Abstract
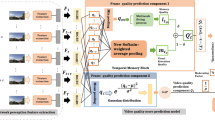
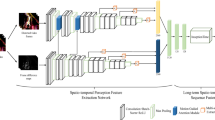
Video quality assessment (VQA) is an important problem in computer vision. The videos in computer vision applications are usually captured in the wild. We focus on automatically assessing the quality of in-the-wild videos, which is a challenging problem due to the absence of reference videos, the complexity of distortions, and the diversity of video contents. Moreover, the video contents and distortions among existing datasets are quite different, which leads to poor performance of data-driven methods in the cross-dataset evaluation setting. To improve the performance of quality assessment models, we borrow intuitions from human perception, specifically, content dependency and temporal-memory effects of human visual system. To face the cross-dataset evaluation challenge, we explore a mixed datasets training strategy for training a single VQA model with multiple datasets. The proposed unified framework explicitly includes three stages: relative quality assessor, nonlinear mapping, and dataset-specific perceptual scale alignment, to jointly predict relative quality, perceptual quality, and subjective quality. Experiments are conducted on four publicly available datasets for VQA in the wild, i.e., LIVE-VQC, LIVE-Qualcomm, KoNViD-1k, and CVD2014. The experimental results verify the effectiveness of the mixed datasets training strategy and prove the superior performance of the unified model in comparison with the state-of-the-art models. For reproducible research, we make the PyTorch implementation of our method available at https://github.com/lidq92/MDTVSFA.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Video-level features of BRISQUE are the average pooling of its frame-level features.
References
Bampis, C. G., Li, Z., Moorthy, A. K., Katsavounidis, I., Aaron, A., & Bovik, A. C. (2017). Study of temporal effects on subjective video quality of experience. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 26(11), 5217–5231.
Barron, J. T. (2019). A general and adaptive robust loss function. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 4331–4339.
Cho, K., Van Merriënboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., & Bengio, Y. (2014). Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.1078.
Choi, L. K., & Bovik, A. C. (2018). Video quality assessment accounting for temporal visual masking of local flicker. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 67, 182–198.
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, LJ., Li, K., & Fei-Fei, L. (2009). ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 248–255.
Dodge, S., & Karam, L. (2016). Understanding how image quality affects deep neural networks. In International conference on quality of multimedia experience (QoMEX), pp. 1–6.
Freitas, P. G., Akamine, W. Y., & Farias, M. C. (2018). Using multiple spatio-temporal features to estimate video quality. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 64, 1–10.
Ghadiyaram, D., & Bovik, A. C. (2017). Perceptual quality prediction on authentically distorted images using a bag of features approach. Journal of Vision, 17(1), 32–32.
Ghadiyaram, D., Pan, J., Bovik, A. C., Moorthy, A. K., Panda, P., & Yang, K. C. (2018). In-capture mobile video distortions: A study of subjective behavior and objective algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 28(9), 2061–2077.
He, H., Zhang, J., Zhang, Q., & Tao, D. (2019). Grapy-ML: Graph pyramid mutual learning for cross-dataset human parsing. arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.12053.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778.
Hosu, V., Hahn, F., Jenadeleh, M., Lin, H., Men, H., Szirányi, T., Li, S., & Saupe, D. (2017). The Konstanz natural video database (KoNViD-1k). In International conference on quality of multimedia experience (QoMEX), pp. 1–6.
Isogawa, M., Mikami, D., Takahashi, K., Iwai, D., Sato, K., & Kimata, H. (2019). Which is the better inpainted image? Training data generation without any manual operations. International Journal of Computer Vision, 127(11–12), 1751–1766.
Juluri, P., Tamarapalli, V., & Medhi, D. (2015). Measurement of quality of experience of video-on-demand services: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 18(1), 401–418.
Kang, L., Ye, P., Li, Y., & Doermann, D. (2014). Convolutional neural networks for no-reference image quality assessment. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 1733–1740.
Kim, W., Kim, J., Ahn, S., Kim, J., & Lee, S. (2018). Deep video quality assessor: From spatio-temporal visual sensitivity to a convolutional neural aggregation network. In European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp. 219–234.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980.
Korhonen, J. (2019). Two-level approach for no-reference consumer video quality assessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 28(12), 5923–5938.
Krasula, L., Yoann, B., & Le Callet, P. (2020). Training objective image and video quality estimators using multiple databases. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 22(4), 961–969.
Lasinger, K., Ranftl, R., Schindler, K., & Koltun, V. (2019). Towards robust monocular depth estimation: Mixing datasets for zero-shot cross-dataset transfer. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.01341.
