Abstract
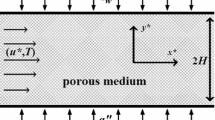
Steady laminar forced convection gaseous slip-flow through parallel-plates micro-channel filled with porous medium under Local Thermal Non-Equilibrium (LTNE) condition is studied numerically. We consider incompressible Newtonian gas flow, which is hydrodynamically fully developed while thermally is developing. The Darcy–Brinkman–Forchheimer model embedded in the Navier–Stokes equations is used to model the flow within the porous domain. The present study reports the effect of several operating parameters on velocity slip and temperature jump at the wall. Mainly, the current study demonstrates the effects of: Knudsen number (Kn), Darcy number (Da), Forchheimer number (Γ), Peclet number (Pe), Biot number (Bi), and effective thermal conductivity ratio (K R) on velocity slip and temperature jump at the wall. Results are given in terms of skin friction (C f Re *) and Nusselt number (Nu). It is found that the skin friction: (1) increases as Darcy number increases; (2) decreases as Forchheimer number or Knudsen number increases. Heat transfer is found to (1) decreases as the Knudsen number, Forchheimer number, or K R increases; (2) increases as the Peclet number, Darcy number, or Biot number increases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bi:
-
Biot number \(({h_{\rm sf} L^2}\mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{h_{\rm sf} L^2} {\varepsilon k_{\rm f}}}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {\varepsilon k_{\rm f}})\)
- c f :
-
Coefficient in the Forchheimer term
- Cf :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- C p :
-
Constant pressure specific heat
- C v :
-
Constant volume specific heat
- D :
-
Pore diameter
- Da :
-
Darcy number \((K/\varepsilon L^2)\)
- h :
-
Local heat transfer coefficient
- h sf :
-
Interstitial heat transfer coefficient
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity
- K :
-
Intrinsic permeability of the porous medium
- Kn :
-
Modified Knudsen number \(\left(\frac{\lambda}{D}\,\frac{D}{L}\right)\)
- K R :
-
Effective thermal conductivity ratio \((\varepsilon {k_{\rm f}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{k_{\rm f}}{(1-\varepsilon)k_{\rm s}}}}\right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {(1-\varepsilon)k_{\rm s}})\)
- L :
-
Half channel width
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number \((hL/\varepsilon k_{\rm f})\)
- p :
-
Pressure
- Pe :
-
Peclet number \(({u_{\rm o} L} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{u_o L} {\varepsilon \alpha}}} \right. \kern-\nulldelimiterspace} {\varepsilon \alpha)}\)
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number (μ /α ρf)
- q w :
-
Heat transfer rate from the plate wall
- Re * :
-
Modified Reynolds number in porous media \((\rho_{\rm f} u_o L/\mu \varepsilon)\)
- t :
-
Time
- t 0 :
-
Reference time(ρ L 2/μ)
- T :
-
Temperature
- u :
-
Axial velocity
- u 0 :
-
Reference axial velocity \((\varepsilon L^2/\mu (-{\rm d}p/{\rm d}x))\)
- U :
-
Non-dimensional axial velocity (u/u o)
- x :
-
Axial coordinate
- X :
-
Dimensionless axial coordinate (x/L)
- y :
-
Transverse coordinate
- Y :
-
Dimensionless transverse coordinate (y/L)
- Greek symbols :
-
- α:
-
Thermal diffusivity
- γ:
-
Specific heat ratio (C p /C ν)
- Γ:
-
Dimensionless coefficient of Forchheimer \((\rho_{\rm f} c_{\rm f} \varepsilon^2(-{\rm d}p/{\rm d}x)L^4/\mu^2\sqrt k)\)
- λ:
-
Mean free path of the gas molecules
- \(\varepsilon \) :
-
Porosity of the porous medium
- μ:
-
Dynamic viscosity
- ρf :
-
Fluid density
- σT :
-
Thermal accommodation coefficient
- σv :
-
Tangential momentum accommodation coefficient
- θ:
-
Non-dimensional temperature (T − T ∞ /T w − T ∞)
- τ:
-
Non-dimensional time (t/t o)
- τw :
-
Shear stress at the wall \((-\mu (\partial u/\partial y)\left.)\right|_{\rm w} \)
- Subscripts :
-
- f :
-
Fluid
- mf :
-
Mean value for the fluid
- s :
-
Solid
- w :
-
Wall
References
Ameel T.A., Barron R.F., Wang X.M., Warrington R.O. (1997). Laminar forced convection in a circular tube with constant heat flux and slip flow. Microscale Thermophys. Eng. 1, 303–320
Arkilic E.B., Breuer K.S., Schmidt M.A. (1994). Gaseous flow in microchannels, application of microfabrication to fluid mechanics. ASME FED 197, 57–66
