Abstract
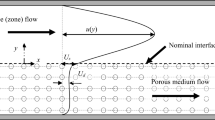
The flow over a porous laminated flat plate is investigated from a flow control perspective through experiments and computations. A square array of circular cylinders is used to model the porous lamination. We determine the velocities at the fluid–porous interface by solving the two-dimensional Navier–Stokes and the continuity equations using a staggered flow solver and using LDV in experiments. The control parameters for the porous region are porosity, \(\phi \) and Reynolds number, Re, based on the diameter of the circular cylinders used to model the porous lamination. Computations are conducted for \(0.4< \phi < 0.9\) and \(25< Re < 1000\), and the experiments are conducted for \(\phi = 0.65\) and 0.8 at \(Re \approx 391,\ 497\) and 803. The permeability of the porous lamination is observed to induce a slip velocity at the interface, effectively making it a slip wall. The slip velocity is seen to be increasing functions of \(\phi \) and Re. For higher porosities at higher Re, the slip velocity shows non-uniform and unsteady behavior and a breakdown Reynolds number is defined based on this characteristic. A map demarcating the two regimes of flow is drawn from the computational and experimental data. We observe that the boundary layer over the porous lamination is thinner than the Blasius boundary layer and the shear stress is higher at locations over the porous lamination. We note that the porous lamination helps maintain a favorable pressure gradient at the interface which delays separation. The suitable range of porosities for effective passive separation control is deduced from the results.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agelinchaab, M., Tachie, M.F., Ruth, D.W.: Velocity measurement of flow through a model three-dimensional porous medium. Phys. Fluids 18(1), 017105-1–11 (2006)
Anderson, T.B., Jackson, R.: Fluid mechanical description of fluidized beds. Equations of motion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 6(4), 527–539 (1967)
Arthur, J.K., Ruth, D.W., Tachie, M.F.: PIV measurements of flow through a model porous medium with varying boundary conditions. J. Fluid Mech. 629, 343–374 (2009)
Beavers, G.S., Joseph, D.D.: Boundary conditions at a naturally permeable wall. J. Fluid Mech. 30, 197–207 (1967)
Beavers, G.S., Sparrow, E.M., Masha, B.A.: Boundary condition at a porous surface which bounds a fluid flow. AIChE J. 20, 596–597 (1974)
Brinkman, H.C.: A calculation of the viscous force exerted by a flowing fluid on a dense swarm of particles. Appl. Sci. Res. A1, 27–34 (1949)
Chandesris, M., Jamet, D.: Boundary conditions at a planar fluid–porous interface for a Poiseuille flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49, 2137–2150 (2006)
Chandesris, M., Jamet, D.: Boundary conditions at a fluid–porous interface: an a priori estimation of the stress jump coefficients. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50(17), 3422–3436 (2007)
Darcy, H.: Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon. Dalmont, Paris (1856)
Goharzadeh, A., Khalili, A., Jorgensen, B.: Transition layer thickness at a fluid–porous interface. Phys. Fluids 17, 057,102 (2005)
Goyeau, B., Lhuillier, D., Gobin, D., Velarde, M.: Momentum transport at a fluid–porous interface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 46, 4071–4081 (2003)
Guermond, J.L., Minev, P., Shen, J.: An overview of projection methods for incompressible flows. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195, 6011–6045 (2006)
Gupte, S.K., Advani, S.G.: Flow near the permeable boundary of a porous medium: an experimental investigation using LDA. Exp. Fluids 22(5), 408–422 (1997)
Gad-el Hak, M.: Flow Control: Passive, Active and Reactive Flow Management, 1st edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
James, D.F., Davis, A.M.J.: Flow at the interface of a fibrous porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 426, 47–72 (2001)
Koch, D.L., Ladd, A.J.C.: Moderate Reynolds number flow through periodic and random arrays of aligned cylinders. J. Fluid Mech. 349, 31–66 (1997)
Kumar, S.A., Mathur, M., Sameen, A., Lal, S.A.: Effects of Prandtl number on the laminar cross flow past a heated cylinder. Phys. Fluids 28(11), 113–603 (2016)
Larson, R.E., Higdon, J.J.L.: Microscopic flow near the surface of two-dimensional porous media. Part 1. Axial flow. J. Fluid Mech. 166, 449–472 (1986)
