T., Schneider, C., Reitzenstein, S., Kamp, M., Höfling, S., Worschech, L., Forchel, A., Rarity, J.G.: Quantum-dot-induced phase shift in a pillar microcavity. Phys. Rev. A 84, 011803(R) (2011)
Reithmaier, J.P., Sek, G., Löffler, A., Hofmann, C., Kuhn, S., Reitzenstein, S., Keldysh, L.V., Kulakovskii, V.D., Reinecke, T.L., Forchel, A.: Strong coupling in a single quantum dot-semiconductor microcavity system. Nature 432, 197–200 (2004)
Yoshie, T., Scherer, A., Hendrickson, J., Khitrova, G., Gibbs, H.M., Rupper, G., Ell, C., Shchekin, O.B., Deppe, D.G.: Vacuum Rabi splitting with a single quantum dot in a photonic crystal nanocavity. Nature 432, 200–203 (2004)
Reitzenstein, S., Hofmann, C., Gorbunov, A., Strauß, M., Kwon, S.H., Schneider, C., Löffler, A., Höfling, S., Kamp, M., Forchel, A.: AlAs/GaAs micropillar cavities with quality factors exceeding 150.000. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 251109 (2007)
Clark, S.M., Fu, K.-M.C., Zhang, Q., Ladd, T.D., Stanley, C., Yamamoto, Y.: Ultrafast optical spin echo for electron spins in semiconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 247601 (2009)
Press, D., De Greve, K., McMahon, P.L., Ladd, T.D., Friess, B., Schneider, C., Kamp, M., Hofling, S., Forchel, A., Yamamoto, Y.: Ultrafast optical spin echo in a single quantum dot. Nat. Photon 4, 367 (2010)
Borri, P., Langbein, W., Schneider, S., Woggon, U., Sellin, R.L., Ouyang, D., Bimberg, D.: Ultralong dephasing time in InGaAs quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 157401 (2001)
Birkedal, D., Leosson, K., Hvam, J.M.: Long lived coherence in self-assembled quantum dots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 227401 (2001)
Gallardo, E., Martinez, L.J., Nowak, A.K., Sarkar, D., van der Meulen, H.P., Calleja, J.M., Tejedor, C., Prieto, I., Granados, D., Taboada, A.G., Garcia, J.M., Postigo, P.A.: Optical coupling of two distant InAs/GaAs quantum dots by a photonic-crystal microcavity. Phys. Rev. B 81, 193301 (2010)
Faraon, A., Majumdar, A., Kim, H., Petroff, P., Vuc̆kovic̀ , J.: Fast electrical control of a quantum dot strongly coupled to a photonic-crystal cavity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 047402 (2010)
Song, S.Y., Wang, C.: Recent development in quantum communication. Chin. Sci. Bull. 57(36), 4694–4700 (2012)
Song, S.Y., Cao, Y., Sheng, Y.B., Long, G.L.: Complete Greenberger- Horne- Zeilinger state analyzer using hyperentanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 381–393 (2013)
Wang, C., He, L.Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, H.Q., Zhang, R.: Complete entanglement analysis on electron spins using quantum dot and microcavity coupled system. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 56, 2054–2058 (2013)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Fundamental Research Program Grant No. 2010CB923202, China National Natural Science Foundation Grant No. 61205117, Beijing Higher Education Young Elite Teacher Project No. YETP0456 and the Open Research Fund Program of the State Key Laboratory of Low-Dimensional Quantum Physics, Tsinghua University Grant No. KF201301.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Cao, C., He, Ly. et al. Hybrid entanglement concentration using quantum dot and microcavity coupled system. Quantum Inf Process 13, 1025–1034 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0707-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0707-5