Li, D., Jiang, T., & Jiang, M. (2019a). Quality assessment of in-the-wild videos. In ACM international conference on multimedia (MM), pp. 2351–2359.
Li, D., Jiang, T., Lin, W., & Jiang, M. (2019b). Which has better visual quality: The clear blue sky or a blurry animal? IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 21(5), 1221–1234.
Li, D., Jiang, T., & Jiang, M. (2020). Norm-in-norm loss with faster convergence and better performance for image quality assessment. In ACM International conference on multimedia (MM), pp. 789–797.
Li, X., Guo, Q., & Lu, X. (2016a). Spatiotemporal statistics for video quality assessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 25(7), 3329–3342.
Li, Y., Po, L. M., Cheung, C. H., Xu, X., Feng, L., Yuan, F., et al. (2016b). No-reference video quality assessment with 3D shearlet transform and convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 26(6), 1044–1057.
Li, YJ., Lin, CS., Lin, YB., & Wang, YCF. (2019c). Cross-dataset person re-identification via unsupervised pose disentanglement and adaptation. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp. 7919–7929.
Lin, KY., & Wang, G. (2018). Hallucinated-IQA: No-reference image quality assessment via adversarial learning. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 732–741.
Liu, W., Duanmu, Z., & Wang, Z. (2018). End-to-end blind quality assessment of compressed videos using deep neural networks. In ACM international conference on multimedia (MM), pp. 546–554.
Liu, X., van de Weijer, J., & Bagdanov, A. D. (2017). RankIQA: Learning from rankings for no-reference image quality assessment. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp. 1040–1049.
Lu, W., He, R., Yang, J., Jia, C., & Gao, X. (2019). A spatiotemporal model of video quality assessment via 3D gradient differencing. Information Sciences, 478, 141–151.
Lv, J., Chen, W., Li, Q., & Yang, C. (2018). Unsupervised cross-dataset person re-identification by transfer learning of spatial-temporal patterns. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 7948–7956.
Ma, K., Wu, Q., Wang, Z., Duanmu, Z., Yong, H., Li, H., & Zhang, L. (2016). Group MAD competition—a new methodology to compare objective image quality models. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 1664–1673.
Ma, K., Duanmu, Z., & Wang, Z. (2018). Geometric transformation invariant image quality assessment using convolutional neural networks. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp. 6732–6736.
Manasa, K., & Channappayya, S. S. (2016). An optical flow-based no-reference video quality assessment algorithm. In IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), 1 pp. 2400–2404.
Men, H., Lin, H., & Saupe, D. (2017). Empirical evaluation of no-reference VQA methods on a natural video quality database. In International conference on quality of multimedia experience (QoMEX), pp. 1–3.
Men, H., Lin, H., & Saupe, D. (2018). Spatiotemporal feature combination model for no-reference video quality assessment. In International conference on quality of multimedia experience (QoMEX), pp. 1–3.
Mittal, A., Moorthy, A. K., & Bovik, A. C. (2012). No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 21(12), 4695–4708.
Mittal, A., Soundararajan, R., & Bovik, A. C. (2013). Making a “completely blind” image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 20(3), 209–212.
Mittal, A., Saad, M. A., & Bovik, A. C. (2016). A completely blind video integrity oracle. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 25(1), 289–300.
Moorthy, A. K., Choi, L. K., Bovik, A. C., & De Veciana, G. (2012). Video quality assessment on mobile devices: Subjective, behavioral and objective studies. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 6(6), 652–671.
Nieto, RG., Restrepo, HDB., & Cabezas, I. (2019). How video object tracking is affected by in-capture distortions? In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp. 2227–2231.
Nuutinen, M., Virtanen, T., Vaahteranoksa, M., Vuori, T., Oittinen, P., & Häkkinen, J. (2016). CVD2014–a database for evaluating no-reference video quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 25(7), 3073–3086.
Park, J., Seshadrinathan, K., Lee, S., & Bovik, A. C. (2013). Video quality pooling adaptive to perceptual distortion severity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 22(2), 610–620.
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J., Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N., Antiga, L., et al. (2019). PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Advances in neural information processing systems (NeurIPS), pp. 8024–8035.
Rippel, O., Nair, S., Lew, C., Branson, S., Anderson, AG., & Bourdev, L. (2019). Learned video compression. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp. 3454–3463.
Saad, M. A., Bovik, A. C., & Charrier, C. (2014). Blind prediction of natural video quality. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 23(3), 1352–1365.
Seshadrinathan, K., & Bovik, A. C. (2010). Motion tuned spatio-temporal quality assessment of natural videos. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 19(2), 335–350.
