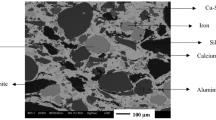
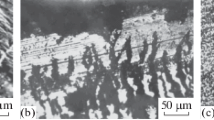
Abstract
Pin-on-disc testing was used to investigate the friction and wear behaviour of a Cu-based metal matrix composite dry sliding against three different martensitic steels. The tests were carried out at two contact pressures (0.5 and 1 MPa) and two sliding velocities (1.57 and 7 m/s), and the results were explained by considering the characteristics of the friction layers formed on the pin and disc surfaces during sliding. At 7 m/s, pin and disc wear was very mild in every condition, because the high flash temperatures achieved during sliding induced intense oxidation of the disc asperities, irrespective of the steel disc compositions. At 1.57 m/s, the steel composition played an important role. When using a heat-treated steel and a conventional martensitic stainless steel, pin and disc wear was by ‘low-sliding speed tribo-oxidation’, regarded as mild wear. However, when using a martensitic stainless steel with a very high Cr-content and a very low C-content, i.e. by a very high oxidation resistance, pin and disc wear was by adhesion/delamination at 0.5 MPa, and thus severe in nature. The results presented herewith clearly suggest the importance of selecting suitable steel counterfaces in the optimization of the tribological systems tribological involving Cu-based metal matrix composites as a mating material.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glaeser, W.A.: Materials for Tribology, Tribology series 20. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1992)
Straffelini, G.: Friction and Wear, Methodologies for Design and Control. Springer, Basel (2015)
Mann, R., Magnier, V., Brunel, J.-F., Brunel, F., Dufrenoy, P., Henrion, M.: Relation between mechanical behavior and microstructure of a sintered material for braking application. Wear 386–387, 1–16 (2017)
Peng, T., Yan, Q., Li, G., Zhang, X.: The influence of Cu/Fe ratio on the tribological behavior of brake friction materials. Tribol. Lett. 66, 18 (2018)
Peng, T., Yan, Q., Li, G., Zhang, X., Wen, Z., Jin, X.: The braking behavior of Cu-based metallic brake pad for high-speed train under different initial braking speed. Tribol. Lett. 65, 135 (2017)
Xiao, Y., Zhang, Z., Yao, P., Fan, K., Zhou, H., Gong, T., Zhao, L., Deng, M.: Mechanical and tribological behaviors of copper metal matrix composites for brake pads used in high-speed trains. Tribol. Int. 119, 585–592 (2018)
Su, L., Gao, F., Han, X., Fu, R., Zhang, E.: Tribological behavior of Copper-graphite powder third body on copper-based friction materials. Tribol. Lett. 60, 30 (2015)
Xiong, X., Chen, J., Yao, P., Li, S., Huang, B.: Friction and wear behaviors and mechanisms of Fe and SiO2 in Cu-based P/M friction materials. Wear 262, 1182–1186 (2007)
Yasar, I., Canakci, A., Arslan, F.: The effect of brush spring pressure on the wear behaviour of copper-graphite brushes with electrical current. Tribol. Int. 40, 1381–1386 (2007)
Moustafa, S.F., El-Badry, S.A., Sanad, A.M., Kiebak, B.: Friction and wear of copper-graphite composited made with Cu-coated and uncoated powders. Wear 253, 699–710 (2002)
Grandin, M., Wiklund, U.: Influence of mechanical and electrical load on copper/copper-graphite sliding electrical contact. Tribol. Int. 121, 1–9 (2018)
Zhan, Y.Z., Zhang, G.: Mechanical mixing and wear-debris formation in the dry sliding wear of copper matrix composite. Tribol. Lett. 17, 581–592 (2004)
Wilson, S., Alpas, A.T.: Wear mechanism maps for metal matrix composites. Wear 212, 41–49 (1997)
Rigney, D.A., Chen, L.H., Naylor., M.G.S.: Wear processes in sliding systems. Wear 100, 195–219 (1984)
Venkataraman, B., Sundararajan, G.: Correlation between the characteristics of the mechanically mixed layer and wear behaviour of aluminium, Al-7075 alloy and Al-MMCs. Wear 245, 22–38 (2000)