Barber, R.W., Emerson, D.R.: A numerical investigation of low Reynolds number gaseous slip flow at the entrance of circular and parallel plate microchannels. Proceedings of the ECCOMAS Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference, Swansea, Wales, UK (2001)
Barron R.F., Wang X.M., Warrington R.O., Ameel T.A. (1996). Evaluation of the eigenvalues for the Graetz problem in slip-flow. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Trans. 23, 563–574
Barron R.F., Wang X.M., Ameel T.A., Warrington R.O. (1996). The Graetz problem extended to slip flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 40, 1817–1823
Bejan A. (2000). Editorial, J. Porous Media 1 i–ii
Bejan A. (2004). Convection Heat Transfer, 3rd edn Chapter 12. John-Wiley, New York
Beskok A., Karniadakis G.E. (1994). Simulation of heat and momentum transfer in complex micro geometries, J. Thermophys. Heat Trans. 8(4): 647–653
Eckert E.G.R., Drake R.M. (1972). Analysis of Heat and Mass Transfer. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 467–486
Gad-El-Hak M. (1999). The fluid mechanics of microdevices—The Freeman scholar lecture, J. Fluids Eng. 121, 5–33
Haddad O.M., Al-Nimr M.A., AbuZaid M.M. (2005a). The effect of frequency of fluctuating driving force on basic gaseous micro-flows. Acta Mechanica 179, 249–259
Haddad O.M., AbuZaid M.M., Al-Nimr M.A. (2005b). Developing free convection gas flow in a vertical open-ended micro-channel filled with porous media. Numer. Heat Trans. Part A 48, 693–710
Haddad, O.M., Al-Nimr, M.A., Taamneh, Y.: Hydrodynamic and thermal behavior of gas flow in micro-channels filled with porous media. Accepted for publication in J. Porous Media (2006a)
Haddad, O.M., Al-Nimr, M.A., AbuZaid, M.M.: The effect of periodically oscillating driving force on basic micro flows in porous media. Accepted for publication in J. Porous Media (2006b)
Hoffman J.D. (2001). Numerical Methods for Engineers and Scientists. Marcel Dekker, New York
Larrode F.E., Housiadas C., Drossinos Y. (2000). Slip-flow heat transfer in circular tubes. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 43, 2669–2680
Liu J.Q., Tai Y.C., Ho C.M.: MEMS for pressure distribution studies of gaseous flows in microchannels. Proc. IEEE Micro-electromech. Syst. 209–215 (1995)
Marafie A., Vafai K. (2001). Analysis of non-Darcian effects on temperature differentials in porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 44, 4401–4411
Shih J.C., Ho C., Liu J., Tai Y. (1996). Monatomic and polyatomic gas flow through uniform microchannels. Microelecromech. Syst. (MEMS) 59, 197–203
Shih Y.P., Huang C.C., Tsay S.Y. (1995). Extended Leveque solution for laminar heat transfer to power-law fluids in pipes with wall slip. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 38, 403–408
Tang G.H., Tao W.Q., He Y.L. (2005). Gas slippage effect on microscale porous flow using the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. Rev. E 72(56301): 1–8
Wang M.L., Ameel T.A., Frazier A.B., Warrington R.O. (1998). Microtube convection heat transfer for a power-law fluid in laminar slip flow with an isoflux boundary condition. Int. Mechanical Eng. Congress and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, HTD-Vol. 361–3, pp. 157–164
Wang, X. M.: Evaluation of the eigenvalues of the Graetz problem in slip-flow. M.Sc. Thesis, Louisiana Tech. University, Ruston, Louisiana (1996)
Yu, S.P., Ameel, T.A.: Slip flow low Peclet number thermal entry problem within a flat microchannel subject to constant wall temperature. Proceedings of the Conference on Heat Transfer and Transport Phenomena in Microsystems, Banff, Alta, Canada (2000)
Yu S.P., Ameel T.A. (2001). Slip-flow heat transfer in rectangular microchannels. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 44, 4225–4234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haddad, O.M., Al-Nimr, M.A. & Al-Omary, J.S. Forced convection of gaseous slip-flow in porous micro-channels under Local Thermal Non-Equilibrium conditions. Transp Porous Med 67, 453–471 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-006-9036-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-006-9036-9