Seshadrinathan, K., & Bovik, AC. (2011). Temporal hysteresis model of time varying subjective video quality. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), pp. 1153–1156.
Seshadrinathan, K., Soundararajan, R., Bovik, A. C., & Cormack, L. K. (2010). Study of subjective and objective quality assessment of video. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 19(6), 1427–1441.
Seufert, M., Egger, S., Slanina, M., Zinner, T., Hoßfeld, T., & Tran-Gia, P. (2014). A survey on quality of experience of HTTP adaptive streaming. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 17(1), 469–492.
Siahaan, E., Hanjalic, A., & Redi, J. A. (2018). Semantic-aware blind image quality assessment. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 60, 237–252.
Sinno, Z., & Bovik, A. C. (2019a). Large scale study of perceptual video quality. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 28(2), 612–627.
Sinno, Z., & Bovik, AC. (2019b). Spatio-temporal measures of naturalness. In IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp. 1750–1754.
Triantaphillidou, S., Allen, E., & Jacobson, R. (2007). Image quality comparison between JPEG and JPEG2000. II. Scene dependency, scene analysis, and classification. Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, 51(3), 259–270.
Varga, D. (2019). No-reference video quality assessment based on the temporal pooling of deep features. Neural Processing Letters, 50, 2595–2608.
Varga, D., & Szirányi, T. (2019). No-reference video quality assessment via pretrained CNN and LSTM networks. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 13, 1569–1576.
VQEG. (2000). Final report from the Video Quality Experts Group on the validation of objective models of video quality assessment. https://www.its.bldrdoc.gov/media/8212/frtv_phase1_final_report.doc.
Wang, H., Katsavounidis, I., Zhou, J., Park, J., Lei, S., Zhou, X., et al. (2017). VideoSet: A large-scale compressed video quality dataset based on JND measurement. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 46, 292–302.
Wang, Y., Jiang, T., Ma, S., & Gao, W. (2012). Novel spatio-temporal structural information based video quality metric. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 22(7), 989–998.
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., & Simoncelli, E. P. (2004a). Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 13(4), 600–612.
Wang, Z., Lu, L., & Bovik, A. C. (2004b). Video quality assessment based on structural distortion measurement. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 19(2), 121–132.
Xu, J., Ye, P., Liu, Y., & Doermann, D. (2014). No-reference video quality assessment via feature learning. In IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp. 491–495.
Yan, P., & Mou, X. (2019). No-reference video quality assessment based on spatiotemporal slice images and deep convolutional neural networks. In Proc. SPIE 11187, Optoelectronic Imaging and Multimedia Technology VI, pp. 74–83.
Yang D, Peltoketo VT, Kamarainen JK (2019) CNN-based cross-dataset no-reference image quality assessment. In ieee international conference on computer vision workshop (ICCVW), pp. 3913–3921
Ye, P., Kumar, J., Kang, L., & Doermann, D. (2012). Unsupervised feature learning framework for no-reference image quality assessment. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 1098–1105.
You, J., & Korhonen, J. (2019). Deep neural networks for no-reference video quality assessment. In IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), pp. 2349–2353.
You, J., Ebrahimi, T., & Perkis, A. (2014). Attention driven foveated video quality assessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 23(1), 200–213.
Zhang, L., Shen, Y., & Li, H. (2014). VSI: A visual saliency-induced index for perceptual image quality assessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 23(10), 4270–4281.
Zhang, R., Isola, P., Efros, AA., Shechtman, E., & Wang, O. (2018). The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 586–595.
Zhang, W., & Liu, H. (2017). Study of saliency in objective video quality assessment. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 26(3), 1275–1288.
Zhang, W., Liu, Y., Dong, C., & Qiao, Y. (2019a). RankSRGAN: Generative adversarial networks with ranker for image super-resolution. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp. 3096–3105.
Zhang, W., Ma, K., & Yang, X. (2019b). Learning to blindly assess image quality in the laboratory and wild. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.00516.
Zhang, Y., Gao, X., He, L., Lu, W., & He, R. (2019c). Blind video quality assessment with weakly supervised learning and resampling strategy. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 29(8), 2244–2255.
Zhang, Y., Gao, X., He, L., Lu, W., & He, R. (2020). Objective video quality assessment combining transfer learning with CNN. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 31(8), 2716–2730.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China under contracts 61572042, 61520106004, and 61527804. This work was also supported in part by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFB1403900). We acknowledge the High-Performance Computing Platform of Peking University for providing computational resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Mei Chen.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Jiang, T. & Jiang, M. Unified Quality Assessment of in-the-Wild Videos with Mixed Datasets Training. Int J Comput Vis 129, 1238–1257 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-020-01408-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-020-01408-w