Straffelini, G., Bonollo, F., Molinari, A., Tiziani, A.: Influence of matrix hardness on the dry sliding behaviour of 20 vol.% Al2O3-particulate-reinforced 6061 Al metal matrix composite. Wear 211, 192–197 (1997)
Straffelini, G.: Experimental observations of subsurface damage and oxidative wear in Al-based metal-matrix composites. Wear 245, 216–222 (2000)
Scardi, P., Leoni, M., Straffelini, G., De Giudici, G.: Microstructure of Cu–Be alloy triboxidative wear debris. Acta mater 55, 2531–2538 (2007)
Quinn, T.F.J., Sullivan, J.L., Rowson, D.M.: Origins and development of oxidational wear at low ambient temperatures. Wear 94, 175–191 (1984)
Stott, F.H.: The role of oxidation in the wear of alloys. Tribol. Int. 31, 61–71 (1998)
Zhang, J., Alpas, A.T.: Transition between mild and severe wear in aluminium alloys. Acta Mater. 45, 513–528 (1997)
Vingsbo, O., Hogmark, S.: Wear of steels. In: Rigney, D.A. (ed.) Fundamentals of Friction and Wear of Materials, pp. 41–52. ASM, Materials Park (1980)
Straffelini, G., Trabucco, D., Molinari, A.: Oxidative wear of heat-treated steels. Wear 250, 485–491 (2001)
Straffelini, G., Trabucco, D., Molinari, A.: Sliding wear of austenitic and austenitic-ferritic stainless steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. 33A, 613–624 (2002)
Lim, F.C., Ashby, M.F.: Wear mechanism maps. Acta metal 35, 1–24 (1987)
APX4 steel: Data sheet, Aubert%Duval (http://www.aubertduval.com)
ASM: Properties and Selection: Iron, Steel and High Performance Alloys, Metals Handbook, 10th edn, vol. 1, ASM, Materials Park (1992)
CRC: Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC Press, Cleveland (1989–1990)
Straffelini, G., Verlinsky, S., Verma, P.C., Valota, G., Gialanella, S.: Wear and contact temperature evolution in pin-on-disc tribotesting of low metallic friction material sliding against pearlitic cast iron. Tribol. Lett. 62, 36 (2016)
Riahi, A.R., Alpas, A.T.: Wear map for grey cast iron. Wear 255, 401–409 (2003)
Lee, P.W., Filip, P.: Friction and wear of Cu-free and Sb-free environmental friendly automotive brake materials. Wear 302, 1404–1413 (2013)
Li, W., Wang, Y., Yang, X.Z.: Frictional hardening and softening of steel 52100 during dry sliding. Tribol. Lett. 18(3), 353–357 (2005)
Ashby, M.F., Kong, H.S., Abulawi, J.: T-maps: User Manual. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1991)
Federici, M., Straffelini, G., Gialanella, S.: Pin-on-Disc testing of low metallic friction material sliding against HVOF coated cast iron: modelling of the contact temperature evolution. Tribol. Lett. 65, 121 (2017)
Stachowiak, G.W., Batchelor, A.W.: Engineering Tribology, Tribology Series 24. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1993)
Miyoshi, K.: Solid Lubrication, Fundamentals and Applications. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York (2001)
Straffelini, G.: A simplified approach to the adhesive theory of friction. Wear 249, 79–85 (2001)
Bushan, B.: Introduction to Tribology, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2013)
Lim, S.C., Ashby, M.F., Brunton, J.H.: The effects of sliding conditions on the dry friction of metals. Acta Metal. 37, 767–772 (1989)
Rabinowicz, E.: Friction and Wear of Materials, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken (1995)
Acknowledgements
The Authors wish to thank Lorena Maines and Alberto Zanellini for wear testing and characterization support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayashree, P., Federici, M., Bresciani, L. et al. Effect of Steel Counterface on the Dry Sliding Behaviour of a Cu-Based Metal Matrix Composite. Tribol Lett 66, 123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1075-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-018-1075-1