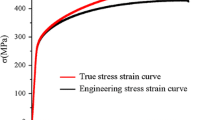
True stress-strain values were obtained from the tensile tests of 7075 aluminum alloy and finite element analysis. The results revealed that different ductile fracture criteria resulted in different accuracy of analysis. Moreover, factors affecting ductile fracture, such as effective stress, effective strain, and damage were analyzed. The maximum damage level occurred in the center, with its value reaching 0.454. The break happened in 12.9 s in the P1 point. In the P3 point, fracture was not revealed. It can be seen that the maximum damage was observed over the fracture area in the P1 point. Finite element analysis as applied to the 7075 aluminum alloy fracture criteria can be used for forging, drawing, and stamping of the materials.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. L. Weng and C. T. Sun, “A study of fracture criteria for ductile materials,” Eng. Fail. Anal., 7, 101–125 (2000).
K. Komori, “Ductile fracture criteria for simulating shear by node separation method,” Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech., 43, 101–114 (2005).
X. Yang, C. Chen, Y. Hu, and C. Wang, “Damage analysis and fracture criteria for piezoelectric ceramics,” Int. J. Non-Linear Mech., 40, 1204–1213 (2005).
R. Hambli and M. Reszka, “Fracture criteria identification using an inverse technique method and blanking experiment,” Int. J. Mech. Sci., 44, 1349–1361 (2002).
V. C. Hoa, D. W. Seo, and J. K. Lim, “Site of ductile fracture initiation in cold forging: a finite element model,” Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech., 44, 58–69 (2005).
R. Narayanasamy, K. Baskaran, and D. Muralikrishna, “Some studies on stresses and strains of aluminium alloy during extrusion-forging at room temperature,” Mater. Des., 29, 1623–1632 (2008).
L. Yang, L. H. Zhan, and W. Wu, “Analysis method of orange peel structure on aluminum-lithium alloy surface during stretch forming process,” Mater. Res. Innov., 18, Issue S2, 5–11 (2014).
Q. J. Zhu, Y. F. He, and Y. Yin, “Finite element analysis of deformation mechanism for porous materials under fluid-solid interaction,” Mater. Res. Innov., 18, Issue S2, 22–27 (2014).
S. F. Jia, L. H. Zhan, and J. Zhang, “Influence of solid solution treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of 2219 aluminum alloy,” Mater. Res. Innov., 18, Issue S2, 52–58 (2014).
V. T. Troshchenko and L. A. Khamaza, “Conditions for the transition from nonlocalized to localized damage in metals and alloys. Part 1. Crack sizes at fatigue limit,” Strength Mater., 46, No. 3, 303–314 (2014).
C. C. Chen, S. I. Oh, and S. Kobayashi, “Ductile fracture in axisymmetric extrusion and drawing,” J. Eng. Ind., 101, 36–44 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Problemy Prochnosti, No. 1, pp. 141 – 147, January – February,2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D.C., You, C.S. Fracture Criterion for the Tensile Test of 7075 Aluminum Alloy. Strength Mater 47, 122–127 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-015-9637-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11223-015-9637-z