Abstract
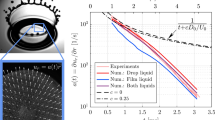
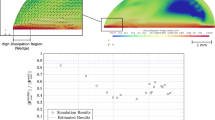
The geometry of micro-scale textures and the relative motion of surfaces in contact may affect the performance of an elastohydrodynamic lubrication interface. Reported in this paper are the investigations of the effects of texture bottom shape and surface relative motion on lubrication enhancement using numerically generated textures by means of model-based virtual texturing and numerical simulation. These textures are on one of the interacting surfaces in a triangular distribution and have the same density. The results suggest that the bottom shapes involving a micro-wedge and/or a micro-step bearing tend to yield thicker films. The lubrication of selected textured surfaces was also studied under three different relative motions: texture surface moving, un-textured surface moving, and both moving. The results indicate that textures on the faster moving surface offer stronger film thickness enhancement.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, X., Kato, K., Adachi, K.: The lubrication effect of micro-pits on parallel sliding faces of SIC in water. Lubr. Eng. 58(8), 27–34 (2002)
Pride, S., Folkert, K., Guichelaar, P., Etsion, I.: Effect of micro-surface texturing on breakaway torque and blister formation on carbon-graphite faces in a mechanical seal. Lubr. Eng. 58, 16–21 (2002)
Brizmer, V., Kligerman, Y., Etsion, I.: A laser surface textured parallel thrust bearing. Tribol. Trans. 46, 397–403 (2003)
Wakuda, M., Yamauchi, Y., Kanzaki, S., Yasuda, Y.: Effect of surface texturing on friction reduction between ceramic and steel materials under lubricated sliding contact. Wear 254, 356–363 (2003)
Tanaka, H., Gomi, K., Miyake, Y.: Micro-tribology of carbon-coated thin film media with well-defined surface texture. IEEE Trans. Magn. 29(1), 270–275 (1993)
Costa, H.L., Hutchings, I.M.: Hydrodynamic lubrication of textured steel surfaces under reciprocating sliding conditions. Tribol. Int. 40, 1227–1238 (2007)
Mourier, L., Mazuyer, D., Lubrecht, A.A., Donnet, C.: Transient increase of film thickness in micro-textured EHL contacts. Tribol. Int. 39, 1745–1756 (2006)
Křupka, I., Hartl, M.: The effect of surface texturing on thin EHL lubrication films. Tribol. Int. 40, 1100–1110 (2007)
Kovalchenko, A., Ajayi, O., Erdemir, A., Fenske, G., Etsion, I.: The effect of laser texturing of steel surfaces and speed-load parameters on the transition of lubrication regime from boundary to hydrodynamic. Tribol. Trans. 47, 299–307 (2004)
Lu, X., Khonsri, M.M.: An experimental investigation of dimple effect on the stribeck curve of journal bearings. Tribol. Lett. 27, 169–176 (2007)
Etsion, I.: State of the art in laser surface texturing. ASME J. Tribol. 127(1), 248–253 (2005)
Wang, X., Kato, K., Adachi, K., Aizawa, K.: Loads carrying capacity map for the surface texture design of SiC thrust bearing sliding in water. Tribol. Int. 36(3), 189–197 (2003)
Siripuram, R.B., Stephens, L.S.: Effect of deterministic asperity geometry on hydrodynamic lubrication. ASME J. Tribol. 126(3), 527–534 (2004)
Ren, N., Nanbu, T., Yasuda, Y., Zhu, D., Wang, Q.: Micro textures in lubricated concentrated-contacts: effect of distribution patterns. Tribol. Lett. 28(3), 275–285 (2007)
Wang, Q., Zhu, D.: Virtual texturing: modeling the performance of lubricated contacts of engineered surfaces. ASME J. Tribol. 127, 722–728 (2005)
Etsion, I.: Improving tribological performance of mechanical components by laser surface texturing. Tribol. Lett. 17, 733–737 (2004)
