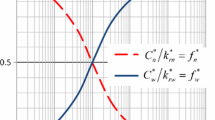
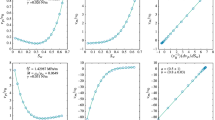
Abstract
Flow in porous media described by Darcy’s law extended to two-phase flow using the concept of relative permeabilities k r naturally assumes a maximum value of 0 ≤ k r ≤ 1. Reports in literature and our own experimental data show endpoint relative permeabilities k r > 1. In the porous medium, the flux of the non-wetting phase is in many cases about 2-4 times higher when a small amount of the wetting phase is present. Here, we draw an analogy between k r > 1 and a slip-boundary condition for the pore scale flow. We use a model description assuming flow in capillary tubes with a slip boundary condition. This model predicts that the flux increase due to slip depends on the equivalent capillary radius of the flow channels. Our k r data specifically follows this dependence indicating that slip is a plausible explanation for the observation of k r > 1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkafeef S.F., Algharaib M.K. and Alajmi A.F. (2006). Hydrodynamic thickness of petroleum oil adsorbed layers in the pores of reservoir rocks. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298: 13–19
Anderson W.G. (1986). Wettability literature survey – part 2: Wettability measurement. J. Pet. Technol. 38(12): 1246–1262
Anderson W.G. (1987). Wettability literature survey – part 5: The effects of wettability on relative permeability. J. Pet. Technol. 39: 1453
Arps J.J. and Roberts T.G. (1955). The effect of the relative permeability ratio, the oil gravity and the solution gas-oil ratio on the primary recovery from a depletion type reservoir. Trans. AIME 204: 120
Ayub M. and Bentsen R.G. (1999). Interfacial viscous coupling: a myth or reality?. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 23: 13–29
Blake, T.D.: Slip between a liquid and a solid. D.M. Tolstoi’s (1952) theory reconsidered. Colloids Surf. 47, 135 (1990)
Blunt M.J. (2001). Flow in porous media pore-network models and multiphase flow. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 6: 197–207
Brochard F. and de Gennes P.G. (1992). Shear-dependent slippage at a polymer/solid interface. Langmuir 8: 3033–3037
Chandler D. (2007). Oil on troubled waters. Nature 445(22): 831–832
Choi C.-H., Westin K.J.A. and Breuer S. (2003). Apparent slip flows in hydrophilic and hydrophobic microchannels. Phys. Fluids 15(10): 2897–2902
Choi C.-H. and Kim C.-J. (2006). Large slip of aqueous liquid flow over a nanoengineered superhydrophobic surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96: 066001
Churaev N.V., Sobolev V.D. and Somov A.N. (1984). Slippage of liquids over lyophobic solid surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 97: 574–581
Cottin-Bizonne C., Cross B., Steinberger A. and Charlaix E. (2005). Boundary slip on smooth hydrophobic surfaces: Intrinsic effects and possible artifacts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94: 056102
Cuiec, L.: Restoration of the natural state of core samples. In: Paper SPE 5634 presented at the 1975 ATCE, Dallas, Sept. 28–Oct. 1 (1975)
Czarnecki J., Radoev B., Schramm L.L. and Slavchev R. (2005). On the nature of athabasca oil sands. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 114–115: 53–60
Dake, L.P.: Fundamentals of Reservoir Engineering. Elsevier B.V. (1978)
de Gennes P.G. (1985). Wetting: statics and dynamics. Rev. Modern Phys. 57(3): 827–863
de Gennes P.G. (2002). On fluid/wall slippage. Langmuir 18: 3413–3414
Hirasaki, G.J.: Wettability: fundamentals and surface forces. SPE Formation Evaluation, pp. 217–226, June (1991)
Deen, W.M.: Analysis of Transport Phenomena. Oxford University Press (1998)
Dong M., Dullien F.A.L., Dai L. and Li D. (2006). Immiscible displacement in the interacting capillary bundle model part ii. applications of model and comparison of interacting and non-interacting capillary bundle models. Transp. Porous Med. 63: 289–304
Doshi D.A., Watkins E.B., Israelachvili J.N. and Majewski J. (2005). Reduced water density at hydrophobic surfaces: effect of dissolved gases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102(27): 9458–9462
Drummond C. and Israelachvili J. (2002). Surface forces and wettability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 33: 123–133
Drummond C. and Israelachvili J. (2004). Fundamental studies of crude oil-surface water interactions and its relationship to reservoir wettability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 45: 61–81
Dullien F.A.L. (1992). Porous Media – Fluid Transport and Pore Structure, 2nd edn. Academia Press, New York
Ehrlich R. (1993). Viscous coupling in two-phase flow in porous media and its effect on relative permeabilities. Transp. Porous Media 11: 201–218
Honarpour, M., Koederitz, L., Harvey, A.H. (eds.) (2000). Relative Permeability of Petroleum Reservoirs. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Horn R., Vinogradova O., Mackay M. and Phan-Thien N. (2000). Hydrodynamic slippage inferred from thin film drainage measurements in a solution of nonadsorbing polymer. J. Chem. Phys. 112: 6424–6433
Hui, M.-H., Blunt, M.J.: Pore-scale modeling of three-phase flow and the effects of wettability. volume SPE 59309. Society of Petroleum Engineers (2000)
Jackson M.D., Valvatne P.H. and Blunt M.J. (2003). Prediction of wettability variation within an oil/water transition zone and its impact on production. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 39: 231–246
Karabakal U. and Bagci S. (2004). Determination of wettability and its effect on waterflood performance in limestone medium. Energy Fuels 18: 438–449
Kokkedee J.A., Boom W., Frens A.M. and Maas J.G. (1996). Improved special core analysis: scope for a reduced residual oil saturation. Society of Core Analysis Conference Paper. 9601: 1–13