Larson, R.E., Higdon, J.J.L.: Microscopic flow near the surface of two-dimensional porous media. Part 2. Transverse flow. J. Fluid Mech. 178, 119–136 (1987)
Morad, M., Khalili, A.: Transition layer thickness in a fluid–porous medium of multi-sized spherical beads. Exp. Fluids 46, 323–330 (2009)
Nield, D.A.: Onset of convection in a fluid layer overlying a layer of porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 81, 513–522 (1977)
Nield, D.A.: Modeling the effect of surface tension on the onset of natural convection in a saturated porous medium. Transp. Porous Media 31, 365–368 (1998)
Nield, D.A.: The Beavers–Joseph boundary condition and related matters: a historical and critical note. Transp. Porous Media 78, 537–540 (2009)
Nield, D.A., Bejan, A.: Convection in Porous Media, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Ochoa-Tapia, J.A., Whitaker, S.: Momentum transfer at the boundary between a porous medium and a homogeneous fluid—I : theoretical development. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 38(4), 2635–2646 (1995a)
Ochoa-Tapia, J.A., Whitaker, S.: Momentum transfer at the boundary between a porous medium and a homogeneous fluid—II: comparison with experiment. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 38(4), 2647–2655 (1995b)
Ochoa-Tapia, J.A., Valdés-Parada, F.J., Goyeau, B., Lasseux, D.: Fluid motion in the fluid/porous medium inter-region. Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química 166(3), 923–938 (2017)
Richardson, S.: A model for the boundary condition of a porous material. Part 2. J. Fluid Mech. 49, 327–336 (1971)
Rosenhead, L. (ed.): Laminar Boundary Layers. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1963)
Saffman, P.G.: On the boundary condition at the surface of a porous medium. Stud. Appl. Math. 50, 93–101 (1971)
Sahraoui, M., Kaviany, M.: Slip and no-slip velocity boundary conditions at interface of porous, plain media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 35(4), 927–943 (1992)
Sangani, A., Acrivos, A.: Slow flow past periodic arrays of cylinders with application to heat transfer. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 8(3), 193–206 (1982)
Sangani, A.S., Yao, C.: Transport processes in random arrays of cylinders. I. Thermal conduction. Phys. Fluids 31, 2426–2434 (1988a)
Sangani, A.S., Yao, C.: Transport processes in random arrays of cylinders. II. Viscous flow. Phys. Fluids 31, 2435–2444 (1988b)
Schlichting, H., Gersten, K.: Boundary-Layer Theory. Springer, New York (2000)
Slattery, J.C.: Flow of viscoelastic fluids through porous media. AIChE J. 13(6), 1066–1071 (1967)
Tachie, M.F., James, D.F., Currie, I.G.: Velocity measurements of a shear flow penetrating a porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 493, 319–343 (2003)
Taylor, G.I.: A model for the boundary condition of a porous material. Part 1. J. Fluid Mech. 49, 319–326 (1971)
Valdés-Parada, F.J., Alvarez-Ramírez, J., Goyeau, B., Ochoa-Tapia, J.A.: Computation of jump coefficients for momentum transfer between a porous medium and a fluid using a closed generalized transfer equation. Transp. Porous Media 78(3), 439–457 (2009)
Valdés-Parada, F.J., Aguilar-Madera, C.G., Ochoa-Tapia, J.A., Goyeau, B.: Velocity and stress jump conditions between a porous medium and a fluid. Adv. Water Resour. 62, 327–339 (2013)
Whitaker, S.: The equations of motion in porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 21(3), 291–300 (1966)
Whitaker, S.: Diffusion and dispersion in porous media. AIChE J. 13(3), 420–427 (1967)
Whitaker, S.: A simple geometrical derivation of the spatial averaging theorem. Chem. Eng. Educ. 19(1) (1985)
Whitaker, S.: The Method of Volume Averaging. Theory and Applications of Transport in Porous Media. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1999)
Zhang, Q., Prosperetti, A.: Pressure-driven flow in a two-dimensional channel with porous walls. J. Fluid Mech. 631, 1–21 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the High Performance Computing Environment (HPCE) at IIT Madras for providing the computational facilities used in this study. The authors also acknowledge the financial support from Aeronautical Research and Development Board (AR&DB), DRDO, Government of India, for the experiments done in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nair, K.A., Sameen, A. & Lal, S.A. Passive Boundary Layer Flow Control Using Porous Lamination. Transp Porous Med 124, 533–551 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1083-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1083-5