Arghir, M., Roucou, N., Helene, M., Frene, J.: Theoretical analysis of the incompressible laminar flow in a macro-roughness cell. ASME J. Tribol. 125(2), 309–318 (2003)
Yu, T.H., Sadeghi, F.: Thermal effects in thrust washer lubrication. ASME J. Tribol. 124(1), 166–177 (2002)
Křupka, I., Hartl, M.: Experimental study of microtextured surfaces operating under thin-film EHD lubrication conditions. ASME J. Tribol. 129(3), 502–508 (2007)
Hu, Y., Zhu, D.: A full numerical solution to the mixed lubrication in point contacts. ASME J. Tribol. 122, 1–10 (2000)
Zhu, D., Hu, Y.Z.: A computer program package for the prediction of EHL and mixed lubrication characteristics, friction, subsurface stresses and flash temperatures based on measured 3-D surface roughness. Tribol. Trans. 44, 383–390 (2001)
Liu, Y., Wang, Q., Hu, Y., Wang, W., Zhu, D.: Effects of differential schemes and mesh density on EHL film thickness in point contacts. ASME J. Tribol. 128, 641–653 (2006)
Liu, S.B., Wang, Q., Liu, G.: A versatile method of discrete convolution and FFT (DC-FFT) for contact analyses. Wear. 243, 101–110 (2000)
Dowson, D., Higginson, G.R.: Elastohydro-Dynamic Lubrication. Pergamon Press, New York (1966)
Liu, Y., Wang, Q., Zhu, D, Wang, W., Hu, Y.: Effects of differential scheme and viscosity model on rough-surface point-contact isothermal EHL. To appear in ASME J. Tribol. (2008)
Liu, Y., Wang, Q., Bair, S., Vergne, P.: A quantitative solution for the full shear-thinning EHL point contact problem including traction. Tribol. Lett. 28(2), 171–181 (2007)
Pinkus, O., Sternlicht, B.: Theory of Hydrodynamic Lubrication. McGraw-Hill, Inc. (1961)
Olver, A.V., Fowell, M. T., Spikes, H.A., Pegg, I.G.: ‘Inlet suction’, a load support mechanism in non-convergent, pocketed, hydrodynamic bearings. Proc. IMechE Part J. J. Eng. Tribol. 220(2), 105–108 (2006)
Fowell, M., Olver, A.V., Gosman, A.D., Spikes, H.A., Pegg, I.G.: Entrainment and inlet suction: two mechanisms of hydrodynamic lubrication in textured bearings. ASME J. Tribol. 129(2), 336–347 (2007)
Hamilton, D.B., Walowit, J.A., Allen, C.M.: A theory of lubrication by micro-irregularities. ASME J. Basic Eng. 88(1), 177–85 (1966)
Anno, J.N., Walowit, J.A., Allen, C.M.: Microasperity lubrication. ASME J. Lubr. Tech. 90, 351–355 (1968)
Tønder, K.: Dynamics of rough slider bearings: effects of one-sided roughness/waviness. Tribol. Int. 29, 117–122 (1996)
Tonder, K.: Inlet roughness tribodevices: dynamic coefficients and leakage. Tribol. Int. 34, 847–852 (2001)
Tønder, K.: Hydrodynamic effects of tailored inlet roughness: extended theory. Tribol. Int. 37, 137–142 (2004)
Tønder, K.: A simplified assessment of the performance of differentially textured hard disk sliders. Tribol. Int. 38, 641–645 (2005)
Etsion, I., Burstein, L.: A model for mechanical seals with regular micro surface structure. Tribol Trans. 139(3), 677–683 (1996)
Patir, N., Cheng, H.S.: An average flow model for determine effects of three dimensional roughness on partial hydrodynamic lubrication. ASME J. Lubr. Tech. 100, 12–17 (1978)
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Nissan Motors for the support and permission to publish the results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nanbu, T., Ren, N., Yasuda, Y. et al. Micro-Textures in Concentrated Conformal-Contact Lubrication: Effects of Texture Bottom Shape and Surface Relative Motion. Tribol Lett 29, 241–252 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9302-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9302-9