Lager A., Webb K.J., Black C.J.J., Singleton M. and Sorbie K.S. (2006). Low salinity oil recovery - an experimental investigation. Society of Core Analysists Conference Paper 31: 1–12
Lake, L.W.: Enhanced Oil Recovery. Prentice Hall (1989)
Lauga E. and Stone H.A. (2003). Effective slip in pressure-driven stokes flow. J. Fluid Mech. 489: 55–77
Li H., Pan C. and Miller C.T. (2005). Pore-scale investigation of viscous coupling effects for two-phase flow in porous media. Phys. Rev. E 72: 026705
Lord D.L. and Buckley J.S. (2002). An afm study of the morphological features that affect wetting at crude oil-water-mica interfaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 206: 531–546
Masalmeh S.K. (2003). The effect of wettability heterogeneity on capillary pressure and relative permeability. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 39: 399–408
McPhee, C.A.: Effects of strong wetting on end-point relative permeability. In Advances in Petrophysics: 5 Years of Dialog, pp. 95–97. The London Petrophysical Society, July (1994)
McPhee C.A. and Arthur K.G. (1994). Relative permeability measurements: an inter-laboratory comparison. SPE 28826: 199–211
Melrose, J.C.: Interpretation of mixed wettability states in reservoir rock. In: 57th Annual Fall Technical Conference and Exhibition for the Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME, number SPE 10971 (1982)
Mezger M., Reichert H., Schöder S., Okasinski J., Schröder H., Dosch H., Palms D., Ralston J. and Honkimäki V. (2006). High-resolution in situ X-ray study of the hydrophobic gap at the water-octadecyl-trichlorosilane interface. PNAS 103: 18401–18404
Migler K.B., Hervet H. and Leger L. (1993). Slip transition of a polymer melt under shear stress. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70: 286
Mikkelsen M. and Scheie A. (1991). Abnormal permeability behavior of a north sea sandstone reservoir. SPE 22600: 145–156
Miksis S.H. and Davis M.J. (1994). Slip over rough and coated surfaces. J. Fluid Mech. 273: 125–139
Morrow, N.R., Melrose, J.C.: Interfacial Phenomena in Petroleum Recovery, Surfactant Science Series vol. 36, chapter Application of Capillary Pressure Measurements to the Determination of Connate Water Saturation, pp. 257–287. Marcel Dekker, New York (1991)
Navier C.L.M.H. (1827). Sur les lois du mouvement des fluides. Mem. Acad. Sci. Inst. Fr. 6: 389
Nguyen V.H., Sheppard A.P., Knackstedt M.A. and Pinczewski W.V. (2006). The effect of displacement rate on imbibition relative permeability and residual saturation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 52: 54–70
Odeh A.S. (1959). Effect of viscosity ratio on relative permeability. Trans. AIME 216: 346–353
Patzek T.W. and Kristensen J.G. (2001). Shape factor correlations of hydraulic conductance in noncircular capillaries. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 236: 305–317
Priezjev N.V. and Troian S.M. (2004). Molecular origin and dynamic behavior of slip in sheared polymer films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(1): 018302
Priezjev N.V. and Troian S.M. (2006). Influence of periodic wall roughness on the slip behavior at liquid/solid interfaces: molecular-scale simulations versus continuum predictions. J. Fluid Mech. 554: 25
Ransohoff T.C. and Radke C.J. (1988). Laminar flow of a wetting liquid along the corners of a predominantly gas-occupied noncircular pore. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 121(2): 392–401
Recommended Practices for Core Analysis, volume Recommended Practice 40 of API RP40, 2nd edn. American Petroleum Institute (API) (1998)
Richardson S. (1973). On the no-slip boundary condition. J. Fluid Mech. 59: 707–719
Schnell E. (1956). Slippage of water over nonwettable surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 27: 1149–1152
Takamura K. (1982). Microscopic structure of athabasca oil sand. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 60: 538–545
Thompson P.A. and Troian S.M. (1997). A general boundary condition for liquid flow at solid surfaces. Nature 389: 360
Tiab, D., Donaldson, E.C.: Petrophysics, 2nd edn. Gulf Professional Publishing (2004)
Tolstoi D.M. (1952). Molecular theory for slippage of liquids over solid surfaces. Dokl. Acad. Nauk. SSSR 85: 1089
Tretheway D.C. and Meinhart C.D. (2002). Apparent fluid slip at hydrophobic microchannel walls. Phys. Fluids 14(3): L9–L12
Tyrrell J.W.G. and Attard P. (2001). Images of nanobubbles on hydrophobic surfaces and their interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87: 176104
Vinogradova O.I. (1995). Drainage of a thin liquid film confined between hydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 11(6): 2213
Vinogradova O.I., Bunkin N.F., Churaev N.V., Kiseleva O.A., Lobeyev A.V. and Ninham B.W. (1995). Effect of salts and dissolved gas on optical cavitation near hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 173: 443
Watanabe K., Udagawa Y. and Udagawa H. (1999). Drag reduction of newtonian fluid in a circular pipe with a highly water-repellent wall. J. Fluid Mech. 381: 225–238
Worthington, P.F., Charair-Rivière, C. (eds.): Advances in Core Evaluation III: Reservoir Management. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers (1992)
Zhu Y. and Granick S. (2001). Rate-dependent slip of newtonian liquid at smooth surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87: 096105
Zhu Y. and Granick S. (2002). Limits of the hydrodynamic no-slip boundary condition. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88: 106102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berg, S., Cense, A.W., Hofman, J.P. et al. Two-Phase Flow in Porous Media with Slip Boundary Condition. Transp Porous Med 74, 275–292 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-007-9194-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-007-9194-4