Abstract
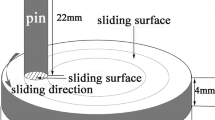
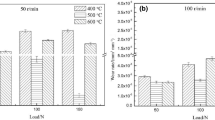
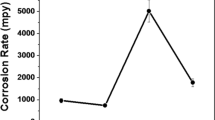
Under atmospheric conditions at 400 °C, we studied the wear mechanism of H21 steel with different tempering states as a function of normal load. Typical oxidative wear was identified by X-ray diffraction patterns with predominant tribo-oxides of Fe3O4 and Fe2O3. Under loads of 50–100 N, mild oxidative wear prevailed for all samples, such that the wear losses of H21 steel with various tempering states showed no significant differences with characteristics of a slight plastic deformation of the substrate and single-layer oxide. In this case, the wear rate was lower, and the tribo-oxide was decisive factor in determining wear rate. Under loads of 150–200 N, the transition of mild wear to severe wear occurred in H21 steel and was characterized by: (1) a significant difference of wear losses for steel with various tempering states; (2) wear loss that started to increase faster and reached a relatively high level; (3) the appearance of significant plastic deformation in the oxide underneath the substrate and multi-layer tribo-oxide. Under a load of 200 N for the steel tempered at 700 °C, plastic extrusion prevailed with a mixed metal-oxide layer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrau, O., Boher, C., Gras, R., Rezai-Aria, F.: Analysis of the friction and wear behavior of hot work tool steel for forging. Wear 255, 1444–1454 (2003). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(03)00280-1
Fontalvo, G.A., Mitterer, C.: The effect of oxide-forming alloying elements on the high temperature wear of a hot work steel. Wear 258, 1491–1499 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2004.04.014
Luong, L.H.S., Heijkoop, T.: The influence of scale on friction in hot metal working. Wear 71, 93–102 (1981). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(81)90142-3
Wang, D.Y., Shu, D.L., Guo, X.C.: Effect of microstructure and properties on the high temperature wear characteristics of 3Cr2W8 V (H21) steel. Wear 119, 101–117 (1987). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(87)90101-3
Fink, M.: Wear oxidation—a new component of wear. Trans. Am. Soc. Steel. Treat. 18, 1026–1034 (1930)
Archard, J.F., Hirst, W.: The wear of metals under unlubricated conditions. Proc. R. Soc. A236, 394–410 (1956)
Wilson, J.E., Stott, F.H., Wood, G.C.: The development of wear protective oxides and their influence on sliding friction. Proc. R. Soc. A369, 557–574 (1980)
Quinn, T.F.J., Sullivan, J.L., Rowson, D.M.: Developments in the oxidational theory of mild wear. Tribol. Int. 13, 153–158 (1980). doi:10.1016/0301-679X(80)90031-6
Quinn, T.F.J.: Oxidational wear modelling Part III, the effects of speed and elevated temperatures. Wear 216, 262–275 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(98)00137-9
So, H., Yu, D.S., Chuang, C.Y.: Formation and wear mechanism of tribo-oxides and the regime of oxidational wear of steel. Wear 253, 1004–1015 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(02)00230-2
Cui, X.H., Wang, S.Q., Wang, F., Chen, K.M.: Research on oxidative wear mechanism of the cast steels. Wear 265, 468–476 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.wear.2007.11.015
Wang, S.Q., Wang, F., Cui, X.H., Chen, K.M.: Effect of secondary carbides on oxidative wear of the Cr-Mo-V cast steels. Mater. Lett. 62, 279–281 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2007.05.018
Wang, Y., Lei, T.Q.: Wear behavior of steel 1080 with different microstructures during dry sliding. Wear 194, 44–53 (1996). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(95)06705-1
Marui, E., Hasegawa, N., Endo, H., Tanaka, K., Hattori, T.: Research on the wear characteristics of hypereutectoid steel. Wear 205, 186–199 (1997). doi:10.1016/S0043-1648(96)07316-4
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports of the open fund project from State Key Laboratory of Materials Modification by Laser, Ion and Electron Beams (No.0708) and advanced talent fund project from Jiangsu University (No.07JDG062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S.Q., Wei, M.X., Wang, F. et al. Transition of Mild Wear to Severe Wear in Oxidative Wear of H21 Steel. Tribol Lett 32, 67–72 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9361-